Polylactic acid (PLA) offers biodegradable and moisture-wicking properties ideal for eco-friendly knitwear, while wool provides natural insulation and superior durability. PLA excels in sustainability and lightweight comfort, whereas wool delivers warmth and breathability for cold-weather garments.
Table of Comparison
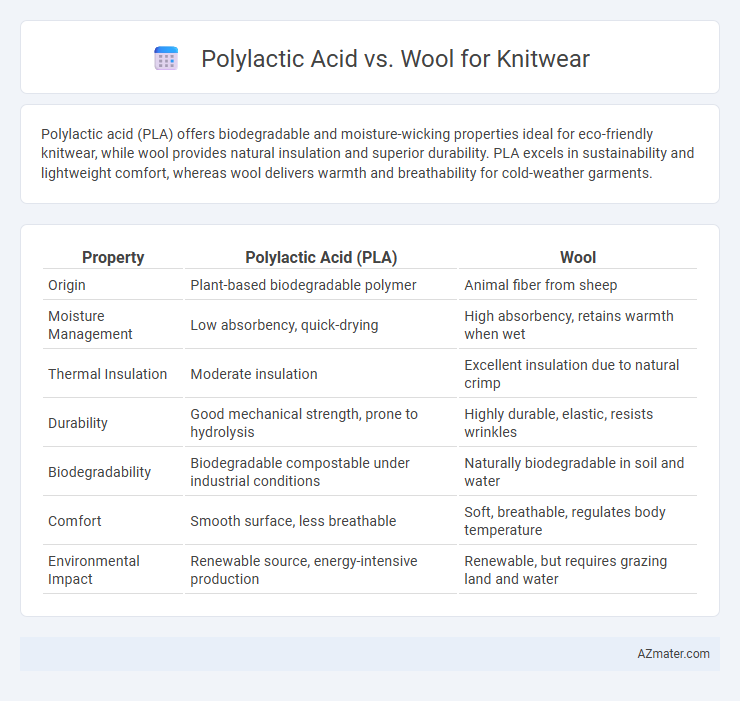
| Property | Polylactic Acid (PLA) | Wool |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Plant-based biodegradable polymer | Animal fiber from sheep |
| Moisture Management | Low absorbency, quick-drying | High absorbency, retains warmth when wet |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate insulation | Excellent insulation due to natural crimp |
| Durability | Good mechanical strength, prone to hydrolysis | Highly durable, elastic, resists wrinkles |
| Biodegradability | Biodegradable compostable under industrial conditions | Naturally biodegradable in soil and water |
| Comfort | Smooth surface, less breathable | Soft, breathable, regulates body temperature |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable source, energy-intensive production | Renewable, but requires grazing land and water |
Introduction to Sustainable Knitwear Materials
Polylactic acid (PLA) and wool represent two key sustainable options for knitwear materials, each offering distinct environmental benefits. PLA, derived from renewable plant sources such as corn starch, features biodegradability and a lower carbon footprint compared to conventional synthetic fibers. Wool, sourced from sheep, provides natural insulation, biodegradability, and a renewable fiber that supports sustainable livestock practices when managed responsibly.
What is Polylactic Acid (PLA) Yarn?
Polylactic Acid (PLA) yarn is a biodegradable fiber derived from renewable plant sources such as corn starch or sugarcane, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional synthetic fibers. PLA yarn is lightweight, moisture-wicking, and exhibits good breathability, making it suitable for knitwear that demands comfort and sustainability. Compared to wool, PLA provides enhanced resistance to shrinkage and mold, while also being an ethical choice free from animal products.
Wool: The Time-Tested Natural Fiber
Wool, a time-tested natural fiber, offers superior moisture-wicking and insulating properties that make it ideal for knitwear, maintaining warmth even when damp. Its durability, biodegradability, and natural elasticity provide long-lasting comfort and shape retention. Unlike polylactic acid, wool is renewable and biodegradable, aligning with sustainable fashion while delivering unmatched thermal regulation and breathability.
Sourcing and Production Processes
Polylactic acid (PLA) is derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane through fermentation and polymerization, providing a biodegradable and sustainable alternative to traditional fabrics. Wool, sourced from sheep, requires extensive animal husbandry, shearing, cleaning, and spinning processes that impact environmental factors such as land use and water consumption. The production of PLA involves industrial-scale bioreactors and extrusion methods, while wool processing relies on mechanical and manual techniques, influencing the sustainability and ecological footprint of knitwear.
Environmental Impact: PLA vs. Wool
Polylactic acid (PLA), derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers a biodegradable alternative to traditional synthetic fibers, reducing reliance on petroleum-based materials in knitwear. Wool, a natural fiber obtained from sheep, is renewable and biodegradable but involves higher land and water use, as well as methane emissions contributing to greenhouse gases. PLA's lower carbon footprint and reduced water consumption provide environmental advantages, while wool's biodegradability and soil-enhancing manure byproduct support sustainable agriculture.
Comfort and Wearability Comparison
Polylactic acid (PLA) fibers offer excellent moisture-wicking properties and lightweight breathability, making them highly comfortable for active wear. Wool, especially merino, provides superior insulation, temperature regulation, and natural odor resistance, enhancing all-day wearability in diverse climates. While PLA is more sustainable and wrinkle-resistant, wool excels in softness and elasticity, ensuring greater comfort during prolonged use.
Durability and Longevity in Knitwear
Polylactic acid (PLA) fibers offer moderate durability in knitwear but tend to degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure and heat compared to wool, which is known for exceptional resilience and long-lasting wear. Wool's natural crimp contributes to excellent elasticity and resistance to abrasion, making it highly suitable for knitwear that endures frequent use and stretching. While PLA provides eco-friendly benefits through biodegradability, wool outperforms in longevity, maintaining structural integrity and softness over extended periods.
Performance in Various Climate Conditions
Polylactic acid (PLA) offers excellent moisture-wicking and quick-drying properties, making it suitable for warm and humid climates, while wool excels in insulation and temperature regulation, providing superior warmth in cold and damp conditions. Wool's natural crimp structure enhances breathability and odor resistance, which benefits prolonged wear in variable climates, whereas PLA's biodegradability and lightweight nature support comfort in activewear under moderate to hot weather. Each fiber presents distinct performance advantages, with wool favored for cold-weather knitwear and PLA preferred for eco-friendly, moisture-managing apparel in milder climates.
Cost Analysis: Affordability and Value
Polylactic acid (PLA) knitwear generally offers a more affordable option compared to wool, benefiting from lower raw material costs and synthetic production efficiencies. Wool, while pricier due to its natural fiber sourcing and labor-intensive processing, provides enhanced durability and thermal insulation, often justifying its higher price for premium garments. Evaluating cost-effectiveness requires balancing PLA's budget-friendly appeal against wool's superior longevity and comfort in knitwear applications.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Eco-Friendly Knitwear
Polylactic acid (PLA), derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers a biodegradable and sustainable alternative to traditional fibers, making it ideal for eco-friendly knitwear. Wool, a natural and biodegradable fiber, provides excellent warmth and breathability but involves animal farming practices that can impact environmental sustainability. Selecting the right fiber depends on balancing biodegradability, renewable sourcing, and the environmental footprint of production processes in eco-conscious knitwear design.
Infographic: Polylactic acid vs Wool for Knitwear
 azmater.com
azmater.com