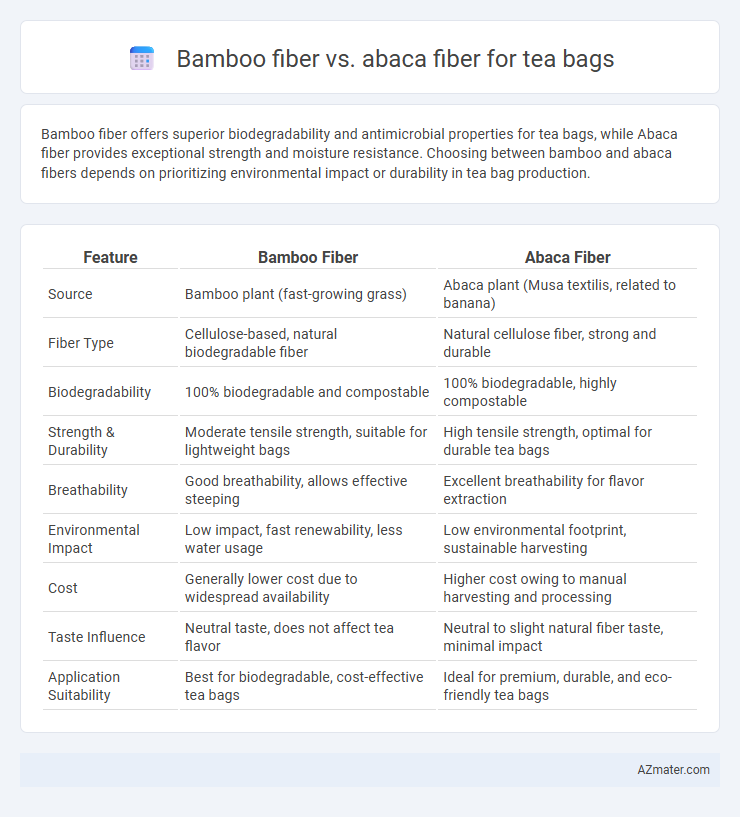
Bamboo fiber offers superior biodegradability and antimicrobial properties for tea bags, while Abaca fiber provides exceptional strength and moisture resistance. Choosing between bamboo and abaca fibers depends on prioritizing environmental impact or durability in tea bag production.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bamboo Fiber | Abaca Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Bamboo plant (fast-growing grass) | Abaca plant (Musa textilis, related to banana) |
| Fiber Type | Cellulose-based, natural biodegradable fiber | Natural cellulose fiber, strong and durable |
| Biodegradability | 100% biodegradable and compostable | 100% biodegradable, highly compostable |
| Strength & Durability | Moderate tensile strength, suitable for lightweight bags | High tensile strength, optimal for durable tea bags |
| Breathability | Good breathability, allows effective steeping | Excellent breathability for flavor extraction |
| Environmental Impact | Low impact, fast renewability, less water usage | Low environmental footprint, sustainable harvesting |
| Cost | Generally lower cost due to widespread availability | Higher cost owing to manual harvesting and processing |
| Taste Influence | Neutral taste, does not affect tea flavor | Neutral to slight natural fiber taste, minimal impact |
| Application Suitability | Best for biodegradable, cost-effective tea bags | Ideal for premium, durable, and eco-friendly tea bags |
Introduction to Natural Fibers in Tea Bags
Natural fibers such as bamboo fiber and abaca fiber are increasingly preferred for tea bag production due to their biodegradability and sustainable sourcing. Bamboo fiber offers strong antimicrobial properties and a smooth texture that enhances infusion, while abaca fiber, derived from the Musa textilis plant, provides exceptional tensile strength and natural resistance to moisture. These characteristics make both fibers ideal choices for producing eco-friendly, durable tea bags that preserve flavor without imparting synthetic contaminants.
Overview of Bamboo Fiber
Bamboo fiber offers exceptional absorbency, biodegradability, and antimicrobial properties, making it an ideal choice for eco-friendly tea bags that enhance infusion quality. Unlike abaca fiber, bamboo fibers are finer, resulting in a softer texture and smoother filtration without compromising strength. Bamboo's rapid renewability and natural resistance to bacteria contribute to sustainable production and improved hygiene in tea bag manufacturing.
Overview of Abaca Fiber
Abaca fiber, derived from the Musa textilis plant native to the Philippines, is renowned for its exceptional strength, durability, and natural resistance to water, making it an ideal material for tea bags requiring robust filtration and biodegradability. Unlike bamboo fiber, Abaca fiber has a coarser texture and higher tensile strength, which enhances breathability and allows for better infusion of tea leaves while maintaining shape integrity during steeping. Its sustainable harvesting process and rapid renewability position Abaca as an environmentally friendly alternative, favored in eco-conscious tea bag production.
Environmental Sustainability Comparison
Bamboo fiber and Abaca fiber both offer eco-friendly alternatives for tea bags with distinct sustainability profiles. Bamboo fiber, derived from fast-growing bamboo plants, requires minimal pesticides and water, making it highly renewable and biodegradable. Abaca fiber, sourced from banana plant leaves, supports biodiversity by thriving in agroforestry systems and decomposes efficiently, promoting soil health and reducing environmental footprints in tea bag production.
Biodegradability and Compostability
Bamboo fiber and Abaca fiber both offer high biodegradability and compostability, making them eco-friendly choices for tea bags. Bamboo fiber decomposes rapidly due to its natural cellulose content, breaking down completely within a few weeks in composting environments. Abaca fiber, derived from the banana plant, also biodegrades efficiently while providing superior strength, ensuring the tea bag retains integrity during brewing without compromising its compostable nature.
Strength and Durability in Tea Bag Use
Bamboo fiber offers superior strength and enhanced durability compared to abaca fiber, making it an excellent choice for tea bag manufacturing. Its natural tensile strength allows it to withstand boiling water and prolonged steeping without tearing or degrading. Abaca fiber, while strong and traditionally used in tea bags, is more prone to wear and breakage under extended exposure to hot water, reducing its overall durability in tea bag applications.
Filtration and Flavor Impact
Bamboo fiber offers excellent filtration properties for tea bags due to its fine, porous structure that effectively retains tea leaves and particles while allowing smooth infusion. Abaca fiber, derived from banana plants, provides superior durability and moisture resistance, ensuring minimal fiber shedding and maintaining clarity in brewed tea. Both fibers are biodegradable and sustainable, but bamboo fiber tends to impart a neutral flavor, whereas abaca fiber may slightly influence the tea's aroma due to its natural plant oils.
Cost and Commercial Availability
Bamboo fiber offers a cost-effective solution for tea bags due to its rapid growth and widespread commercial availability, making it a sustainable choice for large-scale production. Abaca fiber, derived from the banana plant primarily in the Philippines, tends to be more expensive because of its labor-intensive harvesting and limited regional supply. While bamboo fiber dominates global markets with consistent quality and volume, abaca remains niche, favored for its superior strength and biodegradability despite higher costs.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Bamboo fiber offers superior biodegradability and a softer texture, appealing to eco-conscious consumers seeking sustainable tea bag options. Abaca fiber boasts high strength and excellent water resistance, favored in markets prioritizing durability and traditional craftsmanship. Market trends indicate a growing consumer shift towards bamboo fiber due to its rapid renewability and lower environmental impact compared to abaca fiber.
Final Verdict: Which Fiber Is Better for Tea Bags?
Bamboo fiber offers superior biodegradability and a smoother infusion experience, making it highly sustainable and effective for tea bags. Abaca fiber provides excellent strength and natural resistance to water, ensuring durability during steeping but may have a rougher texture that can impact taste clarity. For tea bags, bamboo fiber is generally better due to its eco-friendly properties and ability to maintain the tea's flavor purity.
Infographic: Bamboo fiber vs Abaca fiber for Tea bag
 azmater.com
azmater.com