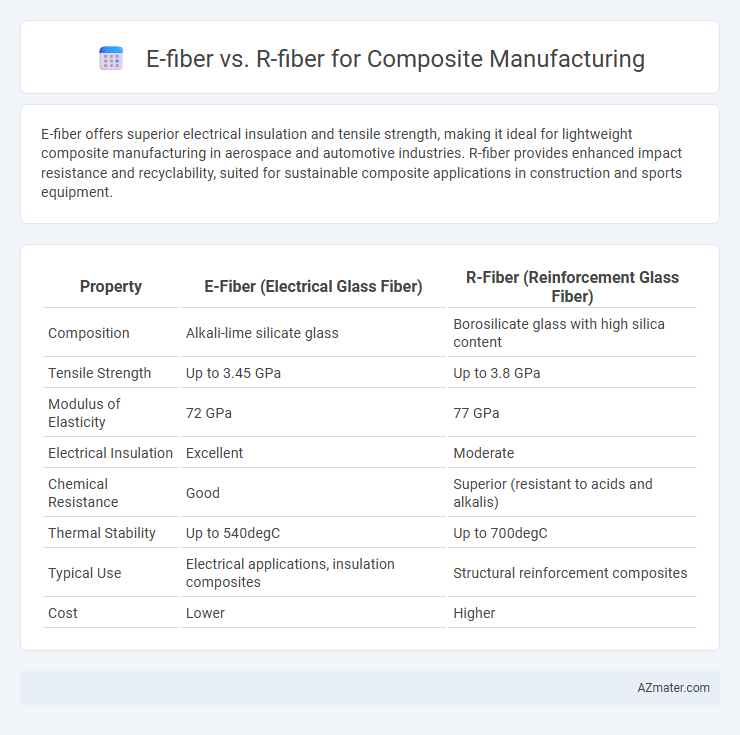
E-fiber offers superior electrical insulation and tensile strength, making it ideal for lightweight composite manufacturing in aerospace and automotive industries. R-fiber provides enhanced impact resistance and recyclability, suited for sustainable composite applications in construction and sports equipment.
Table of Comparison
| Property | E-Fiber (Electrical Glass Fiber) | R-Fiber (Reinforcement Glass Fiber) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Alkali-lime silicate glass | Borosilicate glass with high silica content |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 3.45 GPa | Up to 3.8 GPa |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 72 GPa | 77 GPa |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent | Moderate |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Superior (resistant to acids and alkalis) |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 540degC | Up to 700degC |
| Typical Use | Electrical applications, insulation composites | Structural reinforcement composites |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Composite Fiber Technologies
E-fiber and R-fiber represent two key categories of glass fibers widely used in composite manufacturing, with E-fiber primarily composed of alumino-borosilicate glass offering excellent electrical insulation and mechanical strength, making it ideal for applications in electronics and aerospace. R-fiber, derived from alkali-resistant glass formulations enriched with zirconia, provides superior resistance to chemical degradation and enhanced durability, particularly suitable for reinforcing concrete and corrosive environments. Understanding the material composition and performance characteristics of E-fiber versus R-fiber facilitates optimized selection based on specific mechanical, thermal, and environmental requirements in composite fiber technologies.
What is E-Fiber?
E-fiber, or E-glass fiber, is a type of glass fiber commonly used in composite manufacturing due to its excellent electrical insulation properties, high tensile strength, and resistance to moisture and chemicals. It is made from alumino-borosilicate glass with less than 1% alkali oxides, making it ideal for reinforcing polymers in applications such as aerospace, automotive, and construction. Compared to R-fiber, which is designed primarily for higher mechanical strength and temperature resistance, E-fiber offers superior electrical performance and cost-effectiveness.
What is R-Fiber?
R-Fiber is a type of recycled fiber derived from post-consumer or post-industrial waste, commonly used in composite manufacturing to enhance sustainability and reduce environmental impact. It offers comparable mechanical properties to virgin E-fiber while significantly lowering carbon footprint and production costs. Manufacturers prioritize R-Fiber for eco-friendly composites in automotive, construction, and sports equipment industries.
Material Properties Comparison: E-Fiber vs R-Fiber
E-fiber, primarily composed of alumina-silica and characterized by high tensile strength (3.4 GPa) and excellent electrical insulation, excels in general composite manufacturing with superior fracture toughness and resistance to alkali environments. R-fiber, rich in zirconia with tensile strength around 3.5 GPa, offers enhanced corrosion resistance and improved thermal stability, making it ideal for high-temperature composite applications. While E-fiber provides optimal electrical properties and budget-friendly performance, R-fiber's material properties favor durability and chemical stability in harsh environments.
Mechanical Performance in Composite Manufacturing
E-fiber offers superior tensile strength and stiffness, making it ideal for high-performance composite applications requiring enhanced mechanical durability. R-fiber excels in corrosion resistance and maintains consistent mechanical properties under harsh environmental conditions, benefiting composites exposed to moisture or chemicals. Optimizing composite manufacturing by selecting E-fiber or R-fiber can significantly influence impact resistance, fatigue life, and overall structural integrity in aerospace and automotive industries.
Cost Analysis: E-Fiber vs R-Fiber
E-fiber offers lower initial costs due to its high-volume production and widespread availability, making it ideal for cost-sensitive composite manufacturing. R-fiber, though more expensive per unit, delivers superior mechanical properties and durability, potentially reducing lifecycle costs in high-performance applications. Evaluating total cost of ownership involves considering raw material expense, processing costs, and long-term performance benefits between E-fiber and R-fiber options.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
E-fibers, primarily made from glass, offer a balance of strength and recyclability, making them a popular choice in sustainable composite manufacturing. R-fibers, or recycled fibers, are derived from repurposed materials, significantly reducing environmental footprint by minimizing waste and lowering carbon emissions compared to virgin fibers. Utilizing R-fibers enhances circular economy practices in composites, promoting resource efficiency and reducing dependence on non-renewable raw materials.
Applications in Industry: E-Fiber and R-Fiber
E-fiber and R-fiber are critical in composite manufacturing, with E-fiber primarily used in electrical insulation, automotive panels, and sporting goods due to its high tensile strength and dielectric properties. R-fiber finds applications in aerospace and industrial sectors, offering superior thermal resistance and mechanical performance for structural components. Both fibers optimize composite material properties tailored for specific industrial demands, enhancing durability and performance.
Manufacturing Processes Compatibility
E-fiber and R-fiber differ significantly in compatibility with composite manufacturing processes; E-glass fibers exhibit excellent adaptability to traditional methods like hand lay-up, filament winding, and resin transfer molding due to their balanced mechanical properties and chemical durability. R-glass fibers, characterized by higher tensile strength and improved stiffness, are more suited for high-performance processes such as pultrusion and automated fiber placement, where enhanced structural properties are critical. Manufacturing process selection hinges on balancing mechanical requirements and fiber cost, with E-fibers preferred for cost-effective, versatile applications, while R-fibers target advanced composites demanding superior mechanical performance.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Composite Projects
E-fiber glass offers higher tensile strength and excellent electrical insulation properties, making it ideal for lightweight, high-strength composite applications in aerospace and automotive industries. R-fiber, known for superior chemical resistance and improved mechanical durability, suits projects exposed to harsh environmental conditions like marine and chemical processing sectors. Selecting between E-fiber and R-fiber depends on the specific performance requirements, environmental exposure, and budget constraints of the composite manufacturing project.
Infographic: E-fiber vs R-fiber for Composite Manufacturing
 azmater.com
azmater.com