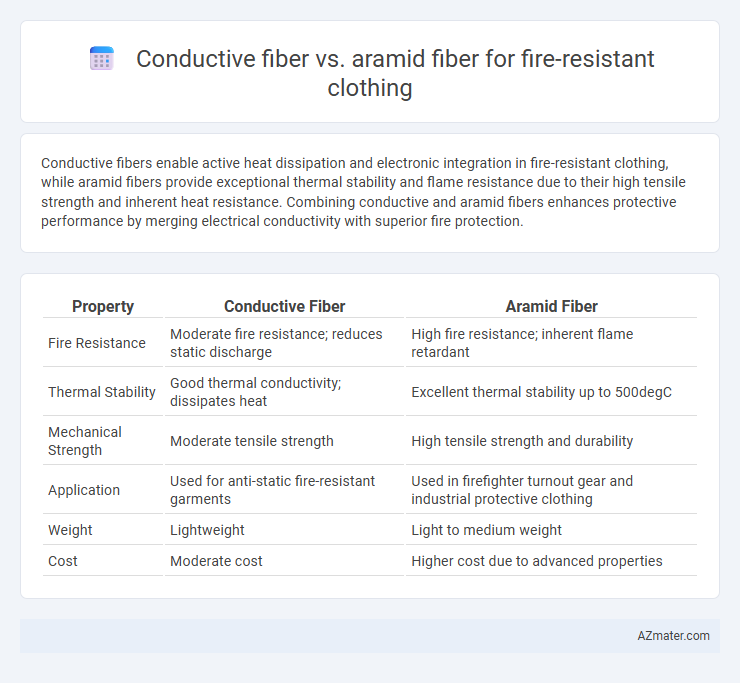
Conductive fibers enable active heat dissipation and electronic integration in fire-resistant clothing, while aramid fibers provide exceptional thermal stability and flame resistance due to their high tensile strength and inherent heat resistance. Combining conductive and aramid fibers enhances protective performance by merging electrical conductivity with superior fire protection.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Conductive Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Moderate fire resistance; reduces static discharge | High fire resistance; inherent flame retardant |
| Thermal Stability | Good thermal conductivity; dissipates heat | Excellent thermal stability up to 500degC |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength and durability |
| Application | Used for anti-static fire-resistant garments | Used in firefighter turnout gear and industrial protective clothing |
| Weight | Lightweight | Light to medium weight |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties |
Introduction to Fire-Resistant Clothing Materials
Fire-resistant clothing materials prioritize safety by combining thermal insulation and durability, with aramid fiber being a primary choice due to its exceptional heat resistance and strength. Conductive fibers are increasingly integrated for static dissipation but lack the inherent flame-retardant properties of aramid fibers like Nomex or Kevlar. Choosing the right fiber depends on balancing protection from high temperatures with additional functionalities such as electrostatic discharge prevention in hazardous environments.
Overview of Conductive Fiber Technology
Conductive fiber technology in fire-resistant clothing integrates metallic or carbon-based fibers to dissipate static electricity, reducing ignition risks in hazardous environments. These fibers enhance wearer safety by preventing electrostatic discharge while maintaining flame resistance and durability. Compared to aramid fibers, which provide inherent thermal protection due to their molecular structure, conductive fibers focus on electrical conductivity without compromising fire-resistant properties.
Properties of Aramid Fiber in Fire Protection
Aramid fiber exhibits exceptional heat resistance with a decomposition temperature above 400degC, providing superior flame retardancy essential for fire-resistant clothing. Its high tensile strength and excellent thermal stability ensure durability and protection against extreme heat and mechanical stress. Aramid fibers also maintain structural integrity without melting or dripping, significantly reducing burn injuries during fire exposure.
Heat Resistance: Conductive Fiber vs Aramid Fiber
Aramid fibers, such as Nomex and Kevlar, exhibit exceptional heat resistance withstanding temperatures up to 370degC (700degF) without melting, making them a standard choice for fire-resistant clothing. Conductive fibers, often made from metal-coated or carbon-based materials, offer limited inherent heat resistance but excel in dissipating static electricity and heat through conduction, which can enhance wearer comfort under thermal stress. In fire-resistant applications, aramid fibers provide superior thermal protection, while conductive fibers complement with electrostatic discharge capabilities rather than direct heat resistance.
Electrical Conductivity and Functional Benefits
Conductive fibers enhance fire-resistant clothing by providing electrical conductivity, enabling antistatic properties that reduce the risk of electrical hazards in hazardous environments. Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional thermal resistance and strength, offer superior flame retardancy and durability without electrical conductivity. Combining conductive fibers with aramid fibers creates fire-resistant garments that protect against flames while dissipating static electricity, improving overall safety and functionality for workers in electrical and high-heat industries.
Durability and Mechanical Strength Comparison
Conductive fibers in fire-resistant clothing offer excellent electrical dissipation but generally have lower mechanical strength and durability compared to aramid fibers, which are engineered for high tensile strength and abrasion resistance. Aramid fibers, such as Nomex and Kevlar, provide superior heat resistance, maintaining structural integrity under extreme thermal stress while delivering long-lasting durability in harsh environments. The robust molecular structure of aramid fibers ensures enhanced mechanical performance, making them more suitable for applications requiring both fire resistance and mechanical toughness.
Comfort and Wearability for End Users
Conductive fiber in fire-resistant clothing enhances comfort by offering excellent moisture-wicking properties and breathability, reducing heat stress for end users during extended wear. Aramid fiber provides superior durability and thermal protection but can be less flexible and heavier, potentially impacting mobility and comfort. Balancing the two materials can optimize wearability by ensuring both safety and a comfortable fit in hazardous environments.
Safety Standards and Regulatory Compliance
Conductive fibers used in fire-resistant clothing help dissipate static electricity, reducing ignition risk and complying with NFPA 70E and IEC 61482 standards for arc flash protection. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, provide intrinsic flame resistance, meeting regulations like NFPA 2112 and ASTM F1506 for thermal and flash fire hazards. Both fiber types ensure compliance with OSHA and ISO safety standards, enhancing worker protection in hazardous environments.
Cost-Effectiveness and Scalability
Conductive fiber offers moderate cost-effectiveness due to its ability to integrate electronic functionalities, but higher production complexity can limit scalability compared to aramid fiber. Aramid fiber excels in cost-efficiency and large-scale manufacturing, providing robust fire resistance with widespread availability and established supply chains. For fire-resistant clothing, aramid fiber delivers a more scalable and economically viable solution, while conductive fiber adds specialized functions at a higher cost.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Fire-Resistant Applications
Conductive fibers enhance fire-resistant clothing by providing static dissipation and electromagnetic shielding, improving safety in explosive environments where sparks must be minimized. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, offer superior thermal resistance and durability, maintaining structural integrity under extreme heat and flame exposure. Selecting the right fiber depends on balancing heat resistance, electrical conductivity, and mechanical strength specific to fire-resistant applications in industrial or firefighting gear.
Infographic: Conductive fiber vs Aramid fiber for Fire-resistant clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com