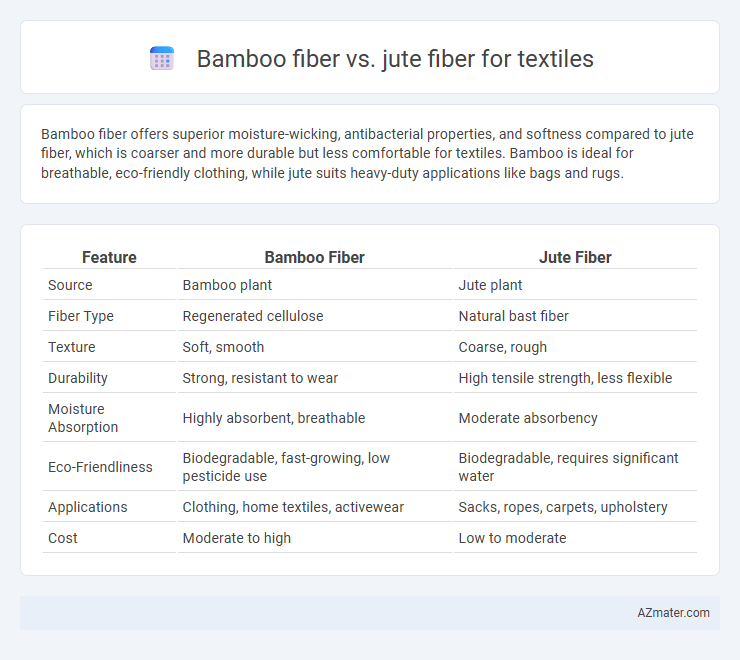
Bamboo fiber offers superior moisture-wicking, antibacterial properties, and softness compared to jute fiber, which is coarser and more durable but less comfortable for textiles. Bamboo is ideal for breathable, eco-friendly clothing, while jute suits heavy-duty applications like bags and rugs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bamboo Fiber | Jute Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Bamboo plant | Jute plant |
| Fiber Type | Regenerated cellulose | Natural bast fiber |
| Texture | Soft, smooth | Coarse, rough |
| Durability | Strong, resistant to wear | High tensile strength, less flexible |
| Moisture Absorption | Highly absorbent, breathable | Moderate absorbency |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable, fast-growing, low pesticide use | Biodegradable, requires significant water |
| Applications | Clothing, home textiles, activewear | Sacks, ropes, carpets, upholstery |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
Introduction to Bamboo Fiber and Jute Fiber
Bamboo fiber, derived from the pulp of bamboo grass, is known for its softness, breathability, and natural antimicrobial properties, making it ideal for textile applications requiring comfort and hygiene. Jute fiber, extracted from the retted stems of the jute plant, is valued for its strength, durability, and biodegradability, commonly used in coarse fabrics and sustainable packaging. Both fibers represent eco-friendly alternatives in textiles, with bamboo offering a smooth texture and moisture-wicking ability, while jute provides robust structural support.
Origin and Production Processes
Bamboo fiber originates from the bamboo plant, primarily processed through mechanical crushing or chemical soaking to extract cellulose, resulting in a soft and breathable textile fiber. Jute fiber is derived from the bark of the jute plant, harvested by retting, a natural microbial fermentation process that separates fibers from the stem, producing coarse and strong textile material. Both fibers are renewable resources with distinct extraction techniques influencing their texture and application in sustainable textiles.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Bamboo fiber exhibits high tensile strength and excellent moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for breathable and durable textiles. Jute fiber, known for its coarse texture and superior tensile strength, provides robust mechanical durability but lacks the softness and flexibility of bamboo. Both fibers offer eco-friendly alternatives, with bamboo excelling in softness and biodegradability, while jute is preferred for its stiffness and resistance to wear in heavy-duty textile applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bamboo fiber production requires less water and pesticides compared to jute fiber, significantly reducing its environmental footprint in textile manufacturing. Jute fiber, being biodegradable and renewable, supports soil health and prevents erosion, promoting sustainable agriculture. Both fibers offer eco-friendly alternatives to synthetic textiles, with bamboo providing faster growth cycles and jute enhancing biodiversity.
Comfort and Wearability in Textiles
Bamboo fiber offers superior softness and moisture-wicking properties, making it highly comfortable for clothing worn close to the skin. Jute fiber, while more coarse and rigid, provides durability but lacks the flexibility and breathability required for prolonged wearability. Bamboo's natural antibacterial qualities enhance comfort by reducing odor, whereas jute is better suited for outerwear or home textiles where strength outweighs softness.
Durability and Maintenance
Bamboo fiber offers high durability with its natural antibacterial properties that resist wear and tear, making it suitable for long-lasting textile applications. Jute fiber is strong and coarse, providing excellent tensile strength but requires careful maintenance to prevent mold and brittleness due to moisture sensitivity. Bamboo textiles demand less frequent washing and are easier to maintain, while jute needs gentle handling to preserve fiber integrity over time.
Dyeability and Aesthetic Appeal
Bamboo fiber exhibits excellent dyeability due to its smooth surface and porous structure, allowing vibrant and long-lasting colors in textile applications. Jute fiber, while more coarse and less absorbent, provides a natural, rustic aesthetic with muted tones that are ideal for eco-friendly and artisanal textile products. The choice between bamboo and jute fiber depends on the desired color intensity and fabric texture, with bamboo offering versatility in dyeing and jute emphasizing organic appeal.
Market Applications and Trends
Bamboo fiber is gaining popularity in the textile industry due to its softness, antibacterial properties, and sustainability, making it ideal for eco-friendly clothing, home textiles, and sportswear. Jute fiber maintains strong demand in industrial textiles, upholstery, and geotextiles, driven by its biodegradability, strength, and cost-effectiveness. Market trends indicate a growing preference for bamboo in fashion and personal care textiles, while jute remains essential for packaging and agricultural applications.
Cost Analysis and Economic Viability
Bamboo fiber offers a cost-effective alternative to jute fiber in textile manufacturing due to its faster growth rate and higher yield per hectare, reducing raw material expenses significantly. Jute fiber, while traditionally cheaper, faces price volatility driven by seasonal harvests and limited cultivation regions, impacting its economic stability. Analyzing the total cost of production and market demand, bamboo fiber demonstrates stronger economic viability with lower processing costs and increasing consumer preference for sustainable fabrics.
Consumer Preference and Future Prospects
Bamboo fiber offers superior softness, moisture-wicking, and antibacterial properties, making it highly preferred by consumers seeking comfort and sustainability in textiles. Jute fiber, valued for its strength, biodegradability, and affordability, remains popular in eco-friendly packaging and home decor but faces limitations in apparel applications. Future prospects for bamboo fiber are strong due to growing demand for eco-conscious fashion, while jute's market is expanding primarily in industrial and agricultural textiles driven by biodegradable material trends.
Infographic: Bamboo fiber vs Jute fiber for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com