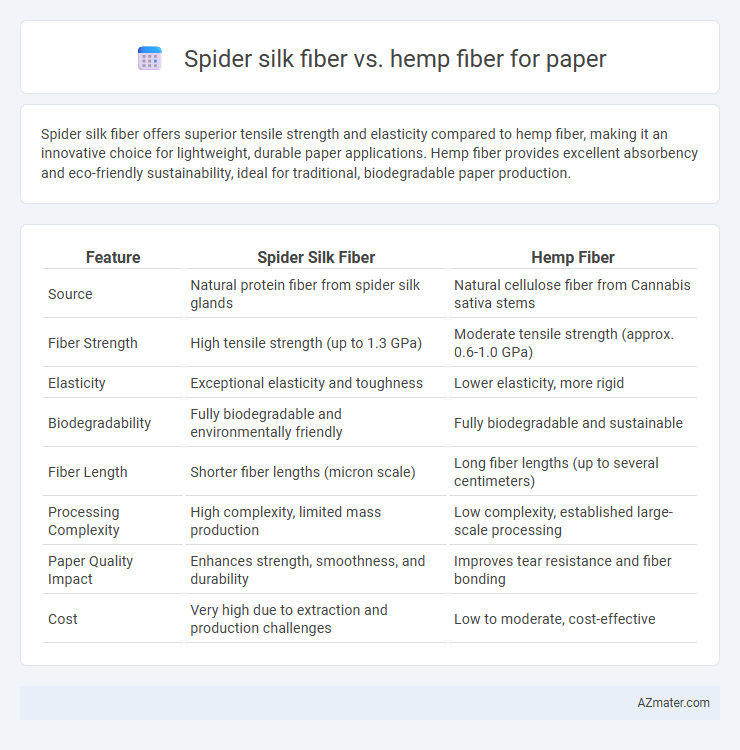
Spider silk fiber offers superior tensile strength and elasticity compared to hemp fiber, making it an innovative choice for lightweight, durable paper applications. Hemp fiber provides excellent absorbency and eco-friendly sustainability, ideal for traditional, biodegradable paper production.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Spider Silk Fiber | Hemp Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural protein fiber from spider silk glands | Natural cellulose fiber from Cannabis sativa stems |
| Fiber Strength | High tensile strength (up to 1.3 GPa) | Moderate tensile strength (approx. 0.6-1.0 GPa) |
| Elasticity | Exceptional elasticity and toughness | Lower elasticity, more rigid |
| Biodegradability | Fully biodegradable and environmentally friendly | Fully biodegradable and sustainable |
| Fiber Length | Shorter fiber lengths (micron scale) | Long fiber lengths (up to several centimeters) |
| Processing Complexity | High complexity, limited mass production | Low complexity, established large-scale processing |
| Paper Quality Impact | Enhances strength, smoothness, and durability | Improves tear resistance and fiber bonding |
| Cost | Very high due to extraction and production challenges | Low to moderate, cost-effective |
Introduction to Spider Silk and Hemp Fibers
Spider silk fiber, known for its exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, offers promising applications in high-performance paper products requiring durability and flexibility. Hemp fiber, derived from the Cannabis sativa plant, is a sustainable and biodegradable material favored in paper manufacturing for its long, coarse fibers that enhance tear resistance and texture. Both fibers provide unique mechanical properties and environmental benefits, making them important alternatives in the evolution of eco-friendly paper production.
Historical Uses of Spider Silk and Hemp in Papermaking
Spider silk fiber and hemp fiber have distinct historical footprints in papermaking, where spider silk was rarely used due to its scarcity and high tensile strength, primarily valued in specialized applications rather than mass production. Hemp fiber boasts a rich history dating back to ancient China, where it was widely utilized for papermaking due to its long fibers, durability, and resistance to decomposition, making it one of the earliest and most sustainable raw materials in paper manufacturing. The robustness of hemp fibers allowed for the creation of strong, high-quality paper, contrasting with spider silk's niche presence in the industry.
Extraction and Processing Methods
Spider silk fiber extraction involves meticulous harvesting from silkworms or spiders using forced silking or silk gland dissection, requiring delicate handling to preserve fiber integrity. Hemp fiber extraction relies on mechanical processes like retting, decortication, and scutching to separate bast fibers, offering scalability and sustainability for paper production. Processing spider silk for paper demands enzymatic treatments to enhance fiber bonding, whereas hemp fibers undergo chemical pulping and bleaching to achieve desired paper quality.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Spider silk fiber exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to hemp fiber for paper production, with tensile strength reaching up to 1.1 GPa, significantly higher than hemp's typical range of 400-800 MPa. The remarkable toughness and elasticity of spider silk enhance paper durability and resistance to tearing, outperforming hemp fibers that offer moderate strength but higher stiffness. This makes spider silk an innovative choice for specialized paper applications requiring exceptional mechanical performance.
Durability and Longevity in Paper Products
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength and flexibility, making paper products more resistant to tearing and wear over time compared to hemp fiber. Hemp fiber, while naturally durable and eco-friendly, tends to have a coarser texture that may result in slightly less longevity under heavy use or environmental stress. Incorporating spider silk into paper enhances durability and prolongs product lifespan, especially for high-strength or archival-quality paper applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional biodegradability and requires minimal water and pesticide input during production, resulting in a significantly lower environmental footprint compared to conventional fibers. Hemp fiber stands out for its fast growth rate, high carbon sequestration, and ability to thrive without synthetic fertilizers, making it one of the most sustainable fibers for paper manufacturing. Both fibers contribute to reducing deforestation and chemical pollution, but spider silk's renewable source and biodegradability may offer superior environmental benefits when produced at scale.
Cost and Scalability of Fiber Production
Spider silk fiber remains prohibitively expensive due to complex harvesting and synthetic production challenges, limiting its scalability for large-scale paper manufacturing. Hemp fiber, by contrast, is cost-effective and produced at industrial scales with established agricultural practices, offering a sustainable and affordable raw material for paper production. The scalability of hemp fiber production significantly outpaces spider silk, making it the preferred choice for cost-sensitive and volume-driven paper industries.
Printability and Surface Texture Differences
Spider silk fiber exhibits superior printability on paper due to its fine, uniform microfibril structure, which creates a smoother surface texture that enhances ink adhesion and precision. Hemp fiber, characterized by its coarser, irregular surface texture, often results in less consistent ink absorption and lower print definition. The nanoscale diameter of spider silk fibers contributes to a high surface area-to-volume ratio, enabling finer print resolution compared to the comparatively larger, lignin-rich hemp fibers.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Considerations
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional biodegradability due to its protein-based composition, breaking down naturally without leaving toxic residues, making it an eco-friendly choice for paper products. Hemp fiber, derived from cellulose, also demonstrates high biodegradability but tends to decompose more slowly compared to spider silk fibers, impacting end-of-life recycling and composting rates. Both fibers support sustainable paper production, but spider silk offers superior rapid degradation benefits for minimizing environmental impact in waste management systems.
Future Prospects and Innovations in Fiber-Based Paper
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and biodegradability, making it a promising material for high-performance, eco-friendly paper products. Innovations in recombinant spider silk production could enable large-scale, cost-effective fiber synthesis, revolutionizing the paper industry with sustainable alternatives to traditional plant-based fibers. Hemp fiber's fast growth and high cellulose content continue to support its role in enhancing paper durability and recyclability, while blending it with spider silk fibers may yield novel hybrid papers with superior mechanical properties and environmental benefits.
Infographic: Spider silk fiber vs Hemp fiber for Paper
 azmater.com
azmater.com