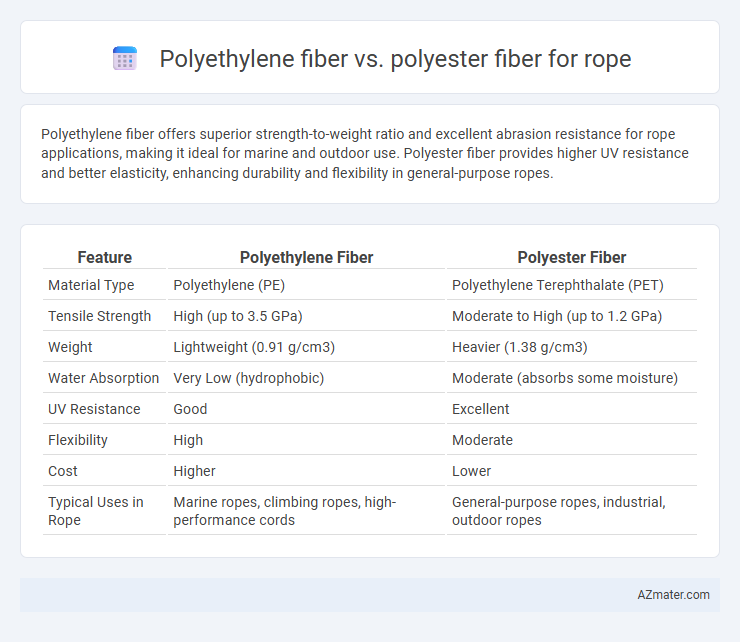
Polyethylene fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and excellent abrasion resistance for rope applications, making it ideal for marine and outdoor use. Polyester fiber provides higher UV resistance and better elasticity, enhancing durability and flexibility in general-purpose ropes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyethylene Fiber | Polyester Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polyethylene (PE) | Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) |
| Tensile Strength | High (up to 3.5 GPa) | Moderate to High (up to 1.2 GPa) |
| Weight | Lightweight (0.91 g/cm3) | Heavier (1.38 g/cm3) |
| Water Absorption | Very Low (hydrophobic) | Moderate (absorbs some moisture) |
| UV Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Flexibility | High | Moderate |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Typical Uses in Rope | Marine ropes, climbing ropes, high-performance cords | General-purpose ropes, industrial, outdoor ropes |
Introduction to Polyethylene and Polyester Fibers
Polyethylene fibers are high-strength, lightweight synthetic fibers known for their excellent abrasion resistance and low water absorption, making them ideal for rope applications requiring durability and buoyancy. Polyester fibers exhibit excellent tensile strength, UV resistance, and minimal stretch, providing reliable performance in marine and industrial ropes exposed to harsh environments. Both fibers serve critical roles in rope manufacturing, with polyethylene favored for lightweight and floatation needs, while polyester is preferred for strength and longevity under UV exposure.
Chemical Composition and Structure Comparison
Polyethylene fiber consists primarily of long chains of ethylene monomers, characterized by a crystalline, linear polymer structure that provides high tensile strength and chemical resistance. Polyester fiber is made from polyethylene terephthalate (PET), featuring aromatic ester linkages within its semi-crystalline structure, offering excellent durability and resistance to moisture and UV degradation. The differences in chemical composition and molecular arrangement influence their performance, with polyethylene fibers excelling in lightweight strength and chemical inertness, while polyester fibers provide superior elasticity and resistance to environmental stress.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyethylene fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and excellent resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for high-performance rope applications requiring maximum load-bearing capacity. Polyester fiber offers greater UV resistance and maintains mechanical integrity under prolonged exposure to sunlight and moisture, enhancing rope durability in outdoor environments. Both fibers provide robust durability, but polyethylene fibers excel in mechanical strength, while polyester fibers perform better against environmental degradation.
Weight and Density Differences
Polyethylene fiber used in ropes typically has a density of about 0.91 g/cm3, making it significantly lighter than polyester fiber, which has a density around 1.38 g/cm3. This lower density translates to polyethylene ropes being more buoyant and easier to handle, especially in marine applications where weight and flotation are critical. Polyester ropes, while heavier, offer higher abrasion resistance and UV stability but are less advantageous when lightweight and low-density materials are required.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Polyethylene fiber rope exhibits superior resistance to water, UV radiation, and chemicals compared to polyester fiber rope, making it ideal for marine and outdoor applications. Its low moisture absorption and excellent UV stability significantly reduce degradation and maintain strength over time in harsh environmental conditions. Polyester fiber, while durable and resistant to abrasion, absorbs more moisture and degrades faster under prolonged UV exposure, limiting its lifespan in extreme environments.
Flexibility and Handling in Rope Applications
Polyethylene fiber offers superior flexibility and lightweight properties, making it ideal for ropes requiring easy handling and minimal stretch, especially in marine and outdoor applications. Polyester fiber provides higher abrasion resistance and better UV stability, which enhances durability but can result in slightly stiffer ropes compared to polyethylene. Choosing between the two depends on the balance between flexibility for ease of use and durability for long-term performance in specific rope applications.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Polyester fiber ropes generally offer better cost efficiency due to their wide availability and lower production costs compared to polyethylene fiber ropes. Polyethylene fibers, especially high-modulus variants like UHMWPE, are more expensive but provide superior strength-to-weight ratios, which can justify the investment for specialized applications. The broader availability of polyester fibers ensures easier sourcing and replacement, making them a more economical choice for standard rope needs.
Typical Applications in Rope Manufacturing
Polyethylene fiber, known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and high resistance to moisture and chemicals, is typically used in marine ropes, fishing lines, and safety ropes where lightweight and buoyancy are critical. Polyester fiber offers superior UV resistance, durability, and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for general-purpose ropes, climbing ropes, and industrial lifting applications. Both fibers provide robust performance, but polyethylene is preferred for water-related uses, whereas polyester excels in high-stress, outdoor environments.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyethylene fiber exhibits lower environmental impact due to its higher recyclability and reduced energy consumption during production compared to polyester fiber, which is derived from petroleum and has a more intensive manufacturing process. Polyethylene ropes are often recyclable through mechanical processes, enabling a circular lifecycle, whereas polyester fibers present challenges in recycling due to their chemical complexity and tendency to degrade in quality after reprocessing. The environmental footprint of polyethylene fiber ropes is further minimized by their biodegradability in certain conditions, contrasting with polyester's persistence in ecosystems.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Rope Needs
Polyethylene fiber offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and superior resistance to moisture and chemicals, making it ideal for marine and outdoor ropes requiring buoyancy and durability. Polyester fiber provides excellent UV resistance, abrasion resistance, and minimal stretch, ensuring long-term performance in climbing ropes and industrial applications. Selecting the right fiber depends on the specific rope use, environmental exposure, and required mechanical properties such as strength, flexibility, and durability.
Infographic: Polyethylene fiber vs Polyester fiber for Rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com