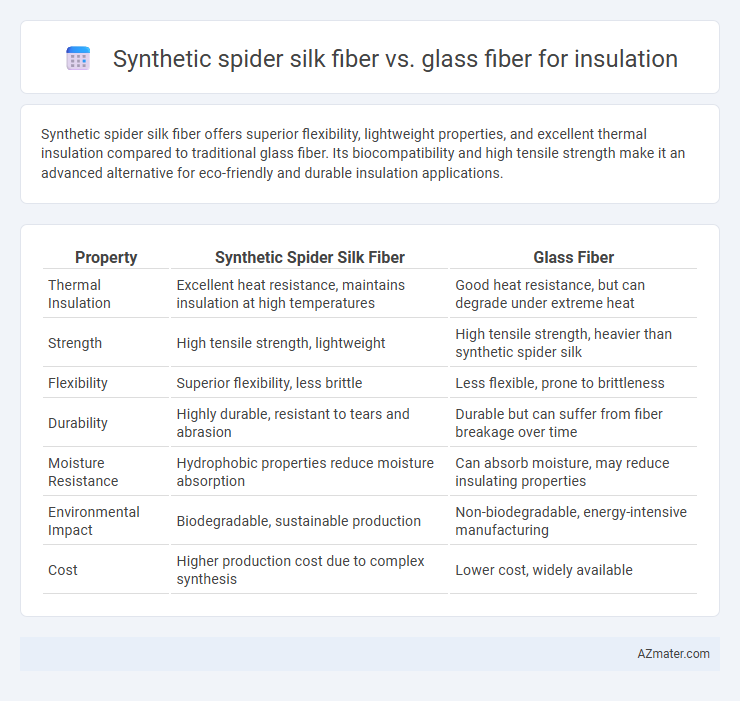
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers superior flexibility, lightweight properties, and excellent thermal insulation compared to traditional glass fiber. Its biocompatibility and high tensile strength make it an advanced alternative for eco-friendly and durable insulation applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Synthetic Spider Silk Fiber | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent heat resistance, maintains insulation at high temperatures | Good heat resistance, but can degrade under extreme heat |
| Strength | High tensile strength, lightweight | High tensile strength, heavier than synthetic spider silk |
| Flexibility | Superior flexibility, less brittle | Less flexible, prone to brittleness |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to tears and abrasion | Durable but can suffer from fiber breakage over time |
| Moisture Resistance | Hydrophobic properties reduce moisture absorption | Can absorb moisture, may reduce insulating properties |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, sustainable production | Non-biodegradable, energy-intensive manufacturing |
| Cost | Higher production cost due to complex synthesis | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Insulation Materials
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and flexibility, making it a promising alternative to traditional insulation materials like glass fiber. Its lightweight structure and superior thermal resistance enhance energy efficiency in building applications. Glass fiber remains widely used due to its cost-effectiveness and fire resistance, but synthetic spider silk's renewable and biodegradable properties provide an innovative edge in sustainable insulation solutions.
Overview of Synthetic Spider Silk Fiber
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength, elasticity, and thermal stability, making it an innovative material for insulation applications. Its lightweight, biodegradable nature and superior durability outperform traditional glass fiber insulation in flexibility and environmental impact. High moisture resistance and low thermal conductivity further enhance synthetic spider silk's efficiency as an eco-friendly alternative for advanced insulation solutions.
Properties of Glass Fiber Insulation
Glass fiber insulation features excellent thermal resistance with an R-value typically ranging from 2.2 to 2.7 per inch, making it highly effective at reducing heat transfer. It is non-combustible, moisture-resistant, and offers soundproofing qualities, contributing to energy efficiency and indoor comfort. Compared to synthetic spider silk fiber, glass fiber insulation is widely available, cost-effective, and maintains stable performance under high temperature and humid conditions.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits superior thermal insulation properties compared to glass fiber due to its natural protein structure, which creates a lightweight, highly porous material with low thermal conductivity. While glass fiber relies primarily on trapped air pockets for insulation, synthetic spider silk fibers maintain better heat retention and offer enhanced flexibility and durability under varying temperatures. This results in more effective energy efficiency and comfort in insulation applications where minimizing heat transfer is critical.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits remarkable mechanical strength with tensile strength up to 1.75 GPa and exceptional elasticity, outperforming traditional glass fiber, which typically has tensile strength around 2.5-3.5 GPa but is much more brittle and prone to cracking under stress. In terms of durability, synthetic spider silk offers superior fatigue resistance and environmental degradation resilience, maintaining integrity under repeated stress and moisture exposure, whereas glass fiber insulation can degrade faster in harsh conditions and suffer from brittleness over time. This combination of high strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced durability makes synthetic spider silk fiber an innovative alternative for insulation applications demanding long-term performance and flexibility.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers a biodegradable and renewable alternative to traditional glass fiber insulation, significantly reducing environmental pollution and landfill waste. Unlike glass fiber, which requires energy-intensive manufacturing processes and often involves hazardous materials, synthetic spider silk is produced through bioengineered proteins with lower carbon emissions and minimal toxic byproducts. The sustainable production and natural decomposition of synthetic spider silk make it a preferable choice for eco-friendly insulation solutions.
Fire Resistance and Safety Considerations
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers superior fire resistance compared to traditional glass fiber, with a higher ignition temperature and reduced smoke production during combustion. Its biodegradable and non-toxic properties enhance safety by minimizing harmful emissions and respiratory hazards often associated with glass fiber insulation. This makes synthetic spider silk a safer and more environmentally friendly option for fire-resistant insulation applications.
Cost and Scalability of Production
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers superior flexibility and thermal resistance compared to glass fiber but currently suffers from higher production costs due to complex bio-engineering processes. Glass fiber insulation benefits from well-established, large-scale manufacturing facilities that ensure lower cost per unit and consistent supply for mass construction applications. While synthetic spider silk presents promising scalability with advancements in biotechnology, its commercial viability remains limited by expensive raw materials and slower production rates relative to glass fiber.
Applications in the Construction Industry
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers superior tensile strength, flexibility, and thermal insulation properties compared to traditional glass fiber, making it ideal for advanced insulation applications in the construction industry. Its lightweight, biodegradable nature enhances sustainability while providing excellent resistance to moisture and mold, which improves building durability and indoor air quality. Glass fiber remains widely used due to cost efficiency and fire resistance, but synthetic spider silk fiber's innovative performance benefits position it as a promising alternative for high-performance green building insulation.
Future Prospects and Research Directions
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers superior thermal insulation properties combined with exceptional strength-to-weight ratio compared to traditional glass fiber, positioning it as a promising material for next-generation insulation technologies. Current research focuses on enhancing the scalability and cost-efficiency of bioengineered spider silk production, targeting applications in aerospace, construction, and wearable technology. Future directions emphasize improving integrated multifunctionality, such as combining insulation with fire resistance and biodegradability, to meet sustainable development goals and industry demands.
Infographic: Synthetic spider silk fiber vs Glass fiber for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com