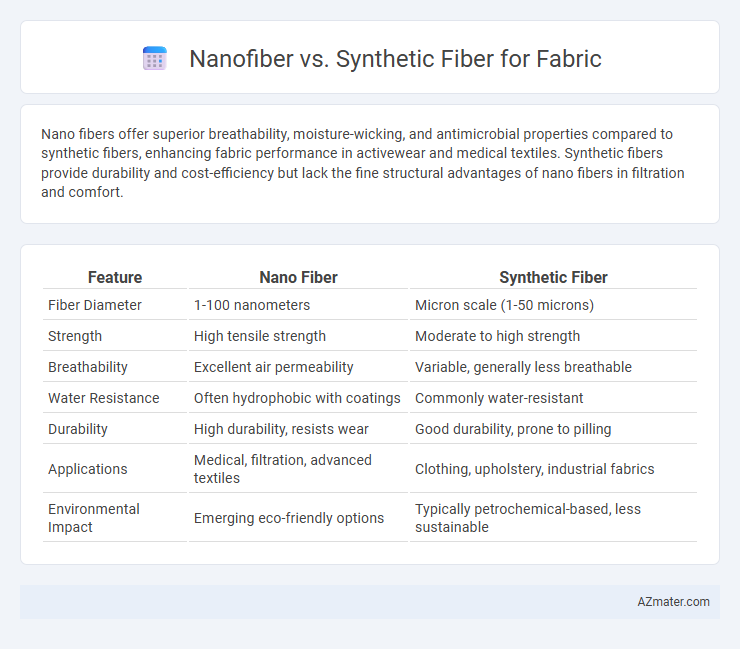
Nano fibers offer superior breathability, moisture-wicking, and antimicrobial properties compared to synthetic fibers, enhancing fabric performance in activewear and medical textiles. Synthetic fibers provide durability and cost-efficiency but lack the fine structural advantages of nano fibers in filtration and comfort.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nano Fiber | Synthetic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Diameter | 1-100 nanometers | Micron scale (1-50 microns) |
| Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate to high strength |
| Breathability | Excellent air permeability | Variable, generally less breathable |
| Water Resistance | Often hydrophobic with coatings | Commonly water-resistant |
| Durability | High durability, resists wear | Good durability, prone to pilling |
| Applications | Medical, filtration, advanced textiles | Clothing, upholstery, industrial fabrics |
| Environmental Impact | Emerging eco-friendly options | Typically petrochemical-based, less sustainable |
Introduction to Nano Fiber and Synthetic Fiber
Nano fibers, characterized by their ultrafine diameter measuring less than 100 nanometers, offer exceptional surface area, flexibility, and breathability, making them ideal for advanced textile applications. Synthetic fibers, typically produced from petrochemical polymers like polyester, nylon, and acrylic, provide durability, resistance to moisture, and easy maintenance, widely used in everyday fabrics. The integration of nano fibers into synthetic fiber fabrics enhances performance by improving filtration, strength, and moisture management.
Key Differences Between Nano Fiber and Synthetic Fiber
Nano fibers exhibit significantly smaller diameters, typically less than 100 nanometers, compared to synthetic fibers that range from micrometers to millimeters. Nano fibers offer superior surface area-to-volume ratios, enhancing properties like filtration efficiency, breathability, and strength, while synthetic fibers generally provide durability and elasticity suited for everyday textile applications. The production methods also differ; nano fibers are often created using electrospinning techniques, whereas synthetic fibers are manufactured through chemical polymerization and extrusion processes.
Manufacturing Processes of Nano and Synthetic Fibers
Nano fibers are produced through electrospinning, a technique that uses high voltage to create ultrafine fibers with diameters in the nanometer range, resulting in fabrics with superior surface area and porosity. Synthetic fibers, such as polyester and nylon, are manufactured primarily by melt spinning or dry spinning, where polymers are melted or dissolved and extruded through spinnerets to form continuous filaments. The electrospinning process for nano fibers offers precise control over fiber morphology, enabling advanced applications in filtration and biomedical textiles compared to conventional synthetic fiber production.
Physical Properties Comparison
Nanofibers exhibit superior mechanical strength and higher surface area-to-volume ratios compared to synthetic fibers, resulting in enhanced durability and breathability. Synthetic fibers such as polyester and nylon typically demonstrate greater elasticity and resistance to abrasion but lack the fine structural properties of nanofibers. The ultrafine diameter of nanofibers contributes to improved filtration efficiency and moisture-wicking capabilities, distinguishing them from conventional synthetic fabric materials.
Durability and Strength Analysis
Nanofiber fabrics exhibit superior durability and strength compared to traditional synthetic fibers due to their ultrafine fiber diameter and enhanced surface area, which improve tensile strength and abrasion resistance. Synthetic fibers like polyester and nylon offer good mechanical strength but often lack the nanoscale reinforcement found in nanofibers, resulting in comparatively lower durability under repetitive stress and environmental exposure. The integration of nanofiber technology in textile manufacturing significantly elevates fabric performance by enhancing resistance to wear and tear, making it ideal for high-performance and long-lasting applications.
Breathability and Comfort Levels
Nanofiber fabrics exhibit superior breathability due to their ultra-fine fiber diameter, enabling enhanced air permeability and moisture-wicking properties compared to synthetic fibers. Synthetic fibers, often constructed from polyester or nylon, can trap heat and moisture, leading to reduced comfort during prolonged wear or physical activity. The advanced structure of nanofiber textiles promotes better temperature regulation and skin ventilation, making them ideal for high-performance and comfort-focused apparel.
Applications in Textile Industry
Nanofiber fabrics offer exceptional breathability, lightweight properties, and high surface area, making them ideal for advanced filtration masks, wearable electronics, and smart textiles in the textile industry. Synthetic fibers, such as polyester and nylon, provide durability, elasticity, and moisture-wicking capabilities, commonly used in sportswear, outdoor apparel, and upholstery. The unique nanostructure of nanofibers enhances functionalities like antimicrobial activity and UV protection, expanding their application spectrum beyond traditional synthetic textiles.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nanofibers, owing to their ultra-fine structure and biodegradability, exhibit a significantly lower environmental footprint compared to synthetic fibers, which are predominantly petroleum-based and contribute to microplastic pollution. The production of nanofibers often involves renewable raw materials and energy-efficient processes, enhancing sustainability in fabric manufacturing. Synthetic fibers, while durable and cost-effective, typically require intensive chemical treatments and generate non-biodegradable waste, posing long-term ecological challenges.
Cost-Effectiveness and Market Availability
Nano fibers offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced durability but come at a higher production cost compared to synthetic fibers, impacting overall cost-effectiveness. Synthetic fibers, such as polyester and nylon, dominate the market due to their low manufacturing costs and widespread availability, making them more accessible for mass production. The balance between nano fiber innovation and synthetic fiber affordability influences fabric selection in industries prioritizing cost and performance.
Future Trends in Fiber Technology
Nano fibers offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced breathability, positioning them as a critical innovation in fabric technology. Synthetic fibers continue to evolve with bio-based and recyclable alternatives, driving sustainable manufacturing practices. Future trends emphasize smart textiles integrating nano fibers for improved performance, durability, and environmental impact reduction.
Infographic: Nano fiber vs Synthetic fiber for Fabric
 azmater.com
azmater.com