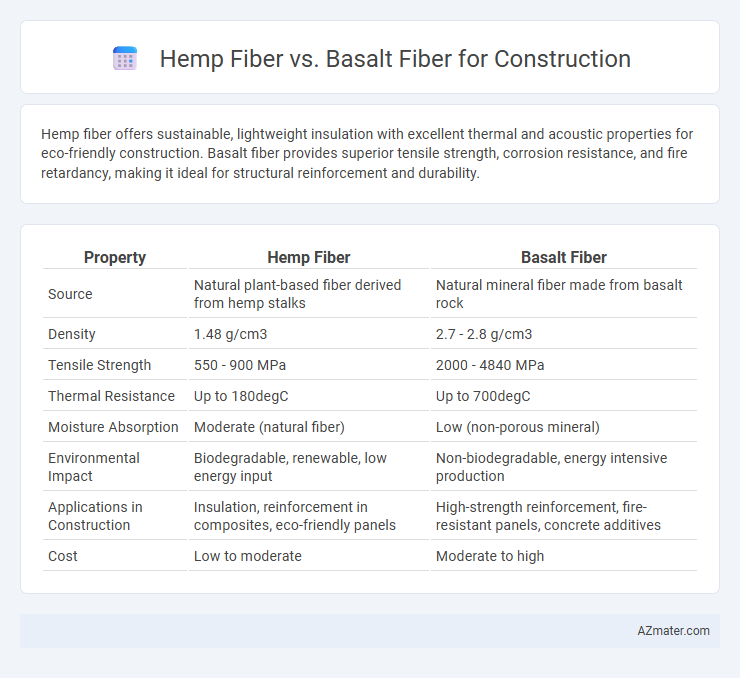
Hemp fiber offers sustainable, lightweight insulation with excellent thermal and acoustic properties for eco-friendly construction. Basalt fiber provides superior tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and fire retardancy, making it ideal for structural reinforcement and durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hemp Fiber | Basalt Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural plant-based fiber derived from hemp stalks | Natural mineral fiber made from basalt rock |
| Density | 1.48 g/cm3 | 2.7 - 2.8 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 550 - 900 MPa | 2000 - 4840 MPa |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 180degC | Up to 700degC |
| Moisture Absorption | Moderate (natural fiber) | Low (non-porous mineral) |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable, low energy input | Non-biodegradable, energy intensive production |
| Applications in Construction | Insulation, reinforcement in composites, eco-friendly panels | High-strength reinforcement, fire-resistant panels, concrete additives |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Moderate to high |
Introduction to Hemp and Basalt Fibers in Construction
Hemp fiber, derived from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, is valued in construction for its lightweight, renewable nature and excellent insulation properties, promoting sustainable building practices. Basalt fiber, produced from crushed volcanic rock, offers superior strength, thermal stability, and resistance to chemical degradation, making it ideal for reinforcement in concrete and composites. Both fibers contribute to eco-friendly construction by enhancing durability and reducing environmental impact, with hemp emphasizing biodegradability and basalt focusing on structural performance.
Overview: Material Properties of Hemp Fiber
Hemp fiber exhibits high tensile strength, natural flexibility, and excellent biodegradability, making it an eco-friendly choice for sustainable construction materials. Its low density and ability to absorb moisture contribute to improved insulation and enhanced indoor air quality in building applications. Compared to basalt fiber, hemp offers superior carbon sequestration potential and reduced environmental impact while maintaining adequate durability for non-structural uses.
Overview: Material Properties of Basalt Fiber
Basalt fiber is produced from natural volcanic basalt rock, offering high tensile strength of approximately 2.8 GPa and a density around 2.7 g/cm3, which surpasses traditional glass fibers. Its excellent thermal stability, withstanding temperatures up to 700degC, makes it suitable for fire-resistant construction materials. The fiber also exhibits superior chemical resistance and low moisture absorption, enhancing durability in harsh environmental conditions compared to organic fibers like hemp.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Hemp fiber offers a renewable, biodegradable alternative with low embodied energy and strong carbon sequestration properties, making it highly sustainable for eco-friendly construction. Basalt fiber, derived from volcanic rock, provides excellent durability and corrosion resistance but involves higher energy consumption during production. The use of hemp fiber significantly reduces environmental impact through natural growth and minimal processing, whereas basalt fiber's sustainability depends on energy-efficient manufacturing practices.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Hemp fiber exhibits tensile strengths typically ranging from 300 to 800 MPa, offering excellent flexibility and impact resistance, making it suitable for lightweight construction applications. Basalt fiber demonstrates superior mechanical strength with tensile values around 1,100 to 3,100 MPa, providing higher stiffness and enhanced load-bearing capacity essential for structural elements. Durability assessments reveal basalt fiber's exceptional resistance to chemical corrosion, UV degradation, and high temperatures, whereas hemp fiber requires treatments to improve moisture resistance and long-term durability in harsh environmental conditions.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Performance
Hemp fiber offers excellent thermal insulation with a low thermal conductivity of around 0.04 W/m*K, making it highly efficient for reducing heat transfer in construction. Basalt fiber, while stronger and more durable, has a slightly higher thermal conductivity near 0.038-0.04 W/m*K but excels in acoustic insulation due to its dense fiber structure that dampens sound effectively. Hemp fiber's porous structure provides superior breathability and moisture regulation, enhancing indoor air quality, whereas basalt fiber's resistance to fire and chemical degradation makes it ideal for high-performance acoustic panels and thermal barriers in demanding environments.
Cost Analysis: Hemp vs Basalt Fiber
Hemp fiber offers a cost-effective alternative to basalt fiber in construction due to its lower raw material and processing expenses, making it suitable for budget-conscious projects. Basalt fiber, while more expensive upfront, provides superior durability and higher tensile strength, potentially reducing long-term maintenance costs and increasing structural lifespan. Evaluating total lifecycle costs reveals hemp's advantage in initial investment, whereas basalt's higher performance may justify its price in demanding applications.
Application Suitability in Modern Construction
Hemp fiber offers exceptional sustainability and thermal insulation, making it ideal for eco-friendly building materials such as insulation panels and composites in modern construction. Basalt fiber provides superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and durability, making it suitable for structural reinforcements, concrete enhancement, and seismic-resistant applications. The choice between hemp and basalt fibers depends on project priorities, with hemp favoring green building certifications and indoor air quality, while basalt excels in structural performance and longevity.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Fiber
Hemp fiber faces challenges such as lower tensile strength and susceptibility to moisture absorption, which can lead to durability issues and require protective treatments in construction applications. Basalt fiber, while offering high strength and corrosion resistance, faces limitations including higher production costs and less availability, potentially impacting large-scale adoption in building projects. Both fibers demand specific processing techniques to optimize bonding with construction matrices, affecting their overall performance and cost-efficiency in structural use.
Future Trends in Fiber Usage for Buildings
Hemp fiber and basalt fiber both offer sustainable alternatives for construction, with hemp providing excellent thermal insulation and breathability while being biodegradable, and basalt fiber delivering superior strength, durability, and fire resistance. Future trends indicate a growing integration of hybrid composites combining both fibers to leverage hemp's sustainability and basalt's structural performance in eco-friendly buildings. Advancements in fiber processing and increased regulatory support for renewable materials are expected to drive wider adoption of hemp and basalt fibers in green construction and smart infrastructure projects.
Infographic: Hemp fiber vs Basalt fiber for Construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com