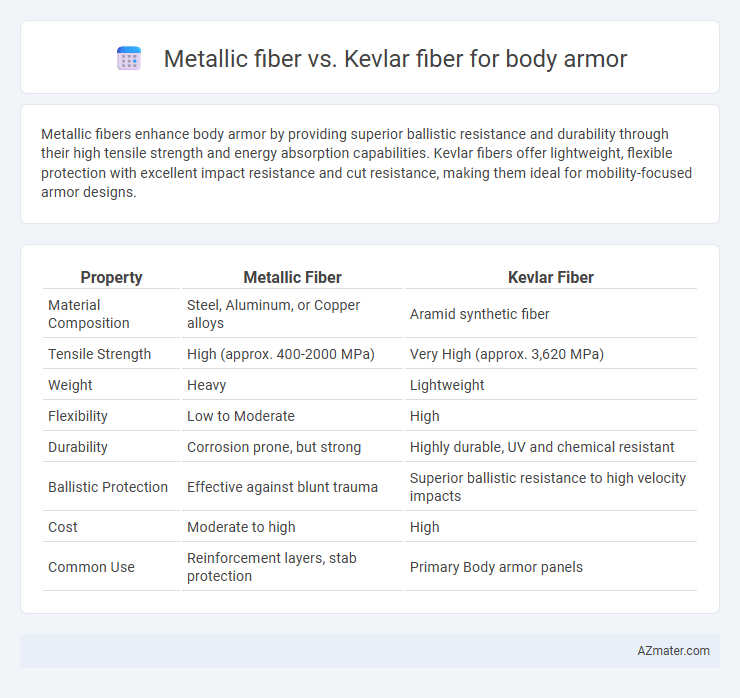
Metallic fibers enhance body armor by providing superior ballistic resistance and durability through their high tensile strength and energy absorption capabilities. Kevlar fibers offer lightweight, flexible protection with excellent impact resistance and cut resistance, making them ideal for mobility-focused armor designs.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Metallic Fiber | Kevlar Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Steel, Aluminum, or Copper alloys | Aramid synthetic fiber |
| Tensile Strength | High (approx. 400-2000 MPa) | Very High (approx. 3,620 MPa) |
| Weight | Heavy | Lightweight |
| Flexibility | Low to Moderate | High |
| Durability | Corrosion prone, but strong | Highly durable, UV and chemical resistant |
| Ballistic Protection | Effective against blunt trauma | Superior ballistic resistance to high velocity impacts |
| Cost | Moderate to high | High |
| Common Use | Reinforcement layers, stab protection | Primary Body armor panels |
Introduction to Body Armor Materials
Metallic fibers offer high tensile strength and excellent resistance to abrasion, making them suitable for reinforcing body armor against sharp objects and ballistic threats. Kevlar fibers, a type of aramid, provide exceptional tensile strength-to-weight ratio and superior energy absorption, widely used in soft and hard body armor panels. Combining metallic and Kevlar fibers can enhance ballistic resistance while reducing overall weight, optimizing protection and comfort for tactical applications.
Overview of Metallic Fibers in Body Armor
Metallic fibers in body armor provide enhanced impact resistance and thermal conductivity, often used to augment protection against high-velocity projectiles and blunt force trauma. These fibers, typically composed of stainless steel, aluminum, or copper alloys, offer superior durability and electromagnetic shielding compared to conventional synthetic fibers like Kevlar. The integration of metallic fibers increases the armor's rigidity and multi-threat resistance, making them ideal for military and law enforcement applications requiring both ballistic protection and environmental durability.
Understanding Kevlar Fiber Technology
Kevlar fiber technology centers on para-aramid synthetic fibers known for their exceptional tensile strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for body armor due to high impact resistance and flexibility. Unlike metallic fibers, Kevlar maintains lightweight durability and superior energy absorption by distributing force across its woven structure, enhancing wearer mobility and comfort. Its molecular composition includes tightly bonded polyaramid chains that provide resistance to heat, cuts, and ballistic threats, distinguishing Kevlar as a top choice in advanced personal protective equipment.
Comparative Strength and Durability
Metallic fibers exhibit high tensile strength and excellent resistance to sharp object penetration, making them effective in dispersing impact energy in body armor applications; however, they tend to be heavier and less flexible compared to Kevlar fibers. Kevlar fibers, composed of aramid synthetic fibers, provide superior tensile strength-to-weight ratios and exceptional resistance to ballistic impacts, maintaining durability under repetitive stress and environmental exposure. When considering long-term durability, Kevlar demonstrates greater resistance to fatigue and degradation, while metallic fibers may suffer from corrosion and reduced performance over time without protective coatings.
Weight and Comfort Differences
Metallic fibers in body armor are heavier, contributing to increased weight and reduced comfort compared to Kevlar fibers, which are lightweight and flexible. Kevlar's high tensile strength-to-weight ratio enhances wearer mobility and reduces fatigue, making it ideal for prolonged use. While metallic fibers provide superior rigidity and cut resistance, their weight impacts overall comfort and agility in body armor applications.
Resistance to Penetration and Ballistics
Metallic fibers offer superior resistance to penetration due to their high tensile strength and hardness, effectively dispersing kinetic energy from ballistic impacts. Kevlar fibers excel in absorbing and distributing energy across the fabric, providing exceptional flexibility and multi-hit protection though they can be more vulnerable to sharp objects compared to metallic composites. Combining metallic fibers with Kevlar often yields enhanced ballistic resistance, optimizing both penetration prevention and impact energy absorption in body armor systems.
Flexibility and Mobility Considerations
Metallic fibers in body armor offer enhanced durability and resistance to abrasion but tend to be less flexible and heavier, potentially restricting mobility during dynamic movements. Kevlar fibers provide exceptional flexibility and lightweight protection, allowing for greater ease of movement and comfort in extended wear situations. For applications prioritizing agility and prolonged use, Kevlar's superior mobility benefits outweigh the added rigidity of metallic fiber composites.
Corrosion and Environmental Resistance
Metallic fibers in body armor are prone to corrosion when exposed to moisture and harsh environmental conditions, leading to reduced durability and protection over time. Kevlar fibers offer superior environmental resistance, maintaining structural integrity against moisture, UV radiation, and chemicals, which enhances the longevity and reliability of body armor. This corrosion resistance makes Kevlar a preferred choice for body armor used in diverse and challenging environments.
Cost-Effectiveness and Accessibility
Metallic fibers in body armor offer high durability and ballistic resistance but tend to be costly and less accessible due to complex manufacturing processes and heavier weight. Kevlar fibers provide a more cost-effective and widely available solution, balancing lightweight comfort with reliable bullet resistance, making them the preferred choice for mass-produced personal protective equipment. While metallic fibers excel in extreme protection scenarios, Kevlar remains the standard for affordable and accessible body armor in civilian and law enforcement markets.
Future Trends in Body Armor Development
Metallic fibers offer enhanced ballistic resistance and conductivity, enabling integration with smart sensors for real-time threat detection in body armor. Kevlar fibers maintain superiority in lightweight flexibility and high tensile strength, driving innovations toward multi-layer composite armor combining both materials. Emerging trends emphasize hybrid fiber technologies and nanomaterial coatings to improve durability, breathability, and multifunctional protection in next-generation body armor.
Infographic: Metallic fiber vs Kevlar fiber for Body armor
 azmater.com
azmater.com