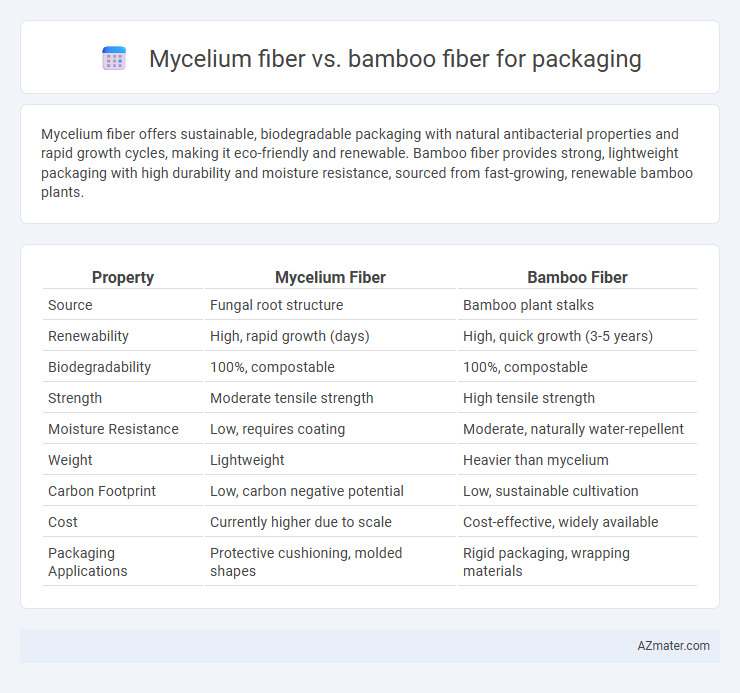
Mycelium fiber offers sustainable, biodegradable packaging with natural antibacterial properties and rapid growth cycles, making it eco-friendly and renewable. Bamboo fiber provides strong, lightweight packaging with high durability and moisture resistance, sourced from fast-growing, renewable bamboo plants.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Mycelium Fiber | Bamboo Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Fungal root structure | Bamboo plant stalks |
| Renewability | High, rapid growth (days) | High, quick growth (3-5 years) |
| Biodegradability | 100%, compostable | 100%, compostable |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength |
| Moisture Resistance | Low, requires coating | Moderate, naturally water-repellent |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier than mycelium |
| Carbon Footprint | Low, carbon negative potential | Low, sustainable cultivation |
| Cost | Currently higher due to scale | Cost-effective, widely available |
| Packaging Applications | Protective cushioning, molded shapes | Rigid packaging, wrapping materials |
Introduction to Sustainable Packaging Solutions
Mycelium fiber and bamboo fiber represent innovative materials reshaping sustainable packaging solutions by offering biodegradable and renewable alternatives to traditional plastics. Mycelium, derived from mushroom roots, decomposes rapidly while providing strong cushioning properties, ideal for protective packaging. Bamboo fiber, sourced from fast-growing bamboo plants, delivers high durability and moisture resistance, making it suitable for rigid packaging and reducing environmental impact through its fast renewability.
What Is Mycelium Fiber?
Mycelium fiber, derived from the root structure of fungi, offers a sustainable and biodegradable alternative to bamboo fiber for packaging applications. Unlike bamboo fiber, which comes from fast-growing grass stalks, mycelium grows rapidly on organic waste, creating a dense, foam-like material ideal for cushioning and protective packaging. Its natural ability to decompose quickly reduces environmental impact while maintaining durability and flexibility comparable to conventional packaging fibers.
What Is Bamboo Fiber?
Bamboo fiber, a natural textile material derived from the pulp of bamboo grass, is renowned for its strength, biodegradability, and antimicrobial properties, making it an eco-friendly choice for sustainable packaging solutions. Bamboo fiber's renewable growth cycle, requiring minimal water and pesticides, contributes to its environmental advantages over traditional packaging materials. Its smooth texture and durability provide excellent protection and aesthetic appeal, positioning bamboo fiber as a competitive alternative to mycelium fiber in the packaging industry.
Environmental Impact: Mycelium vs Bamboo
Mycelium fiber offers a highly sustainable alternative for packaging due to its rapid growth rate and ability to biodegrade within weeks, significantly reducing landfill waste and carbon footprint. Bamboo fiber, while renewable and fast-growing, requires extensive water and pesticide use, which can contribute to environmental degradation and higher energy consumption during processing. Comparing environmental impact, mycelium's minimal resource requirements and compostability provide a greener solution than bamboo fiber in packaging applications.
Production Processes Compared
Mycelium fiber production involves growing fungal mycelium on agricultural waste under controlled conditions, resulting in a biodegradable material formed through natural biological processes without high-energy inputs. Bamboo fiber production requires harvesting bamboo, mechanical or chemical processing to extract fibers, and energy-intensive steps such as pulping, bleaching, and drying, leading to higher environmental impact. Compared to bamboo, mycelium fiber production offers a faster, lower-impact alternative with fewer chemical treatments and reduced water consumption, enhancing sustainability in packaging applications.
Material Strength and Durability
Mycelium fiber exhibits impressive tensile strength and biodegradability, making it a sustainable alternative for packaging that withstands moderate mechanical stress. Bamboo fiber offers superior durability and higher tensile strength, providing robust protection for heavy-duty packaging applications. Both materials excel in eco-friendly packaging, but bamboo fiber outperforms mycelium fiber in long-term resilience and structural integrity.
Biodegradability and Compostability
Mycelium fiber and bamboo fiber both offer excellent biodegradability, but mycelium decomposes faster, typically within 30 to 60 days, making it highly suitable for sustainable packaging solutions. Bamboo fiber, while also compostable, can take several months to break down due to its denser cellulose structure, yet it remains an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic packaging. Both fibers contribute to reducing landfill waste, with mycelium fiber excelling in rapid compostability under industrial and home composting conditions.
Cost Considerations for Manufacturers
Mycelium fiber offers manufacturers a cost-effective alternative to bamboo fiber due to its rapid growth rate and ability to utilize agricultural waste as raw material, significantly lowering production expenses. Bamboo fiber, while durable and biodegradable, often incurs higher costs related to harvesting, processing, and transportation, especially in regions where bamboo is less abundant. Evaluating the balance between scalability, raw material availability, and processing infrastructure is crucial for manufacturers seeking sustainable packaging solutions with optimized cost efficiency.
Applications in the Packaging Industry
Mycelium fiber and bamboo fiber are increasingly used in the packaging industry due to their sustainability and biodegradability. Mycelium fiber is ideal for protective packaging and custom molds because of its cushioning properties and ability to grow into specific shapes, making it suitable for electronics and fragile goods. Bamboo fiber excels in rigid packaging materials and paper-like products, offering high strength and moisture resistance for food containers and eco-friendly shipping boxes.
Future Trends and Innovations
Mycelium fiber is emerging as a sustainable alternative to traditional packaging materials due to its rapid biodegradability and ability to be molded into custom shapes, reducing waste and energy consumption. Bamboo fiber offers exceptional strength and natural antimicrobial properties while being renewable and fast-growing, making it ideal for eco-friendly packaging solutions. Future trends emphasize hybrid composites combining mycelium and bamboo fibers to enhance durability, reduce carbon footprints, and meet increasing consumer demand for biodegradable packaging innovations.
Infographic: Mycelium fiber vs Bamboo fiber for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com