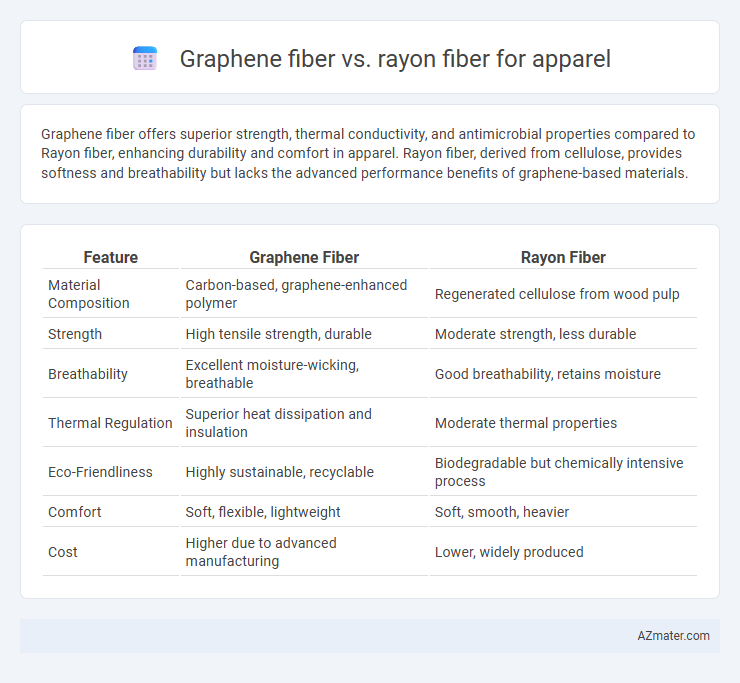
Graphene fiber offers superior strength, thermal conductivity, and antimicrobial properties compared to Rayon fiber, enhancing durability and comfort in apparel. Rayon fiber, derived from cellulose, provides softness and breathability but lacks the advanced performance benefits of graphene-based materials.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Graphene Fiber | Rayon Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Carbon-based, graphene-enhanced polymer | Regenerated cellulose from wood pulp |
| Strength | High tensile strength, durable | Moderate strength, less durable |
| Breathability | Excellent moisture-wicking, breathable | Good breathability, retains moisture |
| Thermal Regulation | Superior heat dissipation and insulation | Moderate thermal properties |
| Eco-Friendliness | Highly sustainable, recyclable | Biodegradable but chemically intensive process |
| Comfort | Soft, flexible, lightweight | Soft, smooth, heavier |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced manufacturing | Lower, widely produced |
Introduction to Graphene and Rayon Fibers
Graphene fiber, composed of a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, offers exceptional strength, flexibility, and conductivity, marking a revolutionary advancement in textile technology. Rayon fiber, derived from regenerated cellulose, is renowned for its softness, breathability, and affordability, widely used in apparel manufacturing to mimic the properties of natural fibers like cotton and silk. The contrast between graphene's cutting-edge nanomaterial properties and rayon's organic origin highlights a shift towards integrating high-performance materials with traditional textile fibers for enhanced apparel functionality.
Composition and Structure Comparison
Graphene fiber is composed of carbon atoms arranged in a single layer of hexagonal lattice, providing exceptional tensile strength and conductivity, while rayon fiber is made from regenerated cellulose derived from wood pulp or cotton waste, characterized by its semi-synthetic, biodegradable polymer structure. In terms of structure, graphene fiber exhibits a two-dimensional, crystalline arrangement with high surface area and mechanical durability, whereas rayon fiber features a linear polymer chain with amorphous and crystalline regions influencing its softness and moisture absorbency. The distinct molecular compositions result in graphene fibers offering superior durability and electrical properties, while rayon fibers excel in comfort and breathability for apparel applications.
Manufacturing Processes: Graphene vs Rayon
Graphene fiber manufacturing involves incorporating graphene oxide into polymer matrices, followed by reduction and spinning processes that enhance mechanical strength, conductivity, and thermal regulation in apparel. Rayon fiber production relies on chemically converting cellulose from wood pulp into a viscous solution, which is then extruded through spinnerets and regenerated into fibers through coagulation techniques. The innovative graphene fiber process results in advanced performance textiles, while rayon's established viscose method offers softness and breathability but lacks graphene's durability and conductivity.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Graphene fiber exhibits exceptional mechanical strength with tensile strength exceeding traditional rayon fiber by up to 30%, making it highly resistant to stretching and tearing in apparel applications. Its durability is enhanced by superior resistance to wear, abrasion, and environmental factors, significantly extending the lifespan of garments compared to rayon fibers. While rayon fiber offers comfort and breathability, graphene fiber's advanced structural integrity and longevity position it as a superior choice for high-performance and long-lasting apparel.
Comfort and Wearability in Apparel
Graphene fiber offers superior thermal regulation and moisture-wicking properties compared to rayon fiber, enhancing comfort during prolonged wear. Its inherent strength and flexibility contribute to increased durability and shape retention, making garments more wearable over time. Rayon fiber, while softer initially, tends to lose shape and absorb moisture, reducing overall comfort and long-term wearability in apparel applications.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Graphene fiber excels in breathability and moisture management due to its high thermal conductivity and hydrophobic surface, which facilitate rapid moisture evaporation and temperature regulation in apparel. Rayon fiber, while breathable and soft, tends to retain moisture longer, leading to slower drying times and reduced comfort during heavy perspiration. The superior moisture-wicking properties of graphene fiber make it ideal for activewear and performance clothing where enhanced ventilation and quick-drying characteristics are critical.
Thermal Regulation Properties
Graphene fiber exhibits superior thermal regulation properties compared to rayon fiber due to its exceptional heat conductivity and ability to dissipate moisture quickly, keeping the wearer cool in warm conditions and warm in cold environments. Rayon fiber, derived from cellulose, lacks advanced thermal conductivity, resulting in less efficient temperature control during wear. The integration of graphene in apparel significantly enhances thermal comfort, making it ideal for performance and activewear applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Graphene fiber offers superior environmental benefits compared to rayon fiber due to its production process that requires less water and chemicals, significantly reducing pollution and resource consumption. Rayon, derived from cellulose of wood pulp, involves extensive chemical treatments and deforestation, contributing to higher carbon emissions and ecosystem degradation. Sustainable graphene fiber production promotes durability and recyclability, enhancing long-term environmental performance in apparel applications.
Cost and Commercial Availability
Graphene fiber offers superior strength and conductivity but tends to be significantly more expensive than rayon fiber, limiting its widespread commercial adoption in apparel. Rayon fiber remains cost-effective and widely available, making it the preferred choice for mass-market textile production. Despite graphene fiber's innovative properties, rayon's established supply chains and affordability sustain its dominance in apparel manufacturing.
Future Trends in Apparel Fiber Innovation
Graphene fiber offers superior strength, flexibility, and thermal conductivity compared to traditional rayon fiber, positioning it as a revolutionary material in apparel innovation. Future trends indicate a shift towards graphene-infused textiles to enhance durability, moisture management, and antimicrobial properties in performance and smart clothing. Emerging research and commercial applications highlight graphene fiber's potential to redefine sustainable and high-tech apparel manufacturing.
Infographic: Graphene fiber vs Rayon fiber for Apparel
 azmater.com
azmater.com