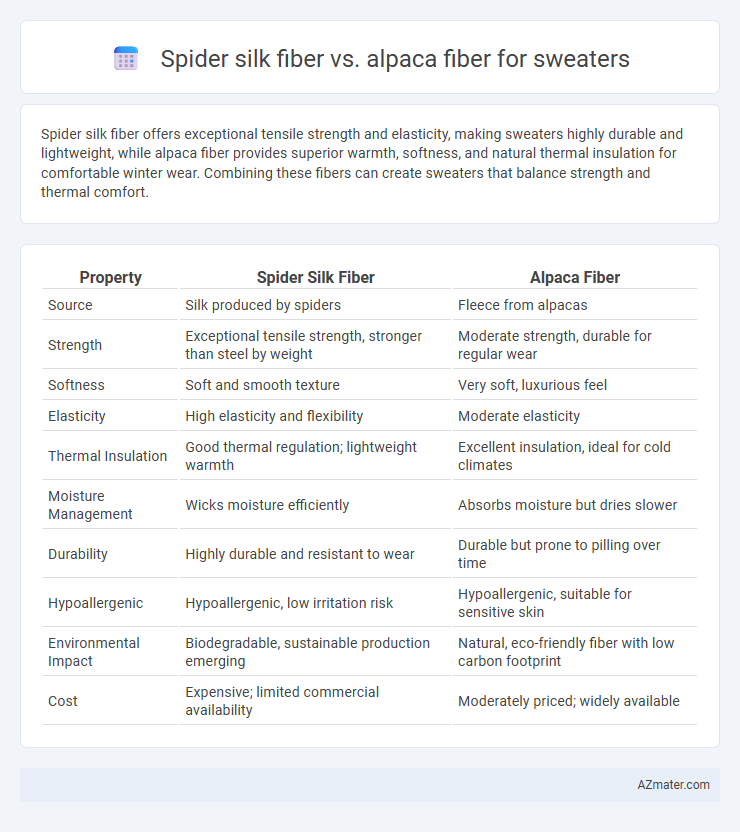
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, making sweaters highly durable and lightweight, while alpaca fiber provides superior warmth, softness, and natural thermal insulation for comfortable winter wear. Combining these fibers can create sweaters that balance strength and thermal comfort.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Spider Silk Fiber | Alpaca Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Silk produced by spiders | Fleece from alpacas |
| Strength | Exceptional tensile strength, stronger than steel by weight | Moderate strength, durable for regular wear |
| Softness | Soft and smooth texture | Very soft, luxurious feel |
| Elasticity | High elasticity and flexibility | Moderate elasticity |
| Thermal Insulation | Good thermal regulation; lightweight warmth | Excellent insulation, ideal for cold climates |
| Moisture Management | Wicks moisture efficiently | Absorbs moisture but dries slower |
| Durability | Highly durable and resistant to wear | Durable but prone to pilling over time |
| Hypoallergenic | Hypoallergenic, low irritation risk | Hypoallergenic, suitable for sensitive skin |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, sustainable production emerging | Natural, eco-friendly fiber with low carbon footprint |
| Cost | Expensive; limited commercial availability | Moderately priced; widely available |
Introduction: Comparing Spider Silk and Alpaca Fiber
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, outperforming many natural fibers in durability and flexibility. Alpaca fiber is prized for its softness, thermal insulation, and hypoallergenic properties, making it ideal for cozy, warm sweaters. While spider silk offers advanced performance characteristics, alpaca fiber remains favored for comfort and natural warmth in knitwear.
Origins and Production Processes
Spider silk fiber, derived from silk-producing spiders primarily found in tropical regions, is harvested through a complex process involving the careful extraction of silk threads from spider spinnerets, often using bioengineering techniques to produce synthetic variants due to the difficulty of large-scale farming. Alpaca fiber originates from the domesticated alpacas native to the Andean highlands of South America, where the fleece is hand-sheared annually during the molting season, followed by washing, carding, and spinning into yarn using traditional artisanal methods. The production of spider silk emphasizes bioengineering and innovative textile manufacturing, whereas alpaca fiber relies on sustainable, natural harvesting practices by indigenous communities, reflecting distinct cultural and technological backgrounds in fiber creation.
Physical Properties of Spider Silk Fiber
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength and elasticity that surpass many natural fibers, including alpaca fiber, making it highly durable for sweater fabrication. Its lightweight and fine diameter contribute to superior softness and thermal regulation, enhancing comfort and insulation in garments. Spider silk's natural biodegradability and resistance to UV radiation and microbial degradation further optimize the longevity and eco-friendliness of sweaters made from this fiber.
Physical Properties of Alpaca Fiber
Alpaca fiber exhibits exceptional thermal insulation and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for sweater fabric that offers warmth without weight. Its natural softness, attributed to a smooth cuticle structure, provides significant comfort compared to the stronger yet less flexible spider silk fiber. The fiber's resilience and resistance to pilling enhance the durability of alpaca sweaters, ensuring long-lasting wear in varying climates.
Warmth and Insulation Capabilities
Spider silk fiber exhibits remarkable thermal insulation due to its unique protein structure, which traps air efficiently, offering superior warmth retention compared to conventional fibers. Alpaca fiber also provides excellent insulation, as its hollow core fibers create natural thermal regulation that keeps heat close to the body while remaining breathable. For sweater applications, spider silk fiber delivers lightweight warmth with enhanced moisture-wicking properties, whereas alpaca fiber emphasizes natural softness and temperature adaptability in cold climates.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Spider silk fiber showcases exceptional tensile strength, surpassing traditional fibers like alpaca, making it highly durable for sweater fabric. Alpaca fiber, known for its softness and thermal insulation, offers moderate strength but is less resistant to wear and tear compared to spider silk. The superior molecular structure of spider silk provides enhanced elasticity and resilience, ensuring longer-lasting sweaters with minimal degradation over time.
Moisture-Wicking and Breathability
Spider silk fiber excels in moisture-wicking due to its highly hydrophilic protein structure, efficiently drawing sweat away from the skin to keep the wearer dry during physical activity. Its exceptional breathability stems from microscopic fiber channels that promote superior airflow, enhancing comfort in fluctuating temperatures. Alpaca fiber, while naturally water-resistant and warm, has less effective moisture-wicking properties and breathability compared to spider silk, making it more suitable for insulation rather than high-performance moisture management in sweaters.
Comfort and Allergenicity
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional softness and breathability for sweaters, providing superior comfort compared to alpaca fiber, which is typically warmer but coarser. Spider silk's hypoallergenic properties reduce the risk of skin irritation, making it ideal for sensitive individuals, whereas alpaca fiber can sometimes cause mild allergic reactions due to lanolin content. The moisture-wicking ability of spider silk further enhances comfort, while alpaca fiber excels in insulation but may not suit those prone to allergies.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Spider silk fiber, renowned for its biodegradability and low environmental footprint, is produced through bioengineered methods that minimize water and chemical use compared to traditional textile fibers. Alpaca fiber, sourced from alpacas with minimal grazing impact and natural resilience to pests, supports sustainable farming practices and carbon sequestration in soils. Both fibers offer sustainable alternatives to synthetic materials, with spider silk promising advanced eco-friendly manufacturing and alpaca fiber benefiting from regenerative agriculture.
Conclusion: Which Fiber is Best for Sweaters?
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional strength, elasticity, and natural moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for high-performance and durable sweaters. Alpaca fiber provides superior warmth, softness, and hypoallergenic qualities, perfect for cozy, luxurious sweaters in cold climates. For sweaters that combine durability and comfort with thermal insulation, alpaca fiber is generally preferred, while spider silk excels in technical, lightweight, and breathable garments.
Infographic: Spider silk fiber vs Alpaca fiber for Sweater
 azmater.com
azmater.com