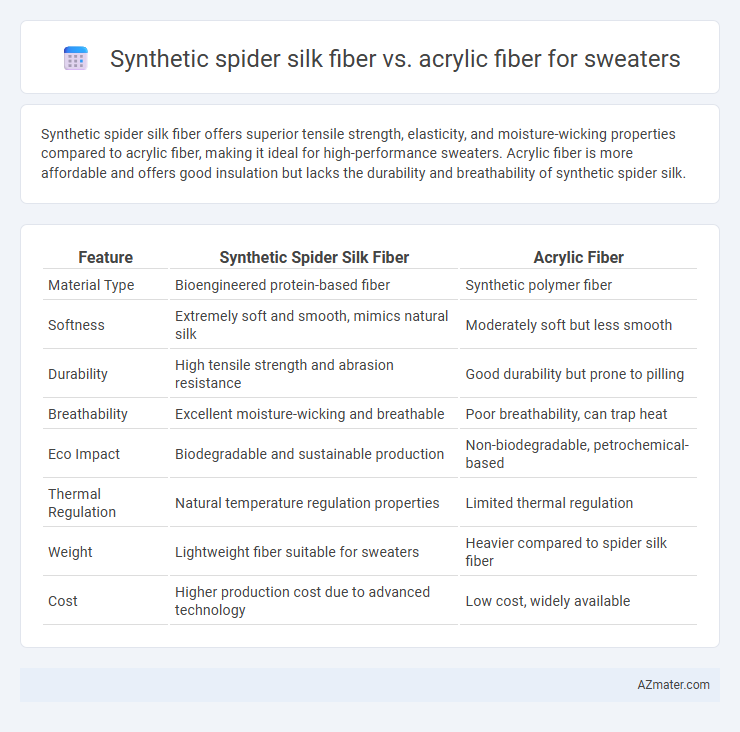
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers superior tensile strength, elasticity, and moisture-wicking properties compared to acrylic fiber, making it ideal for high-performance sweaters. Acrylic fiber is more affordable and offers good insulation but lacks the durability and breathability of synthetic spider silk.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Synthetic Spider Silk Fiber | Acrylic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Bioengineered protein-based fiber | Synthetic polymer fiber |
| Softness | Extremely soft and smooth, mimics natural silk | Moderately soft but less smooth |
| Durability | High tensile strength and abrasion resistance | Good durability but prone to pilling |
| Breathability | Excellent moisture-wicking and breathable | Poor breathability, can trap heat |
| Eco Impact | Biodegradable and sustainable production | Non-biodegradable, petrochemical-based |
| Thermal Regulation | Natural temperature regulation properties | Limited thermal regulation |
| Weight | Lightweight fiber suitable for sweaters | Heavier compared to spider silk fiber |
| Cost | Higher production cost due to advanced technology | Low cost, widely available |
Introduction to Synthetic Spider Silk and Acrylic Fibers
Synthetic spider silk fiber, engineered to mimic the tensile strength and elasticity of natural spider silk, offers superior durability, lightweight comfort, and biodegradability, making it an innovative choice for sweater materials. Acrylic fiber, a petroleum-based synthetic, is valued for its affordability, vibrant color retention, and excellent insulating properties but lacks the environmental benefits and tensile performance of synthetic spider silk. Advances in synthetic spider silk production highlight its potential to revolutionize sustainable fashion by combining high-performance textile characteristics with eco-friendly manufacturing processes.
Origin and Production Processes
Synthetic spider silk fiber is bioengineered through genetic modification of microorganisms, enabling the production of protein-based fibers that mimic natural spider silk's strength and elasticity. Acrylic fiber derives from polyacrylonitrile, a petroleum-based polymer synthesized through a chemical polymerization process involving acrylonitrile monomers. The production of synthetic spider silk emphasizes biotechnology and sustainable raw materials, while acrylic fiber relies on petrochemical refining and traditional chemical manufacturing techniques.
Physical Properties Comparison
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, surpassing acrylic fiber, which tends to be less durable and more prone to stretching. The moisture-wicking capability of synthetic spider silk fiber enhances breathability and comfort, contrasting with acrylic fiber's lower moisture absorption rates that can lead to less comfort during wear. Thermal regulation of synthetic spider silk fiber provides superior insulation and temperature control, whereas acrylic fiber generally offers basic warmth but less adaptability to temperature changes.
Strength and Durability
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and exceptional durability compared to acrylic fiber, making it ideal for high-performance sweaters. Its molecular structure provides greater resistance to wear, stretching, and environmental damage, ensuring longer-lasting garments. Acrylic fiber, while affordable and lightweight, tends to degrade faster under repeated stress and exposure, resulting in decreased fabric longevity.
Comfort and Softness
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers exceptional comfort and softness for sweaters due to its fine, smooth texture and moisture-wicking properties, making it breathable and gentle on the skin. Acrylic fiber, while soft and lightweight, often lacks the natural elasticity and temperature regulation of synthetic spider silk, potentially causing less comfort during prolonged wear. The advanced molecular structure of synthetic spider silk mimics natural silk, providing superior hand-feel and durability compared to standard acrylic materials.
Thermal Insulation Capabilities
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits superior thermal insulation capabilities compared to acrylic fiber due to its microstructure that effectively traps air, providing enhanced warmth without added bulk. Its moisture-wicking properties also contribute to maintaining thermal comfort by regulating sweat and preventing chill. In contrast, acrylic fiber, while lightweight and affordable, tends to retain heat less efficiently and may trap moisture, resulting in diminished insulation performance for sweaters.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits superior breathability and moisture-wicking capabilities compared to acrylic fiber in sweaters. Its unique protein structure allows for efficient air circulation and rapid moisture evaporation, keeping the wearer dry and comfortable. Acrylic fiber tends to trap heat and moisture, making it less effective in managing sweat during physical activity or warm conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers a significantly lower environmental impact compared to acrylic fiber, as it is biodegradable and produced through bioengineered processes that require less energy and water. Acrylic fiber, derived from petrochemicals, contributes to microplastic pollution and has a higher carbon footprint due to its energy-intensive manufacturing. Choosing synthetic spider silk for sweaters supports sustainability by reducing reliance on non-renewable resources and minimizing long-term ecological damage.
Cost and Accessibility
Synthetic spider silk fiber, known for its exceptional strength and elasticity, remains significantly more expensive and less accessible than acrylic fiber due to complex bioengineering production processes. Acrylic fiber, widely available and cost-effective, is favored for sweater manufacturing because it offers affordability and ease of mass production. Consumers seeking premium durability may consider synthetic spider silk despite its higher price point, while acrylic fibers dominate the market for budget-friendly apparel options.
Future Trends in Sweater Fiber Innovation
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers superior tensile strength, elasticity, and biodegradability compared to traditional acrylic fibers, making it a promising candidate for sustainable sweater production. Future trends in sweater fiber innovation emphasize enhanced performance with eco-friendly materials, where synthetic spider silk's ability to mimic natural silk properties while being renewable positions it as a key material. Its potential to improve comfort, durability, and environmental impact drives research and development toward commercial scalability in textile manufacturing.
Infographic: Synthetic spider silk fiber vs Acrylic fiber for Sweater
 azmater.com
azmater.com