Soy protein fiber offers sustainability and biodegradability, making it an eco-friendly option for protective clothing. Aramid fiber provides superior heat resistance and high tensile strength, ensuring enhanced durability and protection in extreme conditions.
Table of Comparison
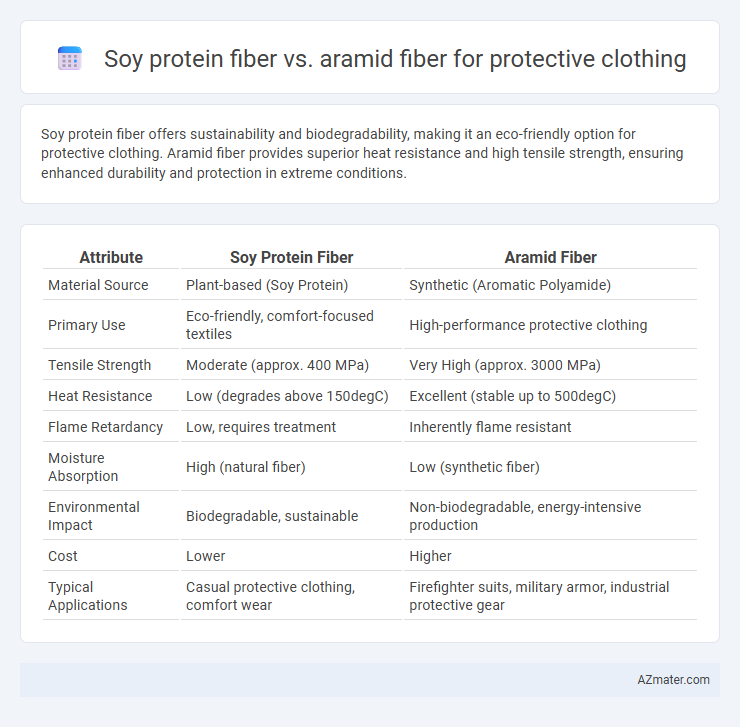
| Attribute | Soy Protein Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Plant-based (Soy Protein) | Synthetic (Aromatic Polyamide) |
| Primary Use | Eco-friendly, comfort-focused textiles | High-performance protective clothing |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate (approx. 400 MPa) | Very High (approx. 3000 MPa) |
| Heat Resistance | Low (degrades above 150degC) | Excellent (stable up to 500degC) |
| Flame Retardancy | Low, requires treatment | Inherently flame resistant |
| Moisture Absorption | High (natural fiber) | Low (synthetic fiber) |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, sustainable | Non-biodegradable, energy-intensive production |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Typical Applications | Casual protective clothing, comfort wear | Firefighter suits, military armor, industrial protective gear |
Introduction to Protective Clothing Materials
Soy protein fiber offers biodegradability, comfort, and moderate strength, making it suitable for lightweight protective clothing with enhanced moisture absorption. Aramid fiber, known for exceptional heat resistance, high tensile strength, and impact protection, is widely used in ballistic and fire-resistant apparel for military and industrial applications. Selection between these fibers depends on the specific protective requirements, balancing sustainability and advanced safety performance.
Overview of Soy Protein Fiber
Soy protein fiber, derived from soybeans, offers a biodegradable and sustainable alternative for protective clothing due to its natural origin and moisture-wicking properties. It provides excellent breathability, comfort, and moderate strength, making it suitable for lightweight protective garments. While soy protein fiber lacks the high heat resistance and durability of aramid fibers, it enhances wearer comfort and environmental sustainability in protective apparel applications.
Overview of Aramid Fiber
Aramid fiber, a synthetic polymer known for its exceptional tensile strength and heat resistance, is widely used in protective clothing to provide superior cut, abrasion, and flame resistance. Unlike soy protein fiber, which offers biodegradability and comfort, aramid fibers such as Kevlar and Nomex deliver unmatched durability and protection in high-risk environments. Its inherent chemical stability and lightweight nature make aramid fiber ideal for military, firefighting, and industrial safety applications.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Soy protein fiber demonstrates moderate tensile strength and flexibility, making it suitable for lightweight protective clothing but limited in heavy-duty applications. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, exhibits exceptional mechanical strength with high tensile strength, impact resistance, and thermal stability, essential for ballistic and cut-resistant garments. The comparison reveals that aramid fibers outperform soy protein fibers significantly in mechanical strength, providing superior durability and protection in high-risk environments.
Heat and Flame Resistance
Aramid fiber exhibits superior heat and flame resistance compared to soy protein fiber, making it a preferred choice for protective clothing in high-risk environments. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, can withstand temperatures up to approximately 370degC (700degF) without melting, whereas soy protein fibers typically degrade at lower temperatures around 150degC (302degF). The inherent flame retardant properties and thermal stability of aramid fibers provide enhanced protection against fire hazards, whereas soy protein fibers require significant chemical treatments to improve heat resistance.
Comfort and Wearability
Soy protein fiber offers superior moisture absorption and breathability compared to aramid fiber, enhancing comfort during extended wear in protective clothing. Aramid fiber provides excellent heat resistance and mechanical strength but tends to be stiffer and less flexible, which can reduce overall wearability. Combining soy protein fiber with aramid fiber in fabric blends can optimize both comfort and protective performance for demanding environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Soy protein fiber offers a biodegradable and renewable alternative to conventional synthetic fibers, significantly reducing environmental impact through lower carbon emissions and minimal chemical use during production. Aramid fiber, while providing superior heat and chemical resistance essential for protective clothing, relies on petroleum-based processes and involves energy-intensive manufacturing that contributes to a larger carbon footprint and challenges in recyclability. Prioritizing soy protein fiber supports sustainability goals by promoting circular economy practices and lowering dependency on fossil fuels, whereas aramid fiber remains critical where long-term durability and high-performance protection are non-negotiable.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Soy protein fiber offers a cost-effective and sustainable alternative to aramid fiber for protective clothing, with lower raw material and production expenses due to its renewable agricultural origin. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, command higher prices because of their complex manufacturing processes and superior performance characteristics, though they benefit from widespread industrial availability and established supply chains. Availability of soy protein fiber is increasing with advancements in biofiber technology, but currently remains less accessible than the well-established aramid fiber, influencing procurement decisions based on budget constraints and performance requirements.
Applications in Protective Clothing
Soy protein fiber offers excellent moisture absorption and biodegradability, making it suitable for lightweight, eco-friendly protective clothing in agricultural and medical fields. Aramid fiber provides superior heat resistance, high tensile strength, and excellent durability, ideal for flame-resistant garments used by firefighters and military personnel. Combining these fibers can enhance comfort and protection, balancing sustainability with high-performance safety requirements.
Future Trends and Innovations
Soy protein fiber offers promising sustainability benefits and biodegradability for protective clothing, attracting future innovation in eco-friendly textile development. Aramid fiber remains dominant for high-performance applications due to its exceptional heat resistance and strength, yet research is advancing to enhance comfort and reduce environmental impact. Emerging hybrid materials combining soy protein fiber with aramid aim to balance durability, protection, and sustainability in next-generation protective apparel.
Infographic: Soy protein fiber vs Aramid fiber for Protective clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com