Chitosan fiber offers superior biodegradability and antimicrobial properties compared to viscose fiber, making it ideal for sustainable and hygienic apparel. Viscose fiber, derived from wood pulp, provides excellent softness and breathability but lacks the natural antibacterial benefits of chitosan.
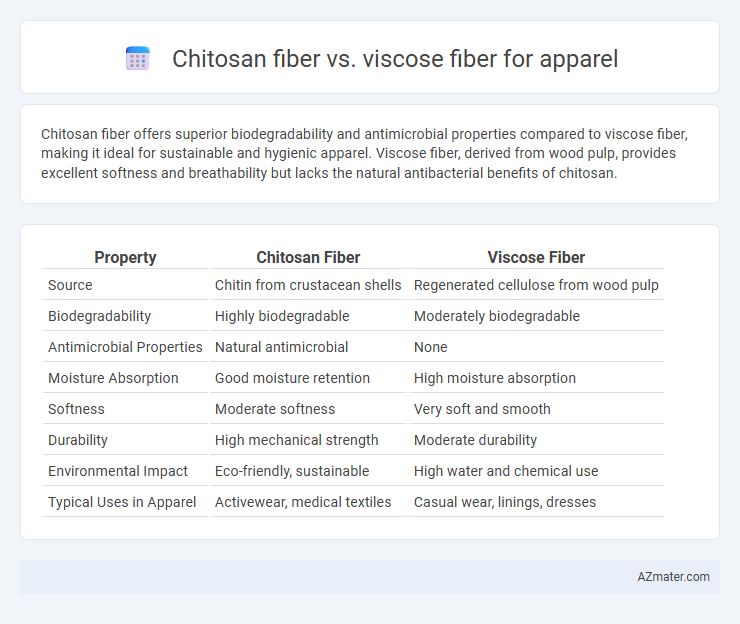
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chitosan Fiber | Viscose Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Chitin from crustacean shells | Regenerated cellulose from wood pulp |
| Biodegradability | Highly biodegradable | Moderately biodegradable |
| Antimicrobial Properties | Natural antimicrobial | None |
| Moisture Absorption | Good moisture retention | High moisture absorption |
| Softness | Moderate softness | Very soft and smooth |
| Durability | High mechanical strength | Moderate durability |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, sustainable | High water and chemical use |
| Typical Uses in Apparel | Activewear, medical textiles | Casual wear, linings, dresses |
Introduction to Chitosan and Viscose Fibers
Chitosan fiber, derived from chitin found in crustacean shells, is a biodegradable and antimicrobial material increasingly used in sustainable apparel, offering advantages like moisture absorption and odor control. Viscose fiber, a semi-synthetic fiber made from regenerated cellulose, provides a soft, breathable, and versatile fabric widely used in clothing production due to its silk-like texture and affordability. Comparing both, chitosan fibers stand out for eco-friendly properties and health benefits, while viscose remains popular for comfort and cost-effectiveness in apparel manufacturing.
Origin and Production Methods
Chitosan fiber is derived from chitin, primarily sourced from crustacean shells, utilizing a biopolymer extraction process involving deacetylation to produce a natural, biodegradable fiber. Viscose fiber originates from cellulose found in wood pulp or cotton linters, produced through chemical treatment with sodium hydroxide and carbon disulfide to create regenerated cellulose fibers. The production of chitosan fibers emphasizes eco-friendly and sustainable methods, while viscose manufacturing relies heavily on chemical regeneration techniques that impact environmental factors.
Physical and Chemical Properties
Chitosan fiber exhibits excellent biodegradability, outstanding antimicrobial properties, and high moisture absorption compared to viscose fiber, which is known for its smooth texture, good dyeability, and moderate breathability. Chemically, chitosan fibers are derived from chitin with amino groups enhancing antibacterial activity and resistance to mold, while viscose fibers, regenerated from cellulose, possess a high degree of polymerization resulting in good tensile strength but lower inherent antimicrobial effects. Physically, chitosan fibers tend to have higher elasticity and durability, making them suitable for functional apparel, whereas viscose fibers offer a soft hand feel and drape preferred for comfort in everyday clothing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Chitosan fiber, derived from chitin in crustacean shells, offers superior biodegradability and antimicrobial properties, reducing synthetic chemical use in apparel production compared to viscose fiber, which relies heavily on wood pulp and intensive chemical processing, contributing to deforestation and pollution. The eco-friendly extraction of chitosan minimizes water and energy consumption, whereas viscose manufacturing emits hazardous effluents and greenhouse gases, challenging its sustainability credentials. As a renewable and biodegradable textile, chitosan fiber supports circular fashion initiatives, whereas viscose's environmental footprint demands stricter regulation and sustainable sourcing.
Comfort and Wearability in Apparel
Chitosan fiber offers superior moisture absorption and antibacterial properties compared to viscose fiber, enhancing comfort and hygiene in apparel. Viscose fiber provides excellent softness and breathability, contributing to lightweight and smooth wearability. The durability and odor resistance of chitosan fiber make it ideal for activewear, while viscose remains popular for casual and formal garments due to its silky texture.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Options
Chitosan fiber, derived from chitin in crustacean shells, offers superior biodegradability compared to viscose fiber, which is regenerated cellulose with additives that slow decomposition. Chitosan fibers naturally break down in soil and marine environments within months, enhancing sustainable end-of-life options including composting and minimal environmental impact. Viscose fibers, although semi-biodegradable, often require industrial processing for decomposition and may release harmful chemicals if incinerated or landfilled, making chitosan a more eco-friendly choice for apparel sustainability.
Performance in Textile Applications
Chitosan fiber offers superior antibacterial and antifungal properties compared to viscose fiber, enhancing hygiene in apparel applications. It exhibits better moisture management and biodegradability, making it an eco-friendly choice for performance textiles. Viscose fiber, while soft and breathable, lacks the bioactive qualities and durability found in chitosan-based fabrics.
Cost Comparison and Commercial Availability
Chitosan fiber, derived from chitin in crustacean shells, is generally more expensive than viscose fiber due to its complex extraction and production processes, limiting its widespread commercial availability in the apparel industry. Viscose fiber, produced from cellulose, offers a cost-effective alternative with extensive global manufacturing infrastructure, making it readily accessible and affordable. The higher cost and niche market presence of chitosan fiber restrict its use primarily to specialized or sustainable textile segments.
Recent Innovations and Research Trends
Recent innovations in chitosan fiber for apparel emphasize its biodegradable properties, antimicrobial activity, and enhanced moisture management, making it a sustainable alternative to conventional fibers. Research trends focus on improving chitosan fiber's mechanical strength and blending it with viscose to combine viscosity's softness and breathability with chitosan's biofunctionality. Advances in nanotechnology enable the development of chitosan-based smart textiles with UV protection and odor control, positioning it as a competitive fiber against viscose in eco-friendly fashion markets.
Future Outlook in the Apparel Industry
Chitosan fiber, derived from natural biopolymers, offers antimicrobial and biodegradable properties that align with the apparel industry's growing emphasis on sustainability and eco-friendly materials. Viscose fiber, while widely used for its breathability and softness, faces challenges due to environmental concerns related to its chemical-intensive production process. The future outlook favors chitosan fiber's innovation potential in enhancing functional apparel, promoting circular fashion, and meeting consumer demand for green textiles.
Infographic: Chitosan fiber vs Viscose fiber for Apparel
 azmater.com
azmater.com