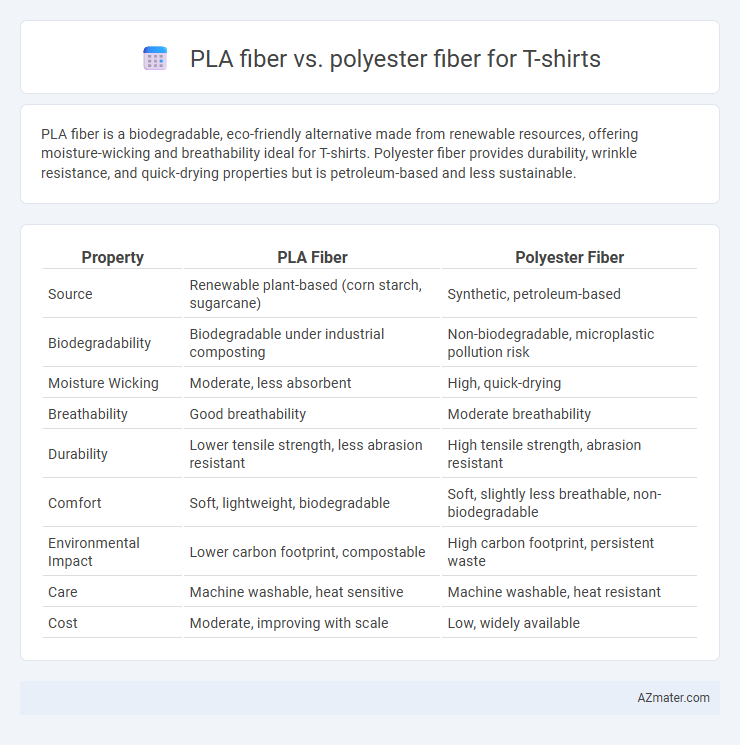
PLA fiber is a biodegradable, eco-friendly alternative made from renewable resources, offering moisture-wicking and breathability ideal for T-shirts. Polyester fiber provides durability, wrinkle resistance, and quick-drying properties but is petroleum-based and less sustainable.
Table of Comparison
| Property | PLA Fiber | Polyester Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Renewable plant-based (corn starch, sugarcane) | Synthetic, petroleum-based |
| Biodegradability | Biodegradable under industrial composting | Non-biodegradable, microplastic pollution risk |
| Moisture Wicking | Moderate, less absorbent | High, quick-drying |
| Breathability | Good breathability | Moderate breathability |
| Durability | Lower tensile strength, less abrasion resistant | High tensile strength, abrasion resistant |
| Comfort | Soft, lightweight, biodegradable | Soft, slightly less breathable, non-biodegradable |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, compostable | High carbon footprint, persistent waste |
| Care | Machine washable, heat sensitive | Machine washable, heat resistant |
| Cost | Moderate, improving with scale | Low, widely available |
Introduction to PLA and Polyester Fibers
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers biodegradability and moisture-wicking properties, making it an eco-friendly alternative to conventional fibers. Polyester fiber, a synthetic material produced from petroleum-based polymers, excels in durability, wrinkle resistance, and quick-drying performance. Both fibers are widely used in T-shirt manufacturing, with PLA favored for sustainability and comfort, while polyester is chosen for strength and cost-effectiveness.
Overview of Fiber Production Processes
PLA fiber is produced using renewable resources like corn starch through a fermentation and polymerization process, making it a biodegradable and eco-friendly option. Polyester fiber is derived from petrochemical products through a polymerization process involving ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid, resulting in a synthetic, durable, and moisture-resistant fabric. The PLA production process emphasizes sustainability, while polyester manufacturing prioritizes cost efficiency and high-volume output.
Environmental Impact Comparison
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers significant advantages in biodegradability and compostability compared to polyester fiber, which is petroleum-based and non-biodegradable. Polyester production generates higher greenhouse gas emissions and relies heavily on fossil fuels, contributing to environmental pollution and microplastic contamination during washing. PLA fibers reduce carbon footprint and landfill waste but require industrial composting facilities to break down efficiently, whereas polyester fibers persist in ecosystems for decades.
Comfort and Feel in T-shirts
PLA fiber T-shirts offer superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties compared to polyester, providing a cooler and more comfortable wear in warm conditions. The natural origin of PLA fibers results in a softer, smoother texture, enhancing the overall tactile experience against the skin. Polyester shirts tend to retain heat and can feel less breathable, often leading to a clammy sensation during extended wear or physical activity.
Durability and Longevity
PLA fiber offers moderate durability with good resistance to wear but tends to degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure and moisture compared to polyester fiber. Polyester fiber exhibits superior durability and longevity, maintaining strength, shape, and color even after multiple washes and extensive use. The enhanced abrasion resistance and moisture-wicking properties of polyester make it a preferred choice for long-lasting T-shirt fabrics.
Moisture Wicking and Breathability
PLA fiber, derived from renewable corn starch, offers superior moisture-wicking properties by efficiently drawing sweat away from the skin, enhancing comfort during physical activities. Compared to traditional polyester fiber, PLA fiber provides better breathability due to its natural fiber structure, which allows increased air circulation and faster moisture evaporation. Polyester fiber, while durable and moisture-resistant, often traps heat and moisture, making PLA fiber the preferred choice for breathable, moisture-wicking T-shirts.
Color Retention and Dyeability
PLA fiber exhibits excellent dyeability due to its natural origin, allowing vibrant and long-lasting colors on T-shirts with less environmental impact. Polyester fiber offers superior color retention, as its synthetic composition resists fading from washing and UV exposure, making it ideal for maintaining bright hues over time. Choosing between PLA and polyester depends on the desired balance between eco-friendly dyeing processes and long-term color durability.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Options
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers superior biodegradability compared to conventional polyester fiber, breaking down under industrial composting conditions within months. Polyester fiber, a petroleum-based synthetic material, is highly durable but resists biodegradation, often persisting in landfills for decades, contributing to microplastic pollution. End-of-life options for PLA fibers include composting and recycling, while polyester primarily relies on mechanical or chemical recycling, which can be energy-intensive and less widespread.
Cost Analysis: PLA vs Polyester
PLA fiber production typically involves higher raw material and processing costs compared to polyester due to its reliance on renewable resources like corn starch and more complex fermentation processes. Polyester fiber benefits from well-established petrochemical supply chains and large-scale production, resulting in lower manufacturing costs and competitive pricing in the T-shirt market. When evaluating cost-effectiveness, polyester remains the more economical choice for mass production, whereas PLA offers potential value in sustainability-driven markets despite its higher price point.
Which Fiber is Best for T-shirts?
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers excellent moisture-wicking, biodegradability, and breathability, making it an eco-friendly option for T-shirts. Polyester fiber, a synthetic material, excels in durability, wrinkle resistance, and quick-drying properties, which enhances the longevity and ease of care for T-shirts. For sustainable and comfortable wear, PLA fiber is best, while polyester fiber suits users prioritizing resilience and low maintenance.
Infographic: PLA fiber vs Polyester fiber for T-shirt
 azmater.com
azmater.com