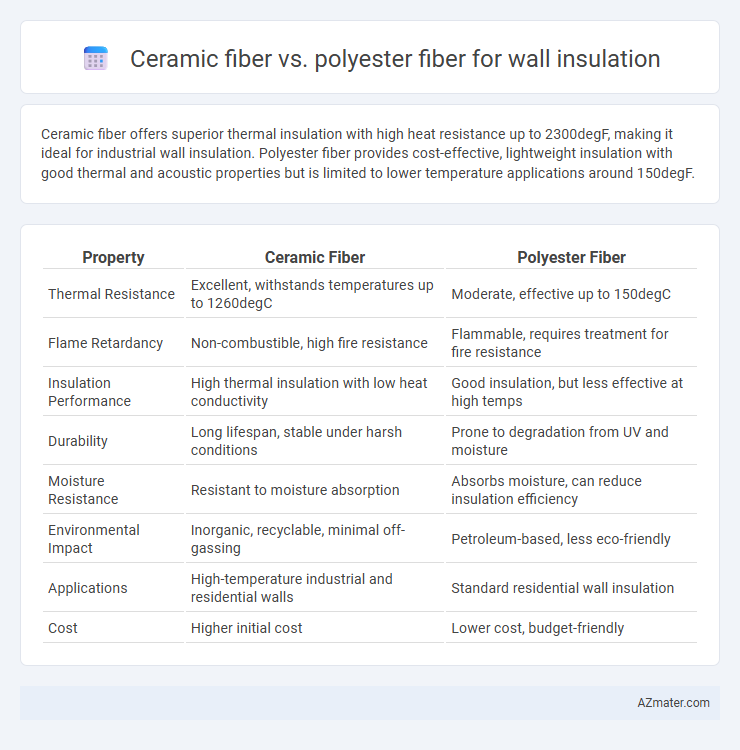
Ceramic fiber offers superior thermal insulation with high heat resistance up to 2300degF, making it ideal for industrial wall insulation. Polyester fiber provides cost-effective, lightweight insulation with good thermal and acoustic properties but is limited to lower temperature applications around 150degF.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Fiber | Polyester Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | Excellent, withstands temperatures up to 1260degC | Moderate, effective up to 150degC |
| Flame Retardancy | Non-combustible, high fire resistance | Flammable, requires treatment for fire resistance |
| Insulation Performance | High thermal insulation with low heat conductivity | Good insulation, but less effective at high temps |
| Durability | Long lifespan, stable under harsh conditions | Prone to degradation from UV and moisture |
| Moisture Resistance | Resistant to moisture absorption | Absorbs moisture, can reduce insulation efficiency |
| Environmental Impact | Inorganic, recyclable, minimal off-gassing | Petroleum-based, less eco-friendly |
| Applications | High-temperature industrial and residential walls | Standard residential wall insulation |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost, budget-friendly |
Introduction to Wall Insulation Materials
Ceramic fiber and polyester fiber serve distinct roles in wall insulation based on their thermal properties and applications. Ceramic fiber offers superior heat resistance and thermal stability, making it ideal for high-temperature environments and industrial insulation. Polyester fiber provides excellent sound absorption and moisture resistance, commonly used in residential and commercial buildings for energy efficiency and comfort.
Overview of Ceramic Fiber Insulation
Ceramic fiber insulation offers exceptional thermal resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 2300degF (1260degC), making it ideal for high-temperature wall insulation applications. Its low thermal conductivity and excellent stability under thermal stress provide superior energy efficiency and fire protection compared to polyester fiber insulation, which is limited to lower temperatures around 250degF (120degC). Ceramic fiber is lightweight, chemically inert, and resistant to thermal shock, ensuring long-lasting performance in demanding industrial and commercial insulation environments.
Overview of Polyester Fiber Insulation
Polyester fiber insulation offers excellent thermal performance with high resistance to moisture, mold, and mildew, making it suitable for wall insulation in both residential and commercial buildings. It is lightweight, flexible, and easy to install, providing sound absorption and durability while being safe and non-toxic compared to ceramic fiber, which can pose health risks due to respirable fibers. Polyester insulation's eco-friendly composition, often made from recycled materials, enhances sustainability while delivering reliable energy efficiency and long-term performance.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Ceramic fiber excels in thermal insulation with a high melting point above 1,200degC, making it ideal for extreme heat resistance and superior thermal performance in industrial and high-temperature wall applications. Polyester fiber, with a lower thermal conductivity around 0.035 W/m*K and maximum operating temperature near 150degC, performs well in residential wall insulation but lacks the heat endurance and insulating efficiency of ceramic fiber. The choice between ceramic and polyester fibers hinges on the specific temperature requirements and thermal conductivity needs of the insulation project.
Fire Resistance and Safety
Ceramic fiber insulation offers superior fire resistance with a melting point above 2300degF (1260degC), making it ideal for high-temperature applications and providing excellent protection against fire hazards. Polyester fiber insulation, while lightweight and cost-effective, has a lower ignition temperature around 482degF (250degC) and emits toxic fumes when burned, posing a higher fire risk and safety concern. Choosing ceramic fiber for wall insulation significantly enhances fire safety by preventing structural damage and reducing the spread of flames compared to conventional polyester fibers.
Moisture and Mold Resistance
Ceramic fiber insulation exhibits superior moisture resistance due to its inorganic composition, preventing water absorption and inhibiting mold growth effectively. Polyester fiber, being synthetic organic material, can retain moisture under certain conditions, increasing the risk of mold development and deterioration over time. For wall insulation applications where moisture control and mold resistance are critical, ceramic fiber provides a more durable and hygienic solution.
Installation Methods and Ease
Ceramic fiber insulation requires specialized installation methods such as precise cutting with sharp tools and safe handling due to its brittleness and dust potential, often demanding protective gear and professional skills. Polyester fiber, by contrast, is easier to install with simple cutting tools and minimal protective equipment, allowing for quick fitting and flexibility in irregular wall cavities. The ease of installation with polyester fiber reduces labor time and costs, while ceramic fiber's installation complexity offers superior thermal resistance but requires careful handling to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ceramic fiber insulation offers superior thermal resistance and durability with minimal environmental degradation, as it is composed of inorganic materials that are non-combustible and recyclable. Polyester fiber insulation, often derived from recycled plastics, reduces landfill waste and has lower embodied energy but may release microplastics and VOCs over time, raising concerns about indoor air quality and long-term sustainability. Selecting ceramic fiber supports enhanced fire safety and longevity, while polyester fiber provides a renewable resource cycle with lower initial carbon footprint.
Cost-Effectiveness and Longevity
Ceramic fiber offers superior thermal resistance and longevity compared to polyester fiber, making it more cost-effective for long-term wall insulation despite higher initial costs. Polyester fiber insulation is cheaper upfront but may degrade faster, requiring more frequent replacement and increasing overall expenses. Choosing ceramic fiber maximizes energy savings and durability, optimizing investment over the insulation's lifespan.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Wall Insulation
Ceramic fiber offers superior thermal resistance and fireproof properties, making it ideal for high-temperature wall insulation applications. Polyester fiber provides excellent sound absorption and moisture resistance, suitable for residential and commercial low-heat environments. Selecting the right fiber depends on factors like required thermal rating, environmental exposure, and insulation budget.
Infographic: Ceramic fiber vs Polyester fiber for Wall insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com