Polylactic acid offers sustainable, biodegradable properties ideal for eco-friendly luxury fabrics, while silk provides unmatched natural luster and softness prized in high-end fashion. Polylactic acid's durability and moisture-wicking contrast with silk's delicate texture and superior breathability, making each suitable for distinct luxury textile applications.
Table of Comparison
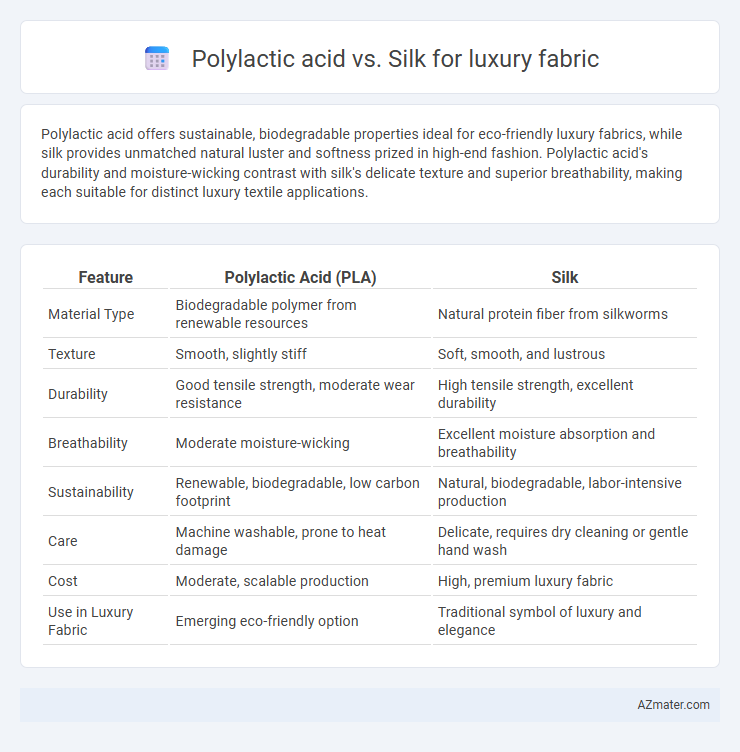
| Feature | Polylactic Acid (PLA) | Silk |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Biodegradable polymer from renewable resources | Natural protein fiber from silkworms |
| Texture | Smooth, slightly stiff | Soft, smooth, and lustrous |
| Durability | Good tensile strength, moderate wear resistance | High tensile strength, excellent durability |
| Breathability | Moderate moisture-wicking | Excellent moisture absorption and breathability |
| Sustainability | Renewable, biodegradable, low carbon footprint | Natural, biodegradable, labor-intensive production |
| Care | Machine washable, prone to heat damage | Delicate, requires dry cleaning or gentle hand wash |
| Cost | Moderate, scalable production | High, premium luxury fabric |
| Use in Luxury Fabric | Emerging eco-friendly option | Traditional symbol of luxury and elegance |
Introduction to Luxury Fabrics: Polylactic Acid vs Silk
Polylactic acid (PLA) and silk represent two distinct categories of luxury fabrics, each with unique properties and sustainability profiles. PLA, a biodegradable polyester derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers a modern alternative with moisture-wicking and antimicrobial qualities, appealing to eco-conscious consumers. Silk, a natural protein fiber produced by silkworms, is renowned for its exceptional softness, luster, and breathability, maintaining its status as a classic symbol of opulence and high-end fashion.
Origins and Production Processes
Polylactic acid (PLA) is a bio-based fabric derived from fermented plant starches such as corn or sugarcane, produced through a chemical polymerization process that transforms lactic acid into fibers. Silk originates from the natural protein fiber spun by silkworms, harvested through a labor-intensive process involving cocoon boiling and reeling to extract continuous filaments. PLA's production emphasizes sustainability through renewable raw materials and lower environmental impact, while silk relies on traditional sericulture practices with a rich historical heritage in luxury textiles.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polylactic acid (PLA) fabric, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers a biodegradable alternative with a lower carbon footprint and reduced water usage compared to silk, which relies on intensive mulberry cultivation and silkworm farming. Silk production demands significant energy and water, alongside ethical concerns regarding animal welfare, whereas PLA's plant-based origins support circular economy principles and compostability. Both materials contribute to sustainability goals, but PLA's eco-friendly lifecycle and scalability increasingly position it as a responsible choice for luxury textiles prioritizing environmental impact.
Texture and Sensory Experience
Polylactic acid (PLA) fabrics offer a smooth, silky texture with a lightweight feel that is breathable and moisture-wicking, making them ideal for luxury garments that prioritize sustainability. Silk provides a naturally soft, lustrous texture with excellent drape and a cool, smooth hand that enhances tactile comfort and visual elegance. While PLA excels in eco-friendly appeal and durability, silk's unmatched sensory experience and sheen remain the gold standard in high-end luxury textiles.
Durability and Longevity
Polylactic acid (PLA) fabric offers excellent durability with high resistance to abrasion and moisture, making it suitable for long-lasting luxury textiles. Silk, renowned for its natural strength and elasticity, provides exceptional longevity when properly cared for but is more susceptible to damage from UV exposure and moisture. In terms of maintenance and everyday wear, PLA tends to outperform silk, offering better resilience without compromising the premium feel desired in luxury fabrics.
Breathability and Comfort
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers excellent moisture-wicking properties and breathability, making it suitable for active luxury wear, while silk excels in natural temperature regulation and soft comfort due to its protein-based fiber structure. Silk provides superior softness and a smooth texture that enhances skin comfort, whereas PLA's lightweight and hypoallergenic nature supports long-lasting freshness. Both fabrics deliver distinct advantages in luxury textiles, with silk favored for elegance and tactile comfort, and PLA praised for sustainability and breathable performance.
Dyeability and Color Retention
Polylactic acid (PLA) fibers exhibit strong dyeability due to their amorphous structure, allowing vibrant, uniform color absorption ideal for luxury fabrics. Silk, a natural protein fiber, offers superior color retention through its inherent affinity for dyes, maintaining brilliance and luster even after repeated washing. While PLA provides eco-friendly advantages with reasonable color fastness, silk's unparalleled dye uptake and long-lasting vibrancy set the standard for high-end textile applications.
Price Comparison and Market Trends
Polylactic acid (PLA) fabric generally offers a more cost-effective alternative to silk, with production expenses significantly lower due to its biodegradable, plant-based origin and scalable manufacturing processes. Silk maintains a premium price point driven by its natural protein fiber, labor-intensive harvesting, and luxury market demand, often exceeding PLA by several times per yard. Market trends show growing interest in PLA for sustainable luxury textiles, reflecting a shift toward eco-friendly materials, while silk remains dominant in traditional high-end fashion sectors due to its unmatched luster and texture.
Applications in High-End Fashion
Polylactic acid (PLA) and silk are prominent materials in luxury fabric applications, with PLA gaining traction for its sustainability and biodegradability, ideal for eco-conscious high-end fashion brands. Silk remains a quintessential choice due to its natural luster, softness, and superior drape, widely used in couture, eveningwear, and premium accessories. Innovations in PLA fibers now enable competitive texture and durability, expanding its application in luxury apparel while maintaining environmental responsibility.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers promising sustainability advantages and biodegradability that align with growing eco-conscious demand in the luxury fabric market, while silk maintains its timeless elegance and natural sheen valued in high-end fashion. Innovations in PLA include enhanced fiber strength, blendability with other natural fibers, and bioengineered variations that improve softness and durability, positioning it as a viable alternative for luxury textiles. Future prospects highlight PLA's potential to revolutionize sustainable luxury fabric production without compromising on quality, challenging silk's market dominance through advances in material science and eco-friendly manufacturing processes.
Infographic: Polylactic acid vs Silk for Luxury fabric
 azmater.com
azmater.com