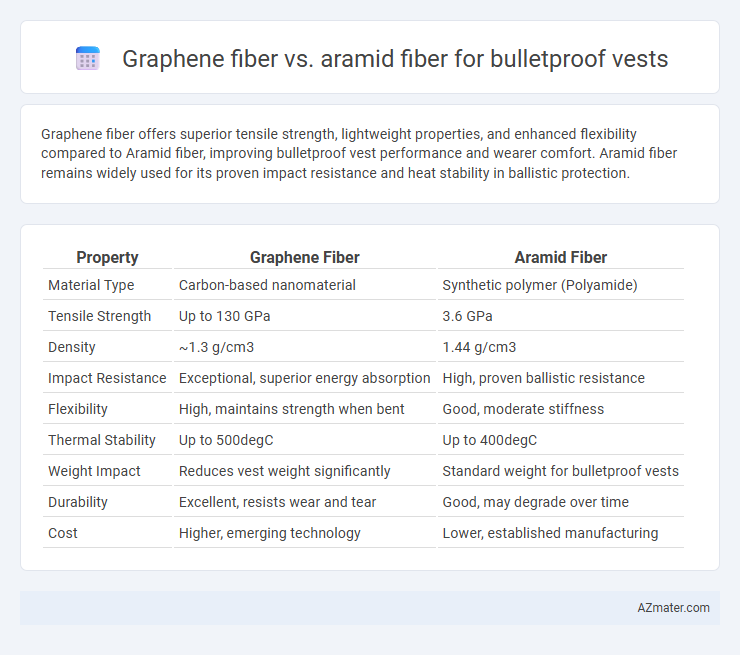
Graphene fiber offers superior tensile strength, lightweight properties, and enhanced flexibility compared to Aramid fiber, improving bulletproof vest performance and wearer comfort. Aramid fiber remains widely used for its proven impact resistance and heat stability in ballistic protection.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Graphene Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Carbon-based nanomaterial | Synthetic polymer (Polyamide) |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 130 GPa | 3.6 GPa |
| Density | ~1.3 g/cm3 | 1.44 g/cm3 |
| Impact Resistance | Exceptional, superior energy absorption | High, proven ballistic resistance |
| Flexibility | High, maintains strength when bent | Good, moderate stiffness |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 500degC | Up to 400degC |
| Weight Impact | Reduces vest weight significantly | Standard weight for bulletproof vests |
| Durability | Excellent, resists wear and tear | Good, may degrade over time |
| Cost | Higher, emerging technology | Lower, established manufacturing |
Introduction to Bulletproof Vest Materials
Graphene fiber and aramid fiber are leading materials used in the manufacturing of bulletproof vests due to their exceptional strength-to-weight ratios. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, are synthetic polymers known for high tensile strength, heat resistance, and impact absorption, making them standard in ballistic protection. Graphene fibers offer revolutionary potential with superior tensile strength, flexibility, and lightweight properties, promising enhanced durability and comfort in next-generation body armor.
What is Graphene Fiber?
Graphene fiber is a cutting-edge material composed of single-layer carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, offering exceptional tensile strength and lightweight properties ideal for bulletproof vests. Compared to Aramid fiber, known for its heat resistance and high strength-to-weight ratio, graphene fiber provides superior durability and enhanced flexibility, potentially improving wearer comfort and impact resistance. Research highlights that graphene's conductivity and mechanical robustness enable the development of thinner, more efficient protective gear with increased energy absorption capabilities.
What is Aramid Fiber?
Aramid fiber is a class of heat-resistant and strong synthetic fibers used in ballistic-rated body armor and bulletproof vests due to its exceptional tensile strength and durability. Known for high abrasion resistance and lightweight characteristics, aramid fibers like Kevlar provide effective protection by dispersing the energy of bullets and shrapnel upon impact. Unlike graphene fiber, which is emerging for its unique conductivity and mechanical properties, aramid fiber remains the industry standard in ballistic protection because of its proven reliability and cost-effectiveness.
Mechanical Strength: Graphene vs Aramid Fiber
Graphene fiber exhibits significantly higher tensile strength, reaching up to 130 GPa, compared to aramid fiber's typical range of 3.6 to 4.1 GPa, making it a superior choice for bulletproof vests requiring exceptional mechanical performance. The exceptional stiffness and lightweight nature of graphene fibers enhance ballistic resistance while reducing vest weight, providing increased mobility for the wearer. Aramid fibers like Kevlar maintain reliable impact absorption and flexibility but cannot match the mechanical strength and durability of graphene-based composites in high-stress penetration scenarios.
Weight and Flexibility Comparison
Graphene fiber exhibits significantly lower weight compared to aramid fiber, enhancing overall armor efficiency and reducing wearer fatigue in bulletproof vests. Its superior flexibility allows for improved movement and comfort without compromising ballistic protection, outperforming the typically stiffer aramid fiber. These properties make graphene fiber an advanced material choice for lightweight, flexible bulletproof vests.
Ballistic Protection Performance
Graphene fiber exhibits superior ballistic protection due to its exceptional tensile strength and energy absorption capabilities, outperforming traditional aramid fibers such as Kevlar. Graphene's atomic thin structure enables lightweight vests that maintain high impact resistance and multi-hit durability. In contrast, aramid fibers provide reliable ballistic resistance but are heavier and less effective at dispersing kinetic energy from high-velocity projectiles.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Graphene fiber offers superior durability due to its exceptional tensile strength and flexibility, providing enhanced impact resistance in bulletproof vests compared to aramid fiber. Its outstanding environmental resistance includes excellent thermal stability and resistance to UV degradation, ensuring prolonged performance in harsh conditions. Aramid fiber, while strong and heat resistant, tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to moisture and sunlight, limiting its lifespan in adverse environments.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Graphene fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to aramid fiber, but its high production cost and complex manufacturing processes limit widespread adoption in bulletproof vests. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, benefits from established, cost-effective mass production techniques, making it more affordable and readily available for body armor applications. Manufacturers often prefer aramid fiber for balance between performance, cost-efficiency, and scalability in protective gear production.
Future Prospects and Innovation Trends
Graphene fiber offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced flexibility compared to Aramid fiber, which positions it as a revolutionary material for next-generation bulletproof vests. Innovations in graphene fiber focus on improved ballistic resistance, thermal management, and durability through advanced nanocomposite integration and scalable manufacturing techniques. Future prospects emphasize combining graphene with existing Aramid structures to create hybrid vests that optimize protection, comfort, and weight reduction in personal armor systems.
Final Verdict: Which Fiber is Superior for Bulletproof Vests?
Graphene fiber exhibits superior tensile strength, lightweight properties, and excellent energy absorption compared to aramid fiber, making it more effective in dissipating ballistic impacts for bulletproof vests. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, provides proven ballistic resistance and flexibility but is heavier and less durable against repeated impacts than graphene composites. The final verdict favors graphene fiber as the superior option for next-generation bulletproof vests due to its enhanced strength-to-weight ratio and advanced protective capabilities.
Infographic: Graphene fiber vs Aramid fiber for Bulletproof vest
 azmater.com
azmater.com