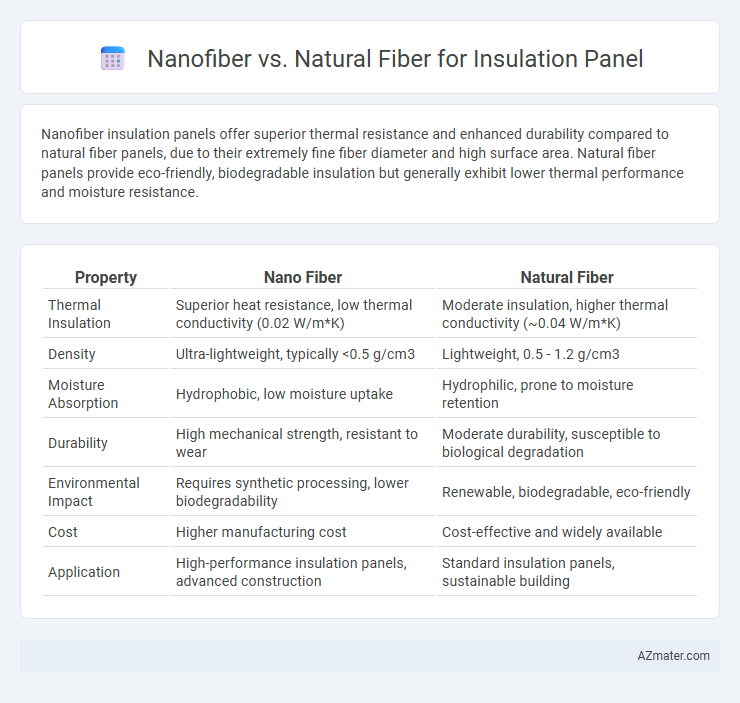
Nanofiber insulation panels offer superior thermal resistance and enhanced durability compared to natural fiber panels, due to their extremely fine fiber diameter and high surface area. Natural fiber panels provide eco-friendly, biodegradable insulation but generally exhibit lower thermal performance and moisture resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nano Fiber | Natural Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | Superior heat resistance, low thermal conductivity (0.02 W/m*K) | Moderate insulation, higher thermal conductivity (~0.04 W/m*K) |
| Density | Ultra-lightweight, typically <0.5 g/cm3 | Lightweight, 0.5 - 1.2 g/cm3 |
| Moisture Absorption | Hydrophobic, low moisture uptake | Hydrophilic, prone to moisture retention |
| Durability | High mechanical strength, resistant to wear | Moderate durability, susceptible to biological degradation |
| Environmental Impact | Requires synthetic processing, lower biodegradability | Renewable, biodegradable, eco-friendly |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Cost-effective and widely available |
| Application | High-performance insulation panels, advanced construction | Standard insulation panels, sustainable building |
Introduction to Insulation Panel Materials
Nano fibers exhibit superior thermal resistance and enhanced mechanical properties compared to natural fibers in insulation panels, offering improved energy efficiency and durability. Natural fibers such as cotton, hemp, and jute provide sustainable and biodegradable options but typically have lower thermal insulation performance and moisture resistance. Advanced nano fiber materials like electrospun nanofibers allow for finer microstructures, contributing to better overall insulation capabilities in modern panel designs.
What Are Nano Fibers?
Nano fibers are ultrafine fibers with diameters typically less than 100 nanometers, characterized by their high surface area-to-volume ratio and exceptional mechanical strength. These fibers enhance insulation panels by providing superior thermal resistance, improved durability, and enhanced moisture control compared to natural fibers such as cotton or wool. Their nanoscale structure enables better air trapping and reduced heat transfer, making them highly efficient for advanced insulation applications.
Overview of Natural Fibers
Natural fibers such as cellulose, cotton, hemp, and wool are widely used in insulation panels due to their renewable origin, biodegradability, and excellent thermal properties. These fibers offer superior moisture regulation, sound absorption, and breathability compared to synthetic alternatives, making them environmentally friendly and energy-efficient insulation solutions. Despite their generally lower thermal resistance than nanofibers, natural fibers provide cost-effective, sustainable performance with reduced environmental impact for building insulation applications.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Nano fibers exhibit superior thermal insulation properties compared to natural fibers due to their extremely fine diameters, which create a denser network that reduces heat transfer through convection and conduction. Natural fibers such as wool, cotton, and hemp offer good thermal resistance but generally have higher thermal conductivity and retain more moisture, which can degrade insulating performance over time. Advanced nano fiber insulation panels typically achieve lower thermal conductivity values, often below 0.03 W/m*K, enhancing energy efficiency in building applications compared to natural fiber panels with values closer to 0.04-0.06 W/m*K.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Nano fibers exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to natural fibers, offering enhanced tensile properties and resistance to deformation in insulation panels. Their high surface area and nanoscale structure contribute to improved load distribution, resulting in greater durability under mechanical stress. In contrast, natural fibers tend to degrade faster due to moisture absorption and biological factors, reducing their long-term performance in insulation applications.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Nano fibers in insulation panels offer enhanced thermal efficiency and reduced material usage, leading to lower overall carbon footprints compared to traditional natural fibers. Natural fibers such as hemp, cotton, and wool are biodegradable, renewable, and contribute to reduced landfill waste but require more extensive agricultural resources and water consumption during production. Environmental Impact Assessments highlight that while nano fibers provide superior performance, natural fibers excel in sustainability through recyclability and lower embodied energy, making the choice dependent on balancing operational efficiency with ecological considerations.
Cost Analysis: Nano Fiber vs Natural Fiber
Nano fiber insulation panels typically have higher initial costs due to advanced manufacturing processes and specialized raw materials, while natural fiber panels offer more cost-effective solutions with readily available resources like hemp, flax, or cotton. However, nano fibers can provide superior thermal performance and durability, potentially reducing long-term expenses on energy and maintenance. When evaluating cost-effectiveness, consider lifecycle costs that include installation, energy savings, and panel longevity alongside upfront purchase prices.
Fire Resistance and Safety Properties
Nano fibers used in insulation panels offer superior fire resistance compared to natural fibers due to their high thermal stability and non-combustible properties. Natural fibers such as wool or cotton are more prone to ignition and combustion, often requiring chemical treatments to enhance fire retardancy, which can impact environmental safety. Fire-safe insulation panels with nano fibers provide enhanced protection by limiting flame spread and reducing toxic smoke emissions, improving overall building safety standards.
Applications in Modern Construction
Nano fibers offer superior thermal insulation and enhanced fire resistance, making them ideal for high-performance insulation panels in modern construction. Natural fibers like hemp and wool provide sustainable, breathable, and moisture-regulating properties, favored in eco-friendly building projects. Combining nano and natural fibers can optimize insulation efficiency, durability, and environmental impact in innovative architectural designs.
Future Trends in Insulation Panel Technology
Nano fibers offer superior thermal insulation and enhanced durability compared to natural fibers, driving innovation in insulation panel technology. Future trends emphasize the integration of nano fiber materials to achieve higher energy efficiency and sustainability in building construction. Advances in nano fiber production techniques will likely reduce costs, making them more competitive with traditional natural fiber insulation.
Infographic: Nano fiber vs Natural fiber for Insulation panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com