Recycled fiber insulation reduces environmental impact by lowering raw material consumption and energy use compared to virgin fiber insulation. Virgin fiber insulation offers higher thermal performance but involves greater resource extraction and emissions during production.
Table of Comparison
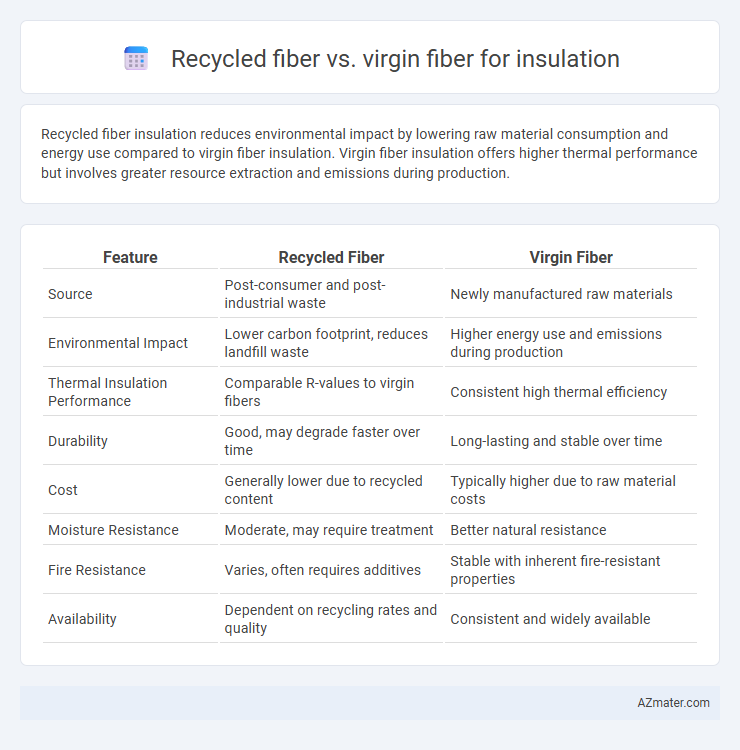
| Feature | Recycled Fiber | Virgin Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Post-consumer and post-industrial waste | Newly manufactured raw materials |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, reduces landfill waste | Higher energy use and emissions during production |
| Thermal Insulation Performance | Comparable R-values to virgin fibers | Consistent high thermal efficiency |
| Durability | Good, may degrade faster over time | Long-lasting and stable over time |
| Cost | Generally lower due to recycled content | Typically higher due to raw material costs |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate, may require treatment | Better natural resistance |
| Fire Resistance | Varies, often requires additives | Stable with inherent fire-resistant properties |
| Availability | Dependent on recycling rates and quality | Consistent and widely available |
Introduction to Insulation Materials
Recycled fiber insulation offers an eco-friendly alternative to virgin fiber by utilizing post-consumer and industrial waste, reducing landfill impact and conserving natural resources. Virgin fiber insulation, typically made from new glass, cellulose, or mineral wool, provides consistent quality and thermal performance but involves higher energy consumption in production. Selection between recycled and virgin fibers depends on factors like environmental goals, cost considerations, and specific insulation requirements for thermal resistance and durability.
What Are Virgin Fibers?
Virgin fibers are natural or synthetic fibers derived directly from raw materials without any prior use or processing, ensuring maximum purity and uniformity in insulation products. These fibers offer superior thermal performance and durability due to their uncontaminated structure, making them ideal for high-efficiency insulation applications. In contrast to recycled fibers, virgin fibers provide consistent quality and lower risk of impurities that can affect insulation effectiveness over time.
Understanding Recycled Fibers
Recycled fibers for insulation are derived from post-consumer and post-industrial waste materials, significantly reducing environmental impact compared to virgin fibers, which are sourced directly from raw materials like wood or mineral ores. These fibers retain essential thermal and acoustic insulating properties while minimizing energy consumption and landfill waste during production. Understanding recycled fibers involves recognizing their role in sustainable construction practices, promoting resource efficiency, and contributing to LEED certification and green building standards.
Environmental Impact: Virgin vs Recycled
Recycled fiber insulation significantly reduces environmental impact by lowering energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions compared to virgin fiber production, which often requires intensive resource extraction and processing. Using recycled materials minimizes landfill waste and conserves natural resources, contributing to a more sustainable insulation lifecycle. Life cycle assessments reveal that recycled fiber insulation can reduce carbon footprints by up to 50%, making it a preferred choice for eco-friendly building practices.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Recycled fiber insulation generally offers comparable thermal performance to virgin fiber, with R-values typically ranging from R-3.2 to R-3.8 per inch depending on density and material composition. Studies show that recycled fibers such as cellulose and denim retain effective heat resistance, maintaining consistent thermal conductivity over time. Choosing recycled fiber supports sustainability without compromising insulation efficiency in residential and commercial applications.
Cost Analysis: Recycled vs Virgin Fiber
Recycled fiber insulation typically costs 10-30% less than virgin fiber due to lower raw material expenses and reduced energy consumption during production. Virgin fiber prices are higher because they require fresh raw materials and more intensive manufacturing processes, affecting overall material and installation costs. Long-term savings with recycled fiber also include improved sustainability incentives and reduced environmental impact fees.
Durability and Lifespan
Virgin fiber insulation generally offers superior durability and a longer lifespan compared to recycled fiber due to its higher purity and structural integrity, which resists moisture and deformation over time. Recycled fiber insulation may contain contaminants that reduce its ability to maintain thermal performance and resilience under stress, leading to a shorter effective lifespan. Proper installation and environmental conditions also impact the durability and longevity of both recycled and virgin fiber insulation materials.
Health and Safety Considerations
Recycled fiber insulation reduces exposure to harmful chemicals typically found in virgin fiber products, as it often undergoes rigorous cleaning and processing to remove contaminants. Virgin fiber insulation may contain formaldehyde-based binders or other volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which can off-gas and impact indoor air quality. Choosing recycled fiber insulation helps minimize respiratory irritants and environmental health risks during installation and throughout the product's lifecycle.
Installation Process and Practicality
Recycled fiber insulation offers easier handling and improved flexibility compared to virgin fiber, reducing installation time and minimizing waste on-site. Virgin fiber insulation tends to maintain consistent density and thermal performance, ensuring straightforward fitting in standard wall cavities and attics. Practicality favors recycled fiber for eco-conscious projects requiring adaptability, while virgin fiber suits scenarios demanding reliable performance and uniform application.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Insulation
Choosing the right fiber for insulation involves balancing environmental impact, thermal performance, and durability. Recycled fiber insulation offers significant sustainability benefits by reducing landfill waste and embodied energy, while virgin fiber insulation typically provides higher thermal efficiency and structural integrity. Evaluating project-specific requirements such as climate conditions, budget, and lifespan ensures optimal fiber selection for effective and eco-friendly insulation solutions.
Infographic: Recycled fiber vs Virgin fiber for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com