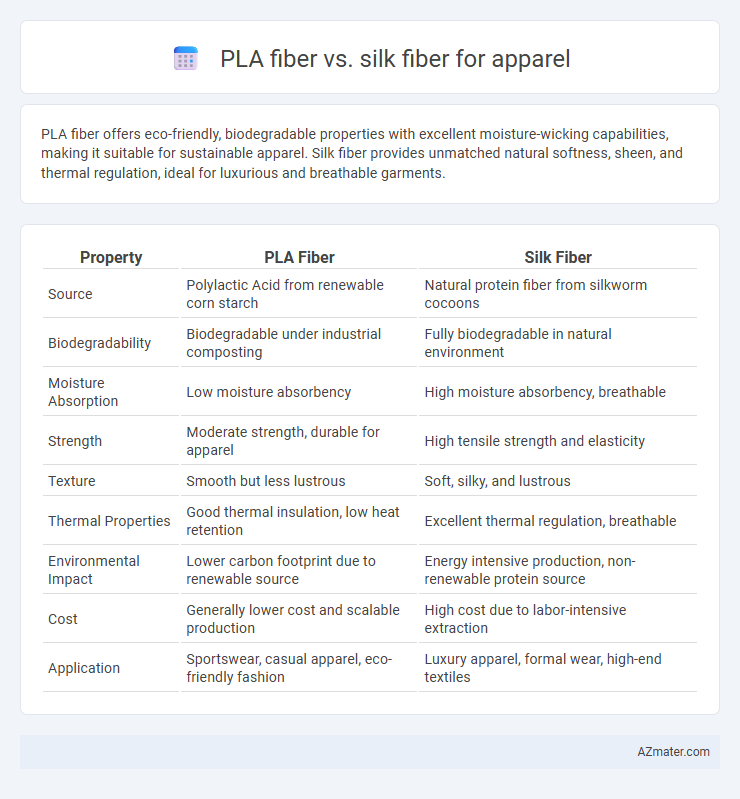
PLA fiber offers eco-friendly, biodegradable properties with excellent moisture-wicking capabilities, making it suitable for sustainable apparel. Silk fiber provides unmatched natural softness, sheen, and thermal regulation, ideal for luxurious and breathable garments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | PLA Fiber | Silk Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Polylactic Acid from renewable corn starch | Natural protein fiber from silkworm cocoons |
| Biodegradability | Biodegradable under industrial composting | Fully biodegradable in natural environment |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorbency | High moisture absorbency, breathable |
| Strength | Moderate strength, durable for apparel | High tensile strength and elasticity |
| Texture | Smooth but less lustrous | Soft, silky, and lustrous |
| Thermal Properties | Good thermal insulation, low heat retention | Excellent thermal regulation, breathable |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint due to renewable source | Energy intensive production, non-renewable protein source |
| Cost | Generally lower cost and scalable production | High cost due to labor-intensive extraction |
| Application | Sportswear, casual apparel, eco-friendly fashion | Luxury apparel, formal wear, high-end textiles |
Introduction: Understanding PLA and Silk Fibers
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers biodegradability and moisture-wicking properties, making it an eco-friendly choice in apparel manufacturing. Silk fiber, produced by silkworms, is prized for its natural luster, strength, and breathability, providing luxurious comfort and durability. Comparing PLA and silk fibers highlights differences in sustainability, texture, and performance crucial for apparel innovation.
Source and Production Process
PLA fiber is derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane through a fermentation process that produces polylactic acid, which is then spun into fibers using melt-spinning techniques. Silk fiber originates from the silkworm cocoon, harvested through sericulture, where cocoons are carefully boiled and unwound to extract long, continuous filaments. The production of PLA fiber offers a more sustainable and eco-friendly alternative by utilizing plant-based inputs and lower water consumption compared to the labor-intensive and animal-derived silk fiber production.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers a biodegradable alternative with lower carbon emissions compared to traditional petroleum-based fibers used in apparel. Silk fiber, produced from silkworm cocoons, is natural and biodegradable but requires intensive water, energy, and pesticide use, impacting the environment significantly. Overall, PLA fiber presents enhanced sustainability benefits due to its renewable sourcing and reduced ecological footprint in apparel manufacturing.
Physical and Chemical Properties
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, exhibits high tensile strength, good moisture-wicking ability, and excellent biodegradability, making it suitable for eco-friendly apparel. Silk fiber, produced by silkworms, is characterized by its luxurious softness, natural protein composition (fibroin), and excellent moisture absorbency, but it is less durable and more sensitive to chemicals compared to PLA. Chemically, PLA is an aliphatic polyester with higher resistance to UV degradation and microbial attack, whereas silk's protein structure is more prone to enzymatic and hydrolytic degradation, influencing durability and care requirements in textile applications.
Comfort and Skin Sensation
PLA fiber offers excellent moisture-wicking properties and breathability, providing a cool and dry sensation ideal for activewear and warm climates. Silk fiber stands out for its natural smoothness and hypoallergenic qualities, delivering a luxurious, soft touch that is gentle on sensitive skin. Both fibers enhance comfort, with PLA focusing on performance-oriented freshness and Silk emphasizing tactile softness and elegance.
Durability and Care Requirements
PLA fiber offers superior durability compared to silk, resisting abrasion and maintaining shape after multiple washes, making it ideal for activewear and everyday apparel. Silk fiber requires delicate handling and gentle laundering to preserve its natural sheen and tensile strength, often necessitating dry cleaning or hand washing. While PLA fibers are more resilient to shrinking and stretching, silk fibers provide a luxurious feel but demand higher maintenance to avoid damage.
Breathability and Moisture Management
PLA fiber offers superior breathability compared to silk fiber, allowing better air circulation and enhanced comfort in apparel. Its moisture-wicking properties efficiently draw sweat away from the skin, promoting quicker evaporation and keeping the wearer dry. Silk fiber, while naturally breathable, tends to retain moisture longer, making PLA fiber a more effective choice for activewear and high-performance clothing.
Dyeability and Color Fastness
PLA fiber exhibits excellent dyeability due to its affinity for disperse dyes, resulting in vibrant and uniform colors, while maintaining strong color fastness even after repeated washing and exposure to light. Silk fiber is renowned for its exceptional dye absorption capabilities, offering rich, lustrous colors with superior color fastness to perspiration, light, and dry cleaning. Both fibers deliver high-quality coloration, but PLA provides enhanced environmental sustainability alongside durable color performance in apparel applications.
Cost and Market Availability
PLA fiber offers a cost-effective alternative to silk fiber, with production costs generally lower due to its bio-based, renewable raw materials and scalable manufacturing processes. Market availability of PLA fiber is expanding in the sustainable apparel sector, driven by growing demand for eco-friendly textiles, whereas silk fiber remains limited by traditional sericulture and higher raw material costs. Apparel manufacturers increasingly consider PLA for its affordability and consistent supply, while silk commands premium pricing and niche market presence due to its natural origin and luxury perception.
Applications in Apparel Industry
PLA fiber offers sustainable, biodegradable alternatives for activewear and casual clothing, providing moisture-wicking and odor-resistant properties ideal for sportswear. Silk fiber remains preferred in luxury apparel due to its natural luster, softness, and excellent drape, commonly used in evening wear, blouses, and scarves. Both fibers serve distinct market segments, with PLA focusing on eco-conscious and performance-driven fabrics, while silk emphasizes premium aesthetics and comfort.
Infographic: PLA fiber vs Silk fiber for Apparel
 azmater.com
azmater.com