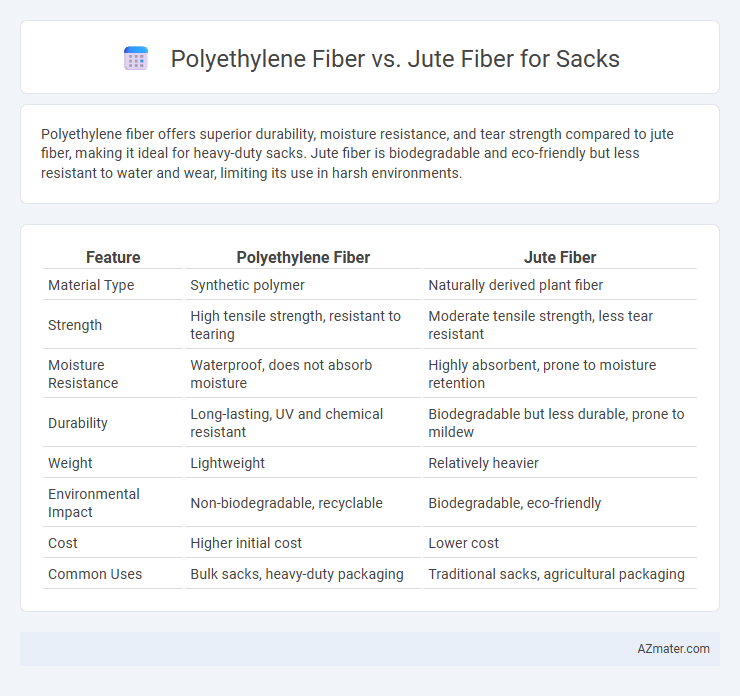
Polyethylene fiber offers superior durability, moisture resistance, and tear strength compared to jute fiber, making it ideal for heavy-duty sacks. Jute fiber is biodegradable and eco-friendly but less resistant to water and wear, limiting its use in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyethylene Fiber | Jute Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic polymer | Naturally derived plant fiber |
| Strength | High tensile strength, resistant to tearing | Moderate tensile strength, less tear resistant |
| Moisture Resistance | Waterproof, does not absorb moisture | Highly absorbent, prone to moisture retention |
| Durability | Long-lasting, UV and chemical resistant | Biodegradable but less durable, prone to mildew |
| Weight | Lightweight | Relatively heavier |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, recyclable | Biodegradable, eco-friendly |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost |
| Common Uses | Bulk sacks, heavy-duty packaging | Traditional sacks, agricultural packaging |
Introduction to Polyethylene Fiber and Jute Fiber
Polyethylene fiber is a synthetic material known for its high tensile strength, durability, and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for heavy-duty sacks used in industrial and agricultural applications. Jute fiber, a natural plant-based material, offers biodegradability, breathability, and cost-effectiveness, commonly utilized in sacks for packaging grains and produce. Both fibers provide distinct advantages, with polyethylene excelling in longevity and water resistance, while jute emphasizes eco-friendliness and sustainability.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Polyethylene fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and elongation at break compared to jute fiber, making it more resistant to tearing and heavy loads in sack applications. Its high resistance to moisture, UV radiation, and chemical exposure significantly enhances durability compared to jute fiber, which tends to degrade faster under environmental stress. While jute fiber offers biodegradability and natural breathability, polyethylene fiber sacks outperform in mechanical strength and long-term durability, making them ideal for industrial and agricultural use.
Environmental Impact and Biodegradability
Polyethylene fibers used in sacks are synthetic polymers derived from petrochemicals, resulting in low biodegradability and long-term environmental persistence, contributing to plastic pollution. In contrast, jute fibers are natural, biodegradable, and renewable, decomposing quickly in soil without leaving toxic residues, making them environmentally sustainable for sack production. The choice between polyethylene and jute fibers significantly affects waste management strategies and ecological footprints due to their differing degradation rates and resource origins.
Cost-Effectiveness and Market Availability
Polyethylene fiber offers superior cost-effectiveness compared to jute fiber due to its lower production costs and longer lifespan, making it a preferred choice for sacks in bulk packaging industries. Market availability of polyethylene fiber is significantly higher globally, driven by extensive industrial production and consistent supply chains, whereas jute fiber is more regionally concentrated, primarily in South Asia. Despite jute's eco-friendly appeal, polyethylene's affordability and widespread distribution provide a pragmatic solution for cost-sensitive markets requiring durable sack materials.
Moisture Resistance and Water Absorption
Polyethylene fiber exhibits superior moisture resistance and minimal water absorption compared to jute fiber, making it ideal for sacks exposed to damp environments. Jute fiber, being natural and hygroscopic, readily absorbs water, leading to increased weight and potential degradation. Polyethylene's hydrophobic properties ensure longer durability and maintain sack integrity under wet conditions.
Weight and Handling Characteristics
Polyethylene fiber sacks are significantly lighter, typically weighing around 50-70 grams per square meter, compared to jute fiber sacks which generally weigh between 200-400 grams per square meter, enhancing ease of transportation and handling. Polyethylene fibers offer smooth surfaces and greater flexibility, allowing for quicker folding and stacking, while jute fibers tend to be coarser and heavier, requiring more effort to manage due to their rough texture and bulkiness. The lightweight nature and superior flexibility of polyethylene fiber sacks contribute to improved ergonomics and operational efficiency in bulk material handling scenarios.
Applications in Sack Manufacturing
Polyethylene fiber in sack manufacturing offers superior moisture resistance, high tensile strength, and durability, making it ideal for packaging heavy and moisture-sensitive goods like grains, fertilizers, and chemicals. Jute fiber sacks provide natural breathability and biodegradability, suitable for agricultural products such as potatoes, onions, and coffee beans that require ventilation during storage. Choosing between polyethylene and jute fibers depends on the specific application needs, balancing strength, environmental impact, and product protection in sack production.
Aesthetic and Printing Qualities
Polyethylene fiber sacks offer a smoother surface and vibrant color retention, making them ideal for high-resolution, detailed printing with sharp graphics. In contrast, jute fiber sacks have a coarse texture that limits print clarity and color intensity, resulting in a more rustic, natural appearance suited for simple logos and designs. Polyethylene's synthetic nature ensures less fading and wear over time, while jute's organic fibers provide a unique aesthetic but sacrifice detailed print quality.
Recycling and End-of-Life Options
Polyethylene fiber sacks offer superior recyclability through mechanical recycling processes, enabling efficient recovery and reuse of plastic materials to reduce environmental impact. In contrast, jute fiber sacks are biodegradable and compostable, breaking down naturally without requiring specialized recycling facilities, making them suitable for eco-friendly disposal. Both fibers present distinct end-of-life options: polyethylene fibers support circular economy models via plastic recycling streams, whereas jute fibers contribute to organic waste cycles through natural decomposition.
Future Trends in Sack Material Innovation
Polyethylene fiber offers superior durability, moisture resistance, and lightweight properties compared to jute fiber, making it increasingly favored in sack manufacturing for industrial and agricultural uses. Emerging trends emphasize the integration of biodegradable polyethylene composites and recycled materials to enhance sustainability while maintaining performance. Innovations in blending natural fibers like jute with polyethylene aim to combine environmental benefits with the strength and cost-effectiveness required for future sack applications.
Infographic: Polyethylene fiber vs Jute fiber for Sack
 azmater.com
azmater.com