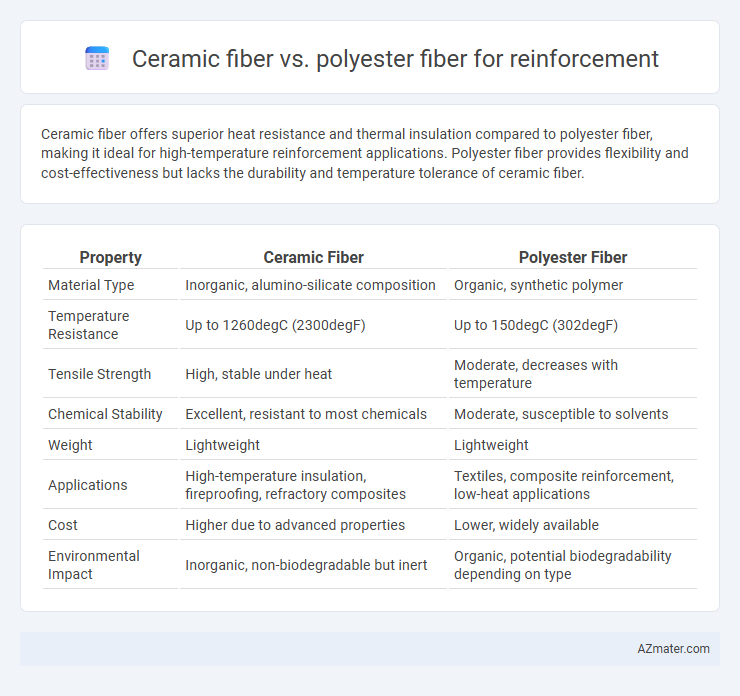
Ceramic fiber offers superior heat resistance and thermal insulation compared to polyester fiber, making it ideal for high-temperature reinforcement applications. Polyester fiber provides flexibility and cost-effectiveness but lacks the durability and temperature tolerance of ceramic fiber.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Fiber | Polyester Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Inorganic, alumino-silicate composition | Organic, synthetic polymer |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1260degC (2300degF) | Up to 150degC (302degF) |
| Tensile Strength | High, stable under heat | Moderate, decreases with temperature |
| Chemical Stability | Excellent, resistant to most chemicals | Moderate, susceptible to solvents |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight |
| Applications | High-temperature insulation, fireproofing, refractory composites | Textiles, composite reinforcement, low-heat applications |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced properties | Lower, widely available |
| Environmental Impact | Inorganic, non-biodegradable but inert | Organic, potential biodegradability depending on type |
Introduction to Fiber Reinforcement
Ceramic fiber and polyester fiber serve distinct functions in fiber reinforcement, with ceramic fiber offering high thermal resistance and durability ideal for high-temperature applications. Polyester fiber provides excellent flexibility, lightweight properties, and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for reinforcement in composites and construction materials. The choice between ceramic and polyester fibers depends on the specific requirements of thermal stability, mechanical strength, and environmental exposure in the intended application.
Overview of Ceramic Fiber
Ceramic fiber is a high-temperature resistant material widely used for reinforcement in thermal insulation applications due to its excellent heat stability, low thermal conductivity, and resistance to chemical corrosion. Unlike polyester fiber, ceramic fiber can withstand temperatures exceeding 1200degC, making it ideal for industrial furnaces, kilns, and fireproofing materials. Its lightweight structure and high tensile strength contribute to enhanced durability and thermal efficiency in demanding environments.
Overview of Polyester Fiber
Polyester fiber offers excellent reinforcement properties due to its high tensile strength, chemical resistance, and durability under various environmental conditions. Its lightweight nature and moisture-wicking capabilities make it suitable for applications requiring flexibility and comfort alongside structural support. Commonly used in composites, textiles, and insulation, polyester fiber provides cost-effective reinforcement with good resistance to abrasion and UV degradation.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Ceramic fiber exhibits superior mechanical properties such as high tensile strength, excellent thermal stability, and outstanding resistance to deformation under high temperatures compared to polyester fiber, which has moderate tensile strength and lower thermal resistance. Polyester fiber reinforcement provides good flexibility and impact resistance at ambient temperatures but significantly loses mechanical integrity when exposed to temperatures above 150degC. Ceramic fiber's mechanical properties make it ideal for applications requiring durability in extreme thermal and mechanical stress environments, whereas polyester fiber is preferred for lightweight, flexible, and cost-effective reinforcement under normal service conditions.
Thermal Resistance and Insulation
Ceramic fiber exhibits superior thermal resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 1,260degC (2,300degF), making it ideal for high-temperature insulation applications compared to polyester fiber, which degrades above 150degC (302degF). The low thermal conductivity of ceramic fiber ensures effective thermal insulation in industrial furnaces and heat shields, while polyester fiber is better suited for low to moderate temperature environments due to its limited thermal stability. Ceramic fiber's inorganic composition provides enhanced fire resistance and durability, whereas polyester fiber, being organic, tends to melt or combust under high heat exposure.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Ceramic fiber offers exceptional chemical resistance, withstanding strong acids, alkalis, and high-temperature environments without degradation, making it ideal for harsh industrial applications. Polyester fiber, while providing good tensile strength and flexibility, is vulnerable to chemical attack from solvents and acids, limiting its durability in aggressive chemical settings. The inherent thermal stability and inertness of ceramic fiber ensure superior long-term reinforcement performance compared to polyester fiber in chemically demanding conditions.
Applications in Construction and Industry
Ceramic fiber offers superior heat resistance and thermal insulation, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial applications such as furnace linings, fireproofing, and insulation in power plants. Polyester fiber provides excellent flexibility and moisture resistance, commonly used in construction for reinforcing concrete, roofing materials, and geotextiles to improve tensile strength and durability. Both fibers enhance structural performance, but ceramic fiber is preferred where extreme heat tolerance is critical, while polyester fiber excels in lightweight, moisture-prone environments.
Cost and Availability
Ceramic fiber offers superior heat resistance and durability for reinforcement but comes with a higher cost and limited availability compared to polyester fiber. Polyester fiber is more affordable and widely accessible, making it suitable for budget-conscious projects requiring moderate reinforcement properties. Selecting between ceramic and polyester fibers depends primarily on the temperature tolerance needed and the overall project budget.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ceramic fiber offers superior thermal resistance and durability with minimal environmental degradation over time, making it a sustainable choice for high-temperature applications. Polyester fiber, while biodegradable and derived from renewable sources, often involves energy-intensive production processes and can release microplastics, impacting ecosystems negatively. Evaluating their lifecycle emissions and recyclability highlights ceramic fiber's advantage in long-term environmental stability versus polyester's quicker degradation and ecological footprint.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Project
Ceramic fiber offers exceptional heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-temperature reinforcement applications such as industrial insulation and fireproofing. Polyester fiber provides flexibility, lightweight strength, and cost-effectiveness, suited for applications requiring moderate heat tolerance and enhanced tensile properties. Selecting the right fiber depends on project temperature demands, mechanical performance requirements, and budget constraints to ensure optimal reinforcement results.
Infographic: Ceramic fiber vs Polyester fiber for Reinforcement
 azmater.com
azmater.com