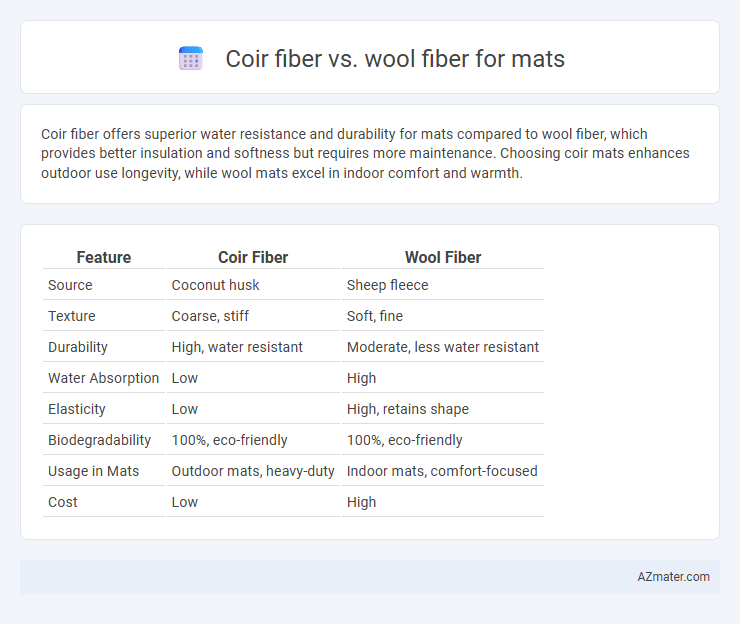
Coir fiber offers superior water resistance and durability for mats compared to wool fiber, which provides better insulation and softness but requires more maintenance. Choosing coir mats enhances outdoor use longevity, while wool mats excel in indoor comfort and warmth.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Coir Fiber | Wool Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Coconut husk | Sheep fleece |
| Texture | Coarse, stiff | Soft, fine |
| Durability | High, water resistant | Moderate, less water resistant |
| Water Absorption | Low | High |
| Elasticity | Low | High, retains shape |
| Biodegradability | 100%, eco-friendly | 100%, eco-friendly |
| Usage in Mats | Outdoor mats, heavy-duty | Indoor mats, comfort-focused |
| Cost | Low | High |
Introduction to Coir Fiber and Wool Fiber
Coir fiber, derived from the outer husk of coconut shells, is a durable natural fiber renowned for its coarse texture and high resistance to moisture, making it ideal for mats that require robustness and water resistance. Wool fiber, obtained from sheep fleece, is a soft, insulating material known for its elasticity and natural flame resistance, providing comfort and warmth in mat applications. Both fibers offer unique properties: coir excels in durability and outdoor use, while wool offers superior softness and thermal regulation.
Origin and Production Processes
Coir fiber is derived from the outer husk of coconut shells, predominantly produced in tropical regions such as India and Sri Lanka, where coconut harvesting is abundant. Wool fiber originates from the fleece of sheep, with major production in countries like Australia, New Zealand, and China, involving shearing followed by cleaning and carding processes. Coir processing includes retting, decorticating, and drying, whereas wool undergoes washing, scouring, and spinning stages to prepare fibers for mat weaving.
Physical Properties Comparison
Coir fiber exhibits higher tensile strength and water resistance compared to wool fiber, making it more durable for mats exposed to moisture and heavy use. Wool fiber offers superior elasticity and insulation properties, providing softness and warmth that coir lacks. The coarse texture of coir results in a rougher surface, while wool fibers create a softer, more comfortable mat surface.
Durability and Longevity
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, offers superior durability and resistance to wear compared to wool fiber, making it ideal for mats in high-traffic areas. Wool fiber, while softer and more flexible, tends to be less resistant to moisture and abrasion, which can shorten its lifespan in rugged use. The natural resilience and water-resistant properties of coir contribute to its longer longevity and robust performance in mat applications.
Comfort and Texture Differences
Coir fiber mats offer a coarse, rough texture that provides firm support and durability, ideal for outdoor or heavy-use areas. Wool fiber mats deliver a soft, plush feel with excellent insulation and cushioning, enhancing indoor comfort underfoot. While coir mats excel in breathability and moisture resistance, wool mats outperform in warmth and softness, making them preferable for cozy indoor environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, is highly sustainable due to its natural biodegradability and the use of agricultural waste, reducing environmental pollution. Wool fiber, sourced from sheep, is renewable and biodegradable but involves higher greenhouse gas emissions and land use challenges linked to livestock farming. Coir mats offer a lower carbon footprint and increased durability, making them an eco-friendlier choice for sustainable home products.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Coir fiber mats require minimal maintenance, thriving with regular shaking or brushing to remove dirt and debris, and occasional spot cleaning with mild soap and water, making them highly durable and resistant to mold in humid conditions. Wool fiber mats demand more careful upkeep, including gentle vacuuming and prompt stain removal using wool-safe detergents to preserve their natural softness and prevent felting or shrinkage. Both fibers benefit from air drying after cleaning, but wool mats are more prone to moisture damage and require a dry environment to maintain their structural integrity and appearance.
Cost and Market Availability
Coir fiber mats typically cost less than wool fiber mats due to the abundant availability of coconut husks in tropical regions, making coir a budget-friendly option for eco-conscious consumers. Wool fiber mats, derived from animal fleece, generally have higher prices reflecting the labor-intensive shearing process and limited supply relative to coir. Market availability favors coir fiber mats in coastal and developing countries, while wool fiber mats dominate premium segments in colder climates with established wool industries.
Ideal Uses and Applications for Mats
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, is ideal for outdoor mats thanks to its coarse texture and excellent water resistance, making it perfect for door mats and anti-slip surfaces. Wool fiber mats offer superior insulation and moisture-wicking properties, making them suitable for indoor use, such as area rugs and decorative mats that require softness and warmth. Both fibers serve distinct applications, with coir excelling in durability for rough use, while wool provides comfort and aesthetic appeal indoors.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Mat
Coir fiber offers exceptional durability and water resistance, making it ideal for outdoor and high-traffic mats, while wool fiber excels in softness, insulation, and moisture absorption, suitable for indoor comfort. Selecting between coir and wool fibers depends on the primary use environment and desired texture; coir is preferred for rugged, weather-resistant mats, whereas wool is favored for warmth and plushness. Evaluating factors like durability, maintenance, and aesthetic appeal ensures the right fiber choice for optimal mat performance.
Infographic: Coir fiber vs Wool fiber for Mat
 azmater.com
azmater.com