Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, making it highly effective for bulletproof vests by absorbing and dissipating impact energy. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, offers superior abrasion resistance and stiffness, providing durable multi-hit protection in ballistic applications.
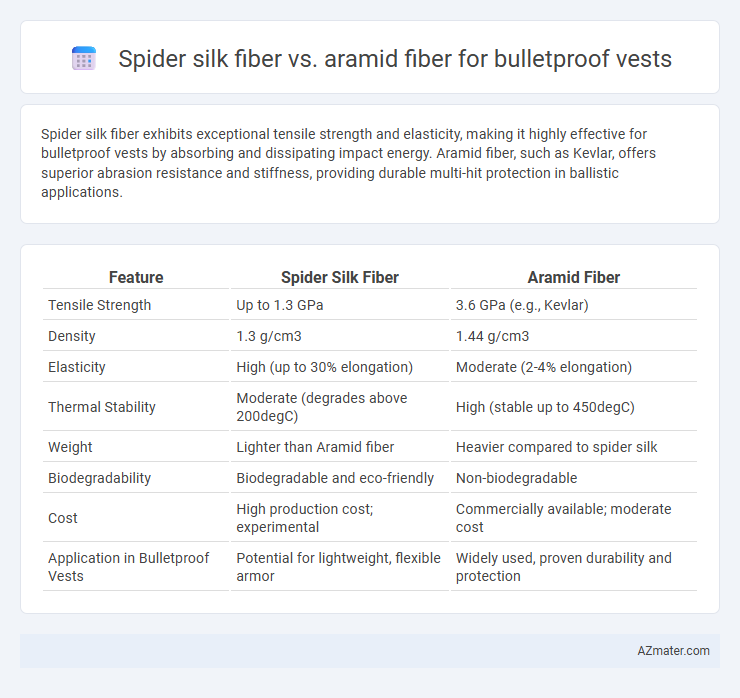
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Spider Silk Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Up to 1.3 GPa | 3.6 GPa (e.g., Kevlar) |
| Density | 1.3 g/cm3 | 1.44 g/cm3 |
| Elasticity | High (up to 30% elongation) | Moderate (2-4% elongation) |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate (degrades above 200degC) | High (stable up to 450degC) |
| Weight | Lighter than Aramid fiber | Heavier compared to spider silk |
| Biodegradability | Biodegradable and eco-friendly | Non-biodegradable |
| Cost | High production cost; experimental | Commercially available; moderate cost |
| Application in Bulletproof Vests | Potential for lightweight, flexible armor | Widely used, proven durability and protection |
Introduction to Bulletproof Vest Materials
Bulletproof vest materials such as spider silk fiber and aramid fiber offer distinct advantages in ballistic protection and flexibility. Spider silk fibers exhibit exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, providing lightweight yet durable armor capable of absorbing impact energy efficiently. Aramid fibers, including Kevlar(r), are renowned for their high resistance to heat and abrasions, making them a standard in bulletproof vests due to their proven performance in stopping various calibers of bullets.
Overview of Spider Silk Fiber
Spider silk fiber demonstrates exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, outperforming many synthetic fibers in energy absorption. Its biocompatibility and lightweight nature offer advantages for bulletproof vests by enhancing wearer comfort and mobility. Research highlights spider silk's potential to revolutionize personal armor, combining flexibility with high durability for improved ballistic resistance.
Properties of Aramid Fiber (Kevlar)
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, are renowned for their exceptional tensile strength, high thermal stability, and resistance to chemical degradation, making them ideal for bulletproof vests. Kevlar exhibits a tensile strength of up to 3,620 MPa and a density of approximately 1.44 g/cm3, providing a high strength-to-weight ratio that enhances both protection and wearability. Its molecular structure, characterized by rigid aromatic polyamide chains, contributes to outstanding impact resistance and energy absorption, critical properties for ballistic performance.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Spider silk fiber exhibits remarkable tensile strength exceeding 1.3 GPa and exceptional elasticity, allowing it to absorb significant impact energy, which enhances its potential for bulletproof vest applications. Aramid fibers such as Kevlar offer tensile strengths around 3.6 GPa and excellent resistance to abrasion and chemical degradation, providing proven durability in extreme conditions. While aramid fibers currently dominate commercial bulletproof vests due to their established performance and durability, spider silk's superior toughness and lightweight nature position it as a promising alternative for next-generation ballistic protection.
Flexibility and Comfort for Wearers
Spider silk fiber surpasses aramid fiber in flexibility, offering superior elasticity that allows bulletproof vests to conform more naturally to the wearer's body. Its lightweight nature significantly enhances comfort by reducing bulk and heat retention compared to the stiffer, denser aramid fibers commonly used in traditional armor. Enhanced breathability and reduced rigidity in spider silk composites contribute to extended wearability and improved mobility for users in dynamic environments.
Weight and Thickness Differences
Spider silk fiber exhibits significantly lower density compared to aramid fiber, resulting in lighter bulletproof vests that enhance comfort and mobility. Its fibers demonstrate superior tensile strength-to-weight ratios, allowing for thinner protective layers without compromising ballistic resistance. In contrast, aramid fibers like Kevlar are thicker and heavier, contributing to bulkier vests that may reduce wearer agility during extended use.
Protection Performance: Ballistic Resistance
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional ballistic resistance due to its high tensile strength and remarkable energy absorption capabilities, making it a promising material for bulletproof vests. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, have long been the industry standard for protective gear because of their proven ability to dissipate impact energy and withstand multiple ballistic strikes. Comparative studies indicate that spider silk fibers can potentially offer superior protection performance by combining lightweight flexibility with enhanced ballistic resistance compared to traditional aramid fibers.
Environmental Impact and Biodegradability
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional environmental benefits for bulletproof vests, being fully biodegradable and produced through sustainable biomimetic processes with minimal energy input. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, have a significantly higher environmental footprint due to energy-intensive petrochemical production and slow degradation, contributing to persistent microplastic waste. The biodegradability of spider silk reduces long-term ecological impact and supports circular economy principles, whereas aramid fibers pose disposal and recycling challenges.
Cost and Manufacturing Challenges
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and flexibility but remains prohibitively expensive due to complex bioengineering and low yield from natural sources. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, are more cost-effective and benefit from established industrial-scale synthetic manufacturing processes that yield consistent quality and availability. The high production cost and scalability issues of spider silk limit its current use in bulletproof vests, whereas aramid fibers continue to dominate the market due to efficient mass production and lower overall expenses.
Future Prospects in Ballistic Material Innovation
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, making it a promising candidate for next-generation bulletproof vests with enhanced flexibility and lightweight properties. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, currently dominate ballistic protection due to their proven durability and resistance to high-impact forces, but ongoing research explores hybrid composites incorporating spider silk proteins to improve energy absorption. Future advancements in genetic engineering and material synthesis could lead to scalable production of spider silk-based ballistic materials, potentially surpassing traditional aramid fibers in both performance and wearer comfort.
Infographic: Spider silk fiber vs Aramid fiber for Bulletproof vest
 azmater.com
azmater.com