Ingeo fiber offers sustainable, biodegradable upholstery with superior moisture-wicking and breathability compared to acrylic fiber, which is synthetic, less eco-friendly, and prone to heat retention. Ingeo's renewable plant-based composition enhances indoor air quality and comfort, making it a preferred choice for eco-conscious upholstery applications.
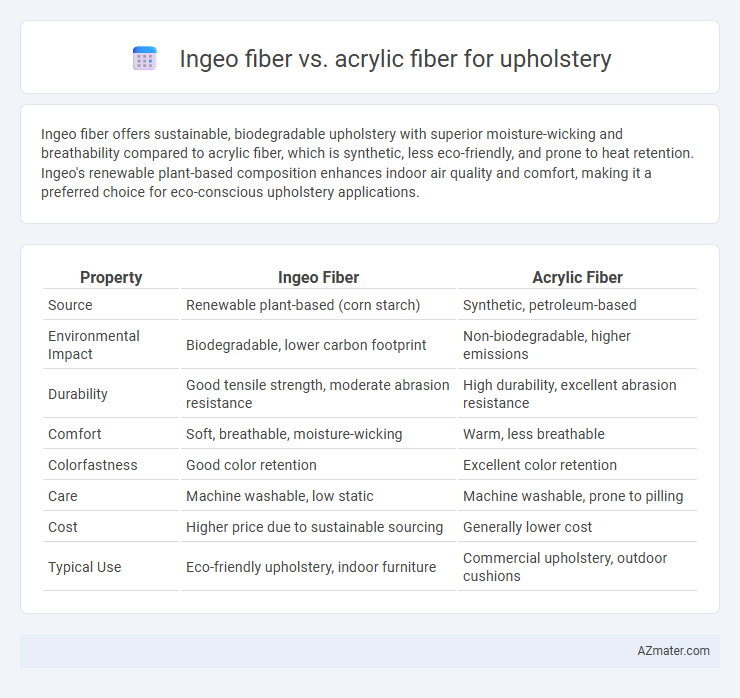
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ingeo Fiber | Acrylic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Renewable plant-based (corn starch) | Synthetic, petroleum-based |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, lower carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, higher emissions |
| Durability | Good tensile strength, moderate abrasion resistance | High durability, excellent abrasion resistance |
| Comfort | Soft, breathable, moisture-wicking | Warm, less breathable |
| Colorfastness | Good color retention | Excellent color retention |
| Care | Machine washable, low static | Machine washable, prone to pilling |
| Cost | Higher price due to sustainable sourcing | Generally lower cost |
| Typical Use | Eco-friendly upholstery, indoor furniture | Commercial upholstery, outdoor cushions |
Introduction to Ingeo and Acrylic Fibers
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based materials such as corn starch, offers a sustainable and biodegradable alternative to traditional upholstery fabrics. Acrylic fiber, a synthetic polymer made from polyacrylonitrile, is known for its durability, vibrant color retention, and resistance to moisture and mildew. Comparing these fibers highlights Ingeo's eco-friendly benefits versus acrylic's performance in upholstery applications.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based polylactic acid (PLA), undergoes fermentation and polymerization of corn starch or sugarcane, leading to a biodegradable and sustainable textile option. Acrylic fiber is a synthetic polymer fiber primarily composed of polyacrylonitrile, produced through a polymerization process involving acrylonitrile monomers and chemical additives, resulting in a strong and lightweight fiber resistant to sunlight and moisture. The biosourced composition of Ingeo fiber offers a lower environmental impact compared to the petrochemical origins of acrylic fiber, while manufacturing Ingeo requires less energy-intensive processes than the chemical synthesis of acrylic fiber.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based resources like corn, offers a significantly lower carbon footprint and biodegradability compared to petroleum-based acrylic fiber, which relies on fossil fuels and contributes to microplastic pollution. The production of Ingeo fiber consumes less energy and generates fewer greenhouse gases, making it a more sustainable choice for upholstery applications. Additionally, Ingeo enhances circular economy efforts through compostability, whereas acrylic fiber's durability presents recycling challenges and environmental persistence.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based materials, offers excellent durability and maintains its structural integrity under prolonged use, making it resistant to pilling and abrasion in upholstery applications. Acrylic fiber, a synthetic polymer, is known for its strong resistance to wear, fading, and chemical damage, ensuring long-lasting upholstery performance even in high-traffic areas. While Ingeo fiber provides eco-friendly durability with good wear resistance, acrylic fiber typically delivers superior abrasion resistance and color retention for heavy-duty upholstery needs.
Comfort and Texture Comparison
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant materials, offers a soft, breathable texture that enhances upholstery comfort by regulating moisture and temperature. Acrylic fiber, a synthetic material, provides durability and resistance to wear but often feels less breathable and can retain heat, reducing overall comfort. The natural smoothness and lightweight nature of Ingeo fiber make it preferable for upholstery where a soft, comfortable seating experience is desired.
Color Retention and Fade Resistance
Ingeo fiber demonstrates superior color retention and fade resistance compared to acrylic fiber, maintaining vibrant hues even after prolonged exposure to sunlight and frequent washing. The biopolymer structure of Ingeo inherently resists UV degradation, ensuring longer-lasting upholstery appearance. Acrylic fiber, while offering initial brightness, tends to fade faster due to its susceptibility to UV radiation and chemical exposure, making Ingeo a more durable choice for upholstery applications requiring lasting color fidelity.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Ingeo fiber offers superior stain resistance and breathability compared to acrylic fiber, making it easier to maintain and clean for upholstery use. Acrylic fiber tends to attract more dust and requires frequent vacuuming and professional cleaning to prevent pilling and fading. Ingeo's natural moisture-wicking properties reduce odor buildup and simplify stain removal, enhancing its practicality for everyday upholstery maintenance.
Cost and Affordability
Ingeo fiber offers a sustainable and eco-friendly option for upholstery with a moderate cost, often higher than acrylic fiber due to its renewable biopolymer base derived from corn. Acrylic fiber remains more affordable and widely used in upholstery, providing budget-friendly durability and resistance to fading. Choosing between Ingeo and acrylic fibers depends on balancing environmental impact with upfront affordability and long-term textile performance.
Best Use Cases in Upholstery
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable corn-based sources, offers excellent breathability, moisture-wicking, and eco-friendly benefits, making it ideal for sustainable upholstery in residential and light commercial settings. Acrylic fiber, known for its durability, colorfastness, and resistance to UV rays and stains, excels in high-traffic or outdoor upholstery applications requiring long-lasting, vibrant fabrics. Choosing Ingeo fiber is best for environmentally conscious projects with moderate wear, while acrylic fiber suits heavy-use or exposed environments demanding robust performance.
Conclusion: Which Fiber is Better for Upholstery?
Ingeo fiber offers superior sustainability and environmental benefits due to its renewable plant-based origins and biodegradability, making it an eco-friendly choice for upholstery. Acrylic fiber provides greater durability, resistance to fading, and easier maintenance, which enhances longevity in high-traffic furniture applications. For upholstery prioritizing environmental impact, Ingeo is better, while acrylic fiber excels in performance and durability.
Infographic: Ingeo fiber vs Acrylic fiber for Upholstery
 azmater.com
azmater.com