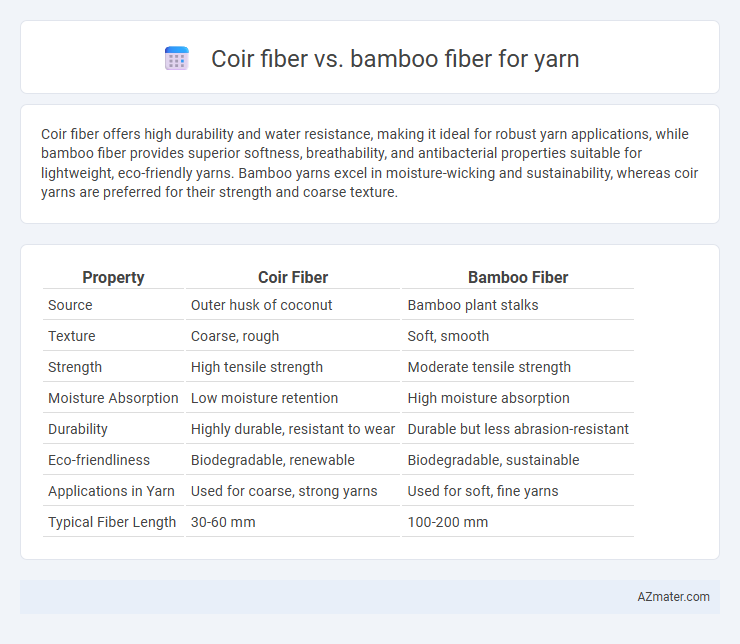
Coir fiber offers high durability and water resistance, making it ideal for robust yarn applications, while bamboo fiber provides superior softness, breathability, and antibacterial properties suitable for lightweight, eco-friendly yarns. Bamboo yarns excel in moisture-wicking and sustainability, whereas coir yarns are preferred for their strength and coarse texture.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Coir Fiber | Bamboo Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Outer husk of coconut | Bamboo plant stalks |
| Texture | Coarse, rough | Soft, smooth |
| Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture retention | High moisture absorption |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to wear | Durable but less abrasion-resistant |
| Eco-friendliness | Biodegradable, renewable | Biodegradable, sustainable |
| Applications in Yarn | Used for coarse, strong yarns | Used for soft, fine yarns |
| Typical Fiber Length | 30-60 mm | 100-200 mm |
Introduction to Coir Fiber and Bamboo Fiber
Coir fiber, derived from the outer husk of coconuts, is known for its durability, natural water resistance, and coarse texture, making it suitable for sturdy yarn applications such as mats, brushes, and ropes. Bamboo fiber, extracted from bamboo pulp through mechanical or chemical processing, offers a soft, breathable, and eco-friendly alternative with inherent antibacterial properties, ideal for textile yarns used in garments and home furnishings. Both fibers provide sustainable options, but coir excels in toughness and moisture resistance, while bamboo fiber delivers softness and antimicrobial benefits for varied yarn uses.
Source and Production Methods
Coir fiber, derived from the husk of coconut shells, is extracted through a process of retting and decortication that separates coarse fibers ideal for coarse yarn production. Bamboo fiber is obtained from bamboo pulp, involving mechanical crushing or chemical processing to create soft, fine fibers suitable for spinning into yarn with a silky texture. Both fibers offer sustainable alternatives, but coir production is more labor-intensive, while bamboo fiber benefits from eco-friendly extraction technologies that enhance yarn quality.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, is highly sustainable due to its natural biodegradability and low water usage during cultivation, making it an eco-friendly option for yarn production. Bamboo fiber, although renewable and fast-growing, requires intensive chemical processing which can impact the environment negatively if not managed properly. Both fibers offer biodegradable alternatives to synthetic yarns, but coir's minimal processing and waste utilization give it an environmental advantage in sustainable textile manufacturing.
Physical Properties Comparison
Coir fiber is coarse, rigid, and highly durable, with a high lignin content that provides excellent resistance to wear and water but results in lower tensile strength and flexibility compared to bamboo fiber. Bamboo fiber is finer, softer, and more flexible, offering superior tensile strength, moisture-wicking properties, and natural antibacterial qualities, making it ideal for comfortable and breathable yarns. The density of coir fiber ranges from 1.15 to 1.46 g/cm3, whereas bamboo fiber has a lower density around 1.0 to 1.3 g/cm3, contributing to the lightweight and smooth texture of bamboo yarn.
Spinnability and Yarn Formation
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, has coarse and stiff characteristics that limit its spinnability, making yarn formation challenging and more suitable for coarse, rough-textured yarns. Bamboo fiber, known for its softer and finer strands, offers superior spinnability, enabling the production of smooth, fine, and uniform yarns with enhanced flexibility. The differential in fiber length, fineness, and tensile strength between coir and bamboo critically influences their adaptability in spinning processes and the quality of the resulting yarn.
Strength and Durability in Yarn Applications
Coir fiber exhibits high tensile strength and excellent abrasion resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty yarn applications requiring durability and resilience. Bamboo fiber, while softer and more flexible, offers moderate strength but superior elasticity and moisture-wicking properties, enhancing comfort in textile products. For yarns demanding maximum strength and long-lasting wear, coir fiber is preferred, whereas bamboo fiber suits applications prioritizing softness and breathability.
Comfort and Wearability Factors
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, offers durability and moisture resistance but is coarser and less breathable, limiting its comfort and wearability in yarn. Bamboo fiber excels in softness, breathability, and moisture-wicking properties, making it a superior choice for garments requiring comfort and enhanced wearability. The natural antibacterial qualities of bamboo fiber also contribute to improved hygiene and overall wearer comfort compared to coir fiber.
Dyeability and Aesthetic Qualities
Coir fiber possesses a coarse texture that limits its dyeability, resulting in muted and earthy tones ideal for rustic yarn applications, whereas bamboo fiber features excellent dye absorption due to its smooth, fine structure, allowing vibrant and diverse color palettes. Bamboo yarn exhibits a silky sheen and soft hand feel, enhancing aesthetic appeal for fashion-forward textiles, while coir yarn's roughness grants a natural, organic look suited for eco-friendly and durable products. The inherent chemical properties of bamboo facilitate better fixation of dyes, providing colorfastness superior to the relatively inert lignin content in coir fiber.
Cost and Market Availability
Coir fiber yarn, derived from coconut husks, offers a low-cost option due to abundant raw material availability in tropical regions, while bamboo fiber yarn tends to be pricier because of more complex extraction and processing methods. Market availability for coir yarn is regionally concentrated, primarily in South Asia, whereas bamboo fiber yarn enjoys broader global distribution owing to rising demand for sustainable textiles. Cost-effectiveness of coir yarn suits eco-friendly, budget-conscious applications, whereas bamboo yarn appeals to premium segments emphasizing softness and biodegradability.
Best Uses and Recommendations for Yarn
Coir fiber, known for its coarse texture and high durability, is best suited for heavy-duty yarn applications such as ropes, mats, and upholstery, offering excellent resistance to moisture and wear. Bamboo fiber, celebrated for its softness, antibacterial properties, and breathability, is ideal for producing lightweight, comfortable yarn used in apparel, baby textiles, and eco-friendly fashion products. For yarn manufacturing, bamboo fiber is recommended when softness and sustainability are priorities, while coir fiber excels in industrial-grade, sturdy yarns requiring robustness and water resistance.
Infographic: Coir fiber vs Bamboo fiber for Yarn
 azmater.com
azmater.com