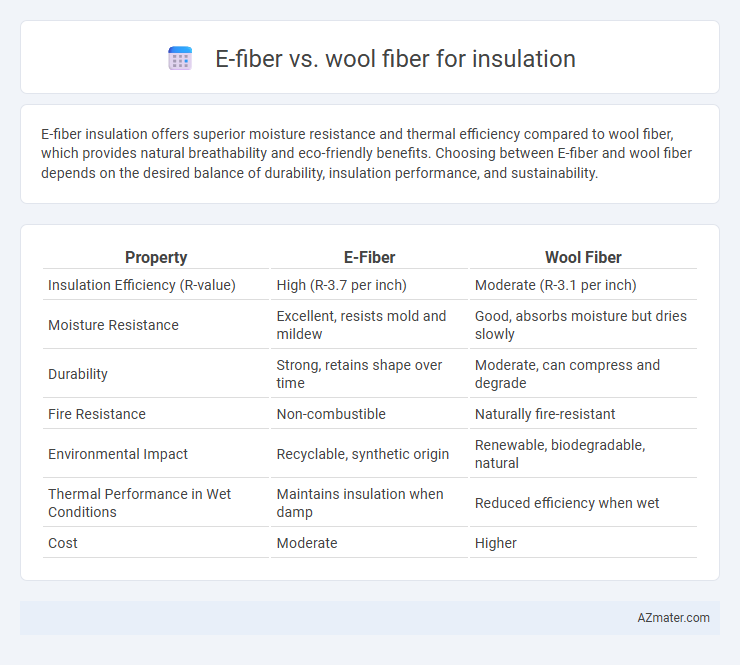
E-fiber insulation offers superior moisture resistance and thermal efficiency compared to wool fiber, which provides natural breathability and eco-friendly benefits. Choosing between E-fiber and wool fiber depends on the desired balance of durability, insulation performance, and sustainability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | E-Fiber | Wool Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Insulation Efficiency (R-value) | High (R-3.7 per inch) | Moderate (R-3.1 per inch) |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent, resists mold and mildew | Good, absorbs moisture but dries slowly |
| Durability | Strong, retains shape over time | Moderate, can compress and degrade |
| Fire Resistance | Non-combustible | Naturally fire-resistant |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, synthetic origin | Renewable, biodegradable, natural |
| Thermal Performance in Wet Conditions | Maintains insulation when damp | Reduced efficiency when wet |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
Introduction to E-Fiber and Wool Fiber Insulation
E-fiber, a synthetic insulation material made from recycled polyester fibers, offers lightweight, moisture-resistant, and durable properties ideal for energy-efficient thermal management. Wool fiber insulation, derived from natural sheep wool, provides excellent thermal regulation, breathability, and natural fire resistance while maintaining eco-friendly and sustainable characteristics. Both materials serve distinct purposes in insulation, with E-fiber excelling in synthetic performance and wool fiber known for its renewable, biodegradable qualities.
Material Composition and Structure
E-fiber insulation consists of continuous glass fibers with high tensile strength and low thermal conductivity, creating a dense, uniform structure ideal for thermal resistance. Wool fiber insulation, derived from natural animal hair, features a crimped, scaly surface that traps air effectively, providing excellent moisture regulation and thermal benefits. The synthetic composition of E-fiber delivers durability and consistency, while wool's organic structure enhances breathability and eco-friendliness in insulation applications.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
E-fiber insulation exhibits superior thermal resistance due to its low thermal conductivity, typically around 0.03 W/m*K, compared to wool fiber's conductivity of approximately 0.04 W/m*K. The synthetic structure of E-fiber traps air more effectively, enhancing heat retention and reducing energy loss in building applications. Wool fiber, while offering natural moisture regulation, generally provides slightly less thermal performance, making E-fiber a preferred choice for high-efficiency insulation solutions.
Moisture Resistance and Breathability
E-fiber insulation outperforms wool fiber in moisture resistance due to its synthetic composition, which repels water and prevents mold growth. Wool fiber excels in breathability by naturally wicking moisture away and regulating humidity, maintaining a dry and comfortable environment. Combining E-fiber's water repellency with wool's moisture management offers optimal insulation performance in varying climates.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
E-fiber insulation, made from recycled polyester, offers a sustainable alternative by utilizing post-consumer plastic waste, significantly reducing landfill contributions and energy consumption during production compared to traditional wool fibers. Wool fibers, sourced from sheep, are biodegradable and renewable but involve higher water usage, land requirements, and methane emissions, impacting their overall environmental footprint. E-fiber's recycled origin and lower resource intensity make it a more eco-friendly choice for insulation focused on minimizing environmental impact and promoting circular economy principles.
Durability and Longevity
E-fiber insulation exhibits superior durability compared to wool fiber, offering resistance to moisture, mold, and pest damage, which extends its lifespan significantly. Wool fiber naturally provides excellent thermal regulation and is biodegradable but tends to degrade faster in humid or wet conditions, reducing its long-term effectiveness. E-fiber's synthetic composition ensures consistent performance over time, making it a preferred choice for long-lasting insulation solutions.
Fire Resistance Properties
E-fiber offers superior fire resistance compared to wool fiber due to its inherent non-combustible properties and higher ignition temperature, making it suitable for high-risk fire zones. Wool fiber naturally resists flames because of its high nitrogen and water content, which helps it self-extinguish when exposed to fire, but it chars rather than melts. Both fibers provide effective insulation, yet E-fiber's enhanced fire retardancy and structural stability under heat make it the preferred choice for stringent fire safety standards.
Installation Process and Flexibility
E-fiber insulation offers superior flexibility due to its lightweight and pliable nature, allowing easier handling and installation in irregular or tight spaces compared to wool fiber. Wool fiber insulation requires careful handling to maintain its natural loft and can be more labor-intensive during installation due to its denser texture. The ease of cutting and shaping E-fiber minimizes installation time, making it a preferred choice in projects demanding quick and precise application.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
E-fiber insulation generally offers a lower initial cost compared to wool fiber due to its synthetic production process, which allows for mass manufacturing and reduced raw material expenses. Wool fiber insulation, while more expensive upfront, provides superior durability and natural moisture regulation that can lead to long-term energy savings and reduced maintenance costs. Economic considerations also include the environmental impact, where wool's biodegradability and renewable sourcing may qualify for green building incentives, potentially offsetting its higher price in sustainable construction projects.
Best Applications: E-Fiber vs Wool Fiber
E-fiber insulation excels in moisture resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-humidity environments and applications requiring long-lasting thermal performance, such as wall cavities and roofing. Wool fiber provides superior natural breathability and excellent thermal regulation, suited for eco-friendly homes, interior insulation, and areas needing humidity control. Choosing between E-fiber and wool fiber depends on specific project needs, with E-fiber favored for synthetic, moisture-prone settings and wool preferred for sustainable, breathable insulation.
Infographic: E-fiber vs Wool fiber for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com