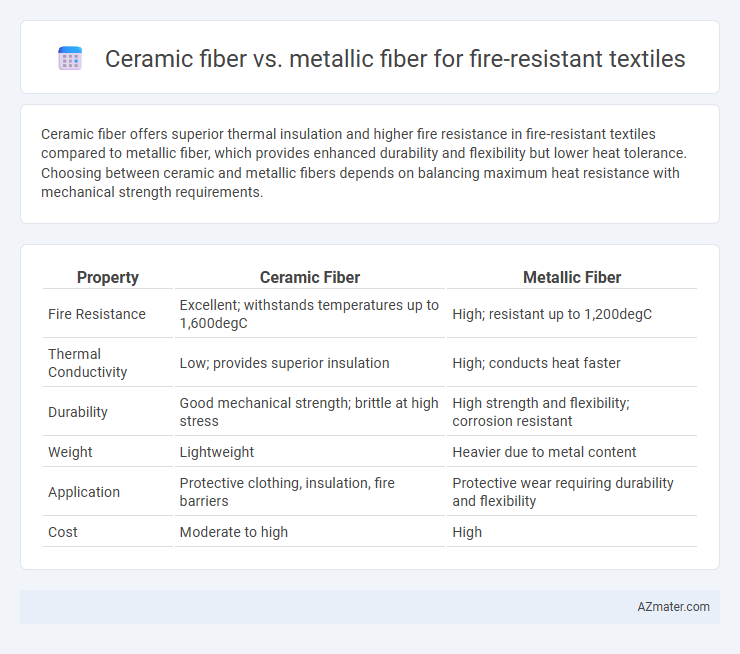
Ceramic fiber offers superior thermal insulation and higher fire resistance in fire-resistant textiles compared to metallic fiber, which provides enhanced durability and flexibility but lower heat tolerance. Choosing between ceramic and metallic fibers depends on balancing maximum heat resistance with mechanical strength requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Fiber | Metallic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Excellent; withstands temperatures up to 1,600degC | High; resistant up to 1,200degC |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low; provides superior insulation | High; conducts heat faster |
| Durability | Good mechanical strength; brittle at high stress | High strength and flexibility; corrosion resistant |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier due to metal content |
| Application | Protective clothing, insulation, fire barriers | Protective wear requiring durability and flexibility |
| Cost | Moderate to high | High |
Introduction to Fire-Resistant Textiles
Fire-resistant textiles utilize advanced fibers like ceramic and metallic fibers to enhance thermal protection and durability in extreme heat conditions. Ceramic fibers offer exceptional heat resistance up to 1260degC, excellent insulation properties, and lightweight comfort, making them ideal for protective clothing and industrial applications. Metallic fibers provide superior mechanical strength, electrical conductivity, and durability, often integrated with other fibers to improve overall fire resistance and structural integrity in harsh environments.
Overview of Ceramic Fiber Properties
Ceramic fibers exhibit exceptional heat resistance, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1,200degC, which makes them ideal for fire-resistant textiles. They possess low thermal conductivity and excellent chemical stability, ensuring long-term durability in harsh environments. These fibers also offer high tensile strength and resistance to thermal shock, providing superior protection in applications requiring consistent flame-retardant performance.
Overview of Metallic Fiber Properties
Metallic fibers exhibit exceptional thermal conductivity, high melting points above 1000degC, and excellent mechanical strength, making them ideal for fire-resistant textiles in extreme heat environments. Their inherent resistance to oxidation and corrosion enhances durability under prolonged exposure to fire and harsh conditions. Unlike ceramic fibers, metallic fibers offer superior flexibility and electrical conductivity, expanding their applications in protective clothing and industrial safety gear.
Heat Resistance Comparison: Ceramic vs Metallic
Ceramic fibers exhibit superior heat resistance compared to metallic fibers, withstanding temperatures up to 1,500degC or higher without melting or degrading. Metallic fibers typically resist heat up to 600degC to 1,000degC but can oxidize or weaken under prolonged high-temperature exposure. The inherent thermal stability of ceramic fibers makes them ideal for fire-resistant textiles requiring extreme heat endurance and insulation.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Analysis
Ceramic fibers exhibit superior thermal stability and mechanical strength at elevated temperatures compared to metallic fibers, making them more suitable for fire-resistant textile applications. Metallic fibers provide enhanced tensile strength and flexibility but tend to oxidize and degrade faster under prolonged high-temperature exposure, reducing durability. The durability analysis reveals ceramic fibers maintain structural integrity longer under cyclic thermal stress, while metallic fibers require protective coatings to enhance lifespan and mechanical performance in fire-resistant fabrics.
Flexibility and Comfort in Textile Applications
Ceramic fibers exhibit high thermal resistance but tend to be rigid and less flexible, limiting comfort in fire-resistant textile applications. Metallic fibers, such as stainless steel or aluminum, offer greater flexibility and improved comfort due to their ductility while maintaining adequate fire resistance. Balancing thermal protection and wearability, metallic fibers provide enhanced comfort in garments requiring both fire resistance and flexibility.
Weight Considerations: Ceramic vs Metallic Fibers
Ceramic fibers offer significantly lower density, typically around 2.5 to 3.0 g/cm3, compared to metallic fibers like stainless steel, which range from 7.8 to 8.0 g/cm3, making ceramic fibers ideal for lightweight fire-resistant textiles. The reduced weight of ceramic fiber composites enhances wearer comfort and mobility in protective clothing without compromising thermal resistance. In contrast, metallic fibers provide greater durability but increase the overall garment weight, potentially limiting long-term use in high-mobility applications.
Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
Ceramic fibers exhibit superior chemical and corrosion resistance compared to metallic fibers, maintaining stability in highly acidic and alkaline environments commonly encountered in fire-resistant textile applications. Metallic fibers, while offering good thermal conductivity, are prone to oxidation and corrosion when exposed to moisture and harsh chemicals, reducing their long-term durability. The inert nature of ceramic fibers ensures they retain mechanical integrity and resist degradation under aggressive chemical exposure, making them ideal for advanced fire-resistant textiles.
Cost and Manufacturing Implications
Ceramic fibers offer superior thermal insulation and higher melting points, making them more expensive due to energy-intensive manufacturing processes and specialized raw materials. Metallic fibers, while generally less costly and easier to produce, provide lower thermal resistance and are prone to oxidation at high temperatures, affecting durability. Choosing between ceramic and metallic fibers involves balancing upfront material costs with long-term performance and manufacturing scalability in fire-resistant textiles.
Best Applications and Industry Preferences
Ceramic fiber excels in high-temperature insulation for fire-resistant textiles, making it ideal for industries such as aerospace, metallurgy, and firefighting gear due to its superior thermal stability and lightweight nature. Metallic fiber, often utilized for its durability and electrical conductivity, finds preference in industrial protective clothing and welding applications where enhanced mechanical strength and spark resistance are critical. Industry preference leans toward ceramic fibers for extreme heat environments, while metallic fibers are chosen for scenarios requiring tough, abrasion-resistant fire protection.
Infographic: Ceramic fiber vs Metallic fiber for Fire-resistant textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com