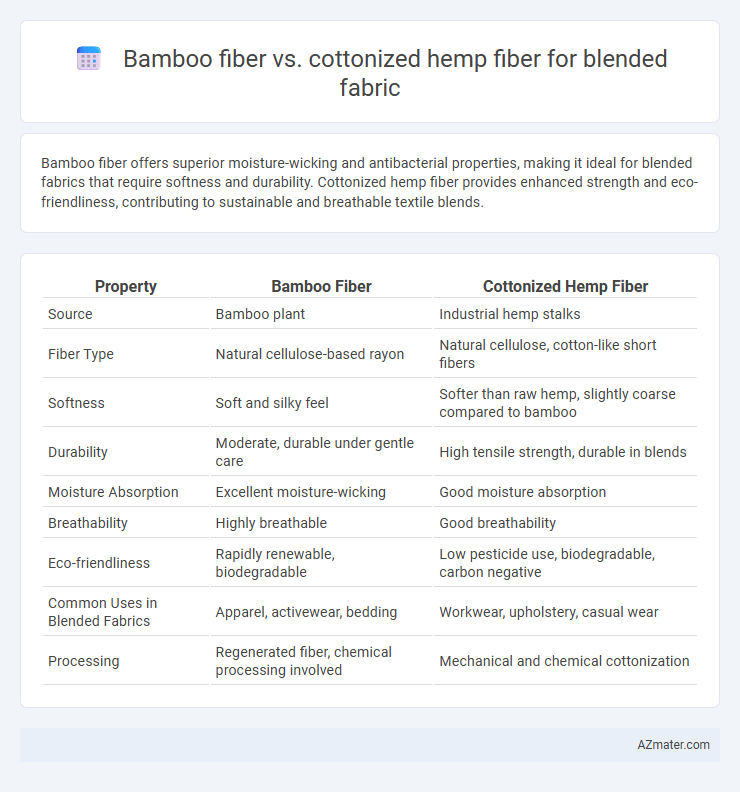
Bamboo fiber offers superior moisture-wicking and antibacterial properties, making it ideal for blended fabrics that require softness and durability. Cottonized hemp fiber provides enhanced strength and eco-friendliness, contributing to sustainable and breathable textile blends.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bamboo Fiber | Cottonized Hemp Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Bamboo plant | Industrial hemp stalks |
| Fiber Type | Natural cellulose-based rayon | Natural cellulose, cotton-like short fibers |
| Softness | Soft and silky feel | Softer than raw hemp, slightly coarse compared to bamboo |
| Durability | Moderate, durable under gentle care | High tensile strength, durable in blends |
| Moisture Absorption | Excellent moisture-wicking | Good moisture absorption |
| Breathability | Highly breathable | Good breathability |
| Eco-friendliness | Rapidly renewable, biodegradable | Low pesticide use, biodegradable, carbon negative |
| Common Uses in Blended Fabrics | Apparel, activewear, bedding | Workwear, upholstery, casual wear |
| Processing | Regenerated fiber, chemical processing involved | Mechanical and chemical cottonization |
Introduction to Bamboo Fiber and Cottonized Hemp Fiber
Bamboo fiber, derived from bamboo pulp, is known for its natural antimicrobial properties, moisture-wicking ability, and soft texture, making it ideal for blended fabrics aimed at comfort and breathability. Cottonized hemp fiber, processed to resemble cotton's softness, offers excellent strength, durability, and sustainability benefits, contributing to eco-friendly textile blends. Combining bamboo fiber with cottonized hemp enhances fabric performance by balancing softness with robust wear, promoting environmentally conscious fashion.
Understanding the Blending Process
Bamboo fiber and cottonized hemp fiber each bring distinct properties to blended fabrics, with bamboo offering softness and moisture-wicking capabilities, while cottonized hemp provides durability and natural antimicrobial qualities. The blending process involves mechanically mixing fibers in precise ratios to achieve a uniform distribution, enhancing fabric strength, breathability, and texture. Critical parameters such as fiber length compatibility, fineness, and moisture content are controlled to ensure optimal blending efficiency and fabric performance.
Environmental Impact: Bamboo vs Cottonized Hemp
Bamboo fiber offers a rapid growth cycle and requires less water and pesticides compared to conventional cotton, making it a more sustainable choice for blended fabrics. Cottonized hemp fiber boasts an even lower environmental footprint due to minimal water needs, natural pest resistance, and durability, which extends fabric life and reduces waste. Both fibers contribute to eco-friendly textiles, but cottonized hemp's regenerative farming properties and lower resource consumption position it as a superior option for sustainable fabric blends.
Fiber Structure and Mechanical Properties
Bamboo fiber exhibits a smooth, cylindrical structure with a high degree of cellulose crystallinity, contributing to its superior tensile strength and flexibility compared to cottonized hemp fiber, which has a coarser, multi-fibrillar structure that enhances durability but reduces softness. The mechanical properties of bamboo fiber, including higher elongation at break and better moisture absorption, improve the overall fabric comfort and resilience in blended textiles. In contrast, cottonized hemp fiber offers increased abrasion resistance and rigidity, making the blend ideal for applications requiring enhanced durability and shape retention.
Moisture Management and Breathability Comparison
Bamboo fiber offers superior moisture management due to its natural wicking properties, efficiently drawing sweat away from the skin and promoting faster evaporation. Cottonized hemp fiber, while breathable, retains more moisture and dries slower, which can reduce comfort in high-humidity conditions. Blended fabrics with bamboo fiber enhance overall breathability and dryness, making them ideal for activewear and hot climates.
Softness and Comfort in Blended Fabrics
Bamboo fiber exhibits superior softness and moisture-wicking properties, enhancing comfort in blended fabrics by providing a smooth, breathable texture ideal for sensitive skin. Cottonized hemp fiber offers durability with moderate softness, contributing to fabric strength without compromising comfort but tends to be coarser compared to bamboo. Blends incorporating bamboo fibers result in softer, more comfortable textiles, while hemp fibers improve structure and longevity, balancing softness and resilience in the final fabric.
Dye Affinity and Color Retention
Bamboo fiber exhibits superior dye affinity due to its smooth surface and porous structure, resulting in vibrant color uptake and excellent color retention in blended fabrics. Cottonized hemp fiber, with its natural coarser texture, tends to absorb dyes unevenly, which can lead to less consistent color retention over time. Blended fabrics combining bamboo fiber with cottonized hemp benefit from enhanced dye affinity and improved colorfastness, offering durable and bright textiles.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Bamboo fiber exhibits superior durability and wear resistance compared to cottonized hemp fiber due to its naturally strong cellulose content and smooth fiber structure, which reduces friction and fabric pilling. Cottonized hemp fiber, while offering excellent breathability and eco-friendliness, tends to be coarser and less flexible, resulting in lower abrasion resistance in blended fabrics. Blended fabrics combining bamboo fiber typically achieve enhanced tensile strength and longer lifespan, making them more suitable for high-performance textile applications.
Cost and Market Availability
Bamboo fiber offers cost efficiency with moderate processing expenses and widespread market availability due to growing demand in eco-friendly textiles. Cottonized hemp fiber, although more expensive because of intensive processing and limited cultivation areas, provides higher durability and breathability. Blended fabrics combining bamboo and cottonized hemp balance affordability and performance, but bamboo's larger production scale ensures greater accessibility in most markets.
Final Verdict: Which Fiber Blend is Superior?
Bamboo fiber offers superior softness, natural antibacterial properties, and excellent moisture-wicking, making it ideal for high-performance and comfortable blended fabrics. Cottonized hemp fiber excels in durability, eco-friendliness, and enhanced breathability due to its coarse yet refined texture when blended, resulting in a more sustainable and long-lasting fabric. For a final verdict, the choice depends on end-use priorities: bamboo blends favor softness and moisture management, while cottonized hemp blends prioritize strength and environmental sustainability.
Infographic: Bamboo fiber vs Cottonized hemp fiber for Blended fabric
 azmater.com
azmater.com