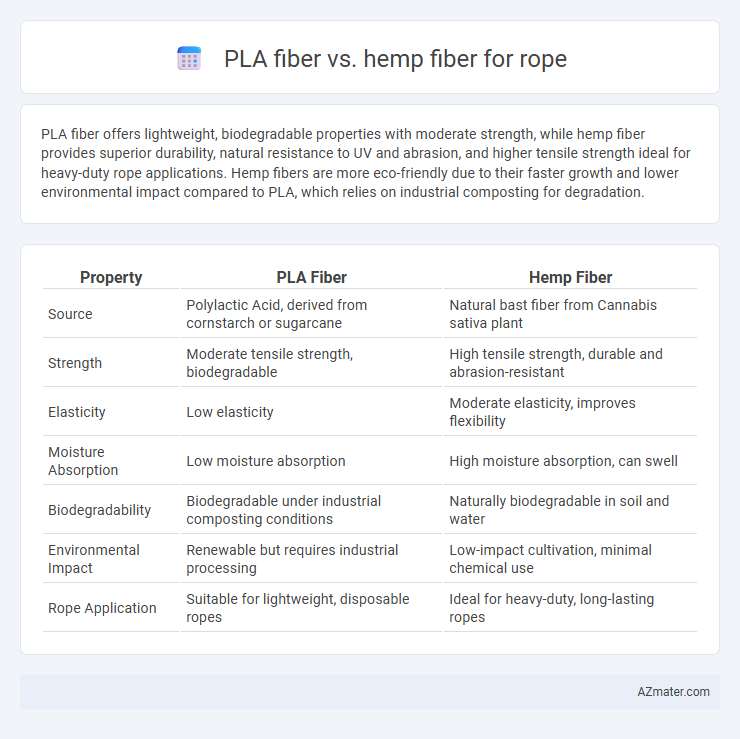
PLA fiber offers lightweight, biodegradable properties with moderate strength, while hemp fiber provides superior durability, natural resistance to UV and abrasion, and higher tensile strength ideal for heavy-duty rope applications. Hemp fibers are more eco-friendly due to their faster growth and lower environmental impact compared to PLA, which relies on industrial composting for degradation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | PLA Fiber | Hemp Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Polylactic Acid, derived from cornstarch or sugarcane | Natural bast fiber from Cannabis sativa plant |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength, biodegradable | High tensile strength, durable and abrasion-resistant |
| Elasticity | Low elasticity | Moderate elasticity, improves flexibility |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorption | High moisture absorption, can swell |
| Biodegradability | Biodegradable under industrial composting conditions | Naturally biodegradable in soil and water |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable but requires industrial processing | Low-impact cultivation, minimal chemical use |
| Rope Application | Suitable for lightweight, disposable ropes | Ideal for heavy-duty, long-lasting ropes |
Introduction to PLA Fiber and Hemp Fiber
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources like cornstarch, offers biodegradability and lightweight strength, making it an eco-friendly alternative in rope manufacturing. Hemp fiber, known for its natural durability and resistance to UV light and abrasion, has been traditionally used in ropes for its high tensile strength and sustainability. Comparing PLA fiber and hemp fiber reveals distinct advantages in biodegradability and mechanical properties, influencing their applications in eco-conscious rope production.
Overview of Rope Applications
PLA fiber offers lightweight, biodegradable properties ideal for short-term rope applications in packaging and agriculture. Hemp fiber boasts exceptional tensile strength, durability, and resistance to UV and moisture, making it suitable for heavy-duty maritime, construction, and outdoor ropes. Hemp's natural rot resistance outperforms PLA in long-lasting, high-stress environments.
Material Source and Sustainability
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane, offers biodegradability and compostability, reducing environmental impact compared to petroleum-based fibers. Hemp fiber, sourced from the fast-growing Cannabis sativa plant, is highly sustainable due to its low water and pesticide requirements and carbon sequestration ability. Both fibers promote eco-friendly rope production, but hemp's natural durability and minimal agricultural inputs often make it a superior sustainable choice.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
PLA fiber exhibits moderate tensile strength, typically ranging from 300 to 600 MPa, while hemp fiber offers higher mechanical strength, often between 550 and 900 MPa, making hemp more durable for heavy-duty rope applications. Hemp fibers demonstrate superior abrasion resistance and elongation at break compared to PLA, resulting in enhanced toughness and longevity in rope performance. The biodegradability and environmental benefits of both fibers complement their mechanical properties, but for strength-critical uses, hemp fiber remains the preferred choice.
Durability and Weather Resistance
PLA fiber offers moderate durability and limited weather resistance, making it less ideal for prolonged outdoor rope use as it can degrade under UV exposure and moisture. Hemp fiber exhibits exceptional durability and superior weather resistance, maintaining strength and flexibility even in harsh environmental conditions. This makes hemp fiber the preferred choice for ropes requiring long-lasting performance in outdoor and marine applications.
Biodegradability and Environmental Impact
PLA fiber, derived from renewable corn starch, offers biodegradability under industrial composting conditions but decomposes slowly in natural environments, reducing its overall eco-friendliness for rope applications. Hemp fiber, a natural bast fiber from Cannabis plants, exhibits excellent biodegradability in soil and water, breaking down more rapidly and enriching the environment with minimal chemical inputs during cultivation. The environmental impact of hemp fiber ropes is lower, as hemp cultivation demands less water and pesticides compared to the industrial processing required for PLA fiber production.
Cost and Production Efficiency
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, generally incurs higher production costs compared to hemp fiber due to its synthetic processing requirements and reliance on industrial-scale bioplastic manufacturing. Hemp fiber, cultivated through traditional agricultural methods, offers lower material costs and greater production efficiency, benefiting from rapid growth cycles and minimal chemical inputs. Cost analysis reveals hemp rope production is more economical, with scalability in fiber extraction techniques enhancing overall manufacturing efficiency compared to the more energy-intensive PLA fiber processing.
Flexibility and Knot Retention
PLA fiber offers moderate flexibility and maintains a reasonable knot retention, making it suitable for lightweight rope applications. Hemp fiber exhibits superior flexibility and exceptional knot retention due to its natural coarseness and fibrous texture. The high tensile strength and durability of hemp make it preferable for ropes requiring strong, reliable knots and enhanced pliability.
Safety and Allergen Concerns
PLA fiber for rope offers hypoallergenic properties and reduced skin irritation risks due to its synthetic origin and biocompatibility. Hemp fiber, while naturally durable and antimicrobial, may cause allergic reactions in sensitive individuals because of its plant-based proteins and dust particles. Selecting PLA rope minimizes exposure to allergens and ensures safer handling in environments requiring strict health standards.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Fiber for Rope
Choosing the right fiber for rope depends on durability, environmental impact, and application needs. Hemp fiber offers superior strength, biodegradability, and natural resistance to UV and mold, making it ideal for outdoor and heavy-duty uses. PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources, provides a biodegradable alternative but lacks the same durability and UV resistance, limiting its suitability for high-stress rope applications.
Infographic: PLA fiber vs Hemp fiber for Rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com