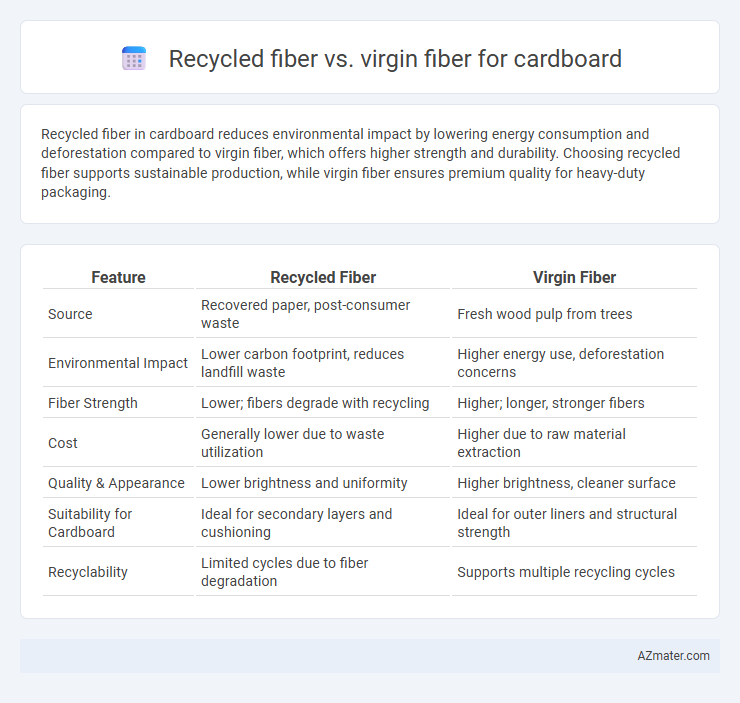
Recycled fiber in cardboard reduces environmental impact by lowering energy consumption and deforestation compared to virgin fiber, which offers higher strength and durability. Choosing recycled fiber supports sustainable production, while virgin fiber ensures premium quality for heavy-duty packaging.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled Fiber | Virgin Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Recovered paper, post-consumer waste | Fresh wood pulp from trees |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, reduces landfill waste | Higher energy use, deforestation concerns |
| Fiber Strength | Lower; fibers degrade with recycling | Higher; longer, stronger fibers |
| Cost | Generally lower due to waste utilization | Higher due to raw material extraction |
| Quality & Appearance | Lower brightness and uniformity | Higher brightness, cleaner surface |
| Suitability for Cardboard | Ideal for secondary layers and cushioning | Ideal for outer liners and structural strength |
| Recyclability | Limited cycles due to fiber degradation | Supports multiple recycling cycles |
Introduction to Recycled and Virgin Fiber in Cardboard
Recycled fiber in cardboard is sourced from post-consumer and post-industrial paper products, offering an eco-friendly alternative that reduces environmental impact by minimizing deforestation and landfill waste. Virgin fiber, derived directly from wood pulp, provides superior strength, durability, and print quality, making it essential for high-performance cardboard applications. Balancing recycled and virgin fibers optimizes both sustainability and functional properties in cardboard production.
What Is Recycled Fiber?
Recycled fiber in cardboard production consists of post-consumer and post-industrial paper materials that are reprocessed to form new pulp, reducing the need for virgin fiber sourced directly from trees. This fiber maintains structural integrity through advanced deinking and cleaning processes, making it a sustainable alternative that lowers environmental impact by conserving natural resources and reducing landfill waste. Compared to virgin fiber, recycled fiber supports circular economy principles while delivering sufficient strength and durability for most cardboard packaging applications.
What Is Virgin Fiber?
Virgin fiber refers to natural fibers extracted directly from trees and other plants that have not been previously processed or recycled. In cardboard manufacturing, virgin fiber offers superior strength, durability, and structural integrity compared to recycled fiber due to its longer, more intact cellulose fibers. While virgin fiber provides higher quality performance, its production impacts include greater energy consumption and deforestation concerns.
Environmental Impact: Recycled vs Virgin Fiber
Recycled fiber in cardboard production significantly reduces environmental impact by lowering deforestation rates and conserving natural resources compared to virgin fiber, which requires cutting down new trees. The use of recycled fiber also decreases energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint. Waste diversion from landfills is another key benefit of recycled fiber, promoting a circular economy in the packaging industry.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Recycled fiber in cardboard typically offers lower strength and durability compared to virgin fiber due to shorter fiber length and fiber degradation from previous processing. Virgin fiber cardboard provides superior tensile strength and stiffness, making it ideal for heavy-duty packaging that demands high structural integrity. Incorporating a blend of recycled and virgin fibers can enhance sustainability while optimizing performance for specific cardboard applications.
Cost Differences and Economic Implications
Recycled fiber for cardboard production typically costs 10-30% less than virgin fiber due to reduced raw material expenses and lower energy consumption during processing. The use of recycled fiber supports circular economy principles by minimizing landfill waste and reducing reliance on deforestation, which contributes to long-term cost savings and environmental compliance benefits. However, virgin fiber often provides superior strength and quality, potentially increasing product value and justifying higher costs in certain applications where performance is critical.
Applications: When to Use Recycled vs Virgin Fiber
Recycled fiber in cardboard is ideal for packaging applications requiring environmental sustainability, such as food containers, shipping boxes, and product packaging where cost efficiency and eco-friendliness are prioritized. Virgin fiber cardboard offers superior strength, durability, and print quality, making it the preferred choice for heavy-duty packaging, luxury goods, and applications demanding high structural integrity or premium aesthetics. Choosing recycled fiber suits mass production with moderate performance needs, while virgin fiber fits specialized uses requiring enhanced mechanical properties and appearance.
Fiber Quality and Performance Factors
Recycled fiber in cardboard often exhibits lower tensile strength and shorter fiber lengths compared to virgin fiber, resulting in reduced durability and stiffness. Virgin fiber provides superior fiber quality with longer, intact cellulose strands that enhance board rigidity, printability, and moisture resistance. Performance factors such as burst strength and tear resistance are consistently higher in cardboard made from virgin fibers, making it preferable for packaging requiring maximum protection.
Availability and Industry Trends
Recycled fiber dominates cardboard production due to increasing sustainability demands and higher availability from post-consumer waste streams, reducing reliance on virgin fiber sourced from logging. Industry trends reveal a growing shift toward closed-loop recycling systems and investments in advanced sorting technologies that improve recycled fiber quality and supply consistency. Virgin fiber remains crucial for premium cardboard grades requiring superior strength, but its market share is gradually declining as recycled materials become more cost-effective and widely adopted.
Sustainability and the Future of Cardboard Manufacturing
Recycled fiber significantly reduces environmental impact by conserving natural resources and lowering energy consumption compared to virgin fiber in cardboard production. The shift towards recycled fiber supports sustainable manufacturing practices, minimizing deforestation and decreasing greenhouse gas emissions associated with virgin pulp processing. Advancements in recycling technologies and increased demand for eco-friendly packaging position recycled fiber as the cornerstone for the future of sustainable cardboard manufacturing.
Infographic: Recycled fiber vs Virgin fiber for Cardboard
 azmater.com
azmater.com