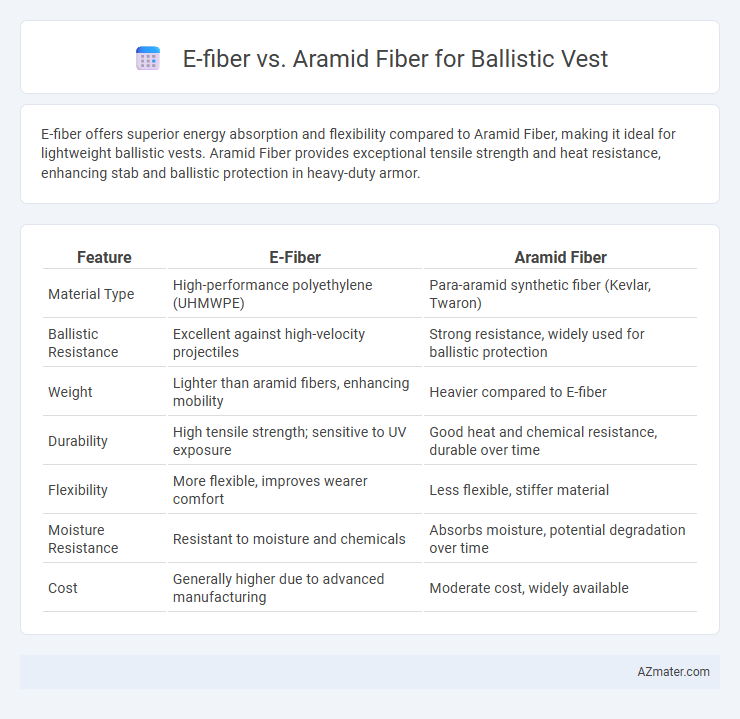
E-fiber offers superior energy absorption and flexibility compared to Aramid Fiber, making it ideal for lightweight ballistic vests. Aramid Fiber provides exceptional tensile strength and heat resistance, enhancing stab and ballistic protection in heavy-duty armor.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | E-Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-performance polyethylene (UHMWPE) | Para-aramid synthetic fiber (Kevlar, Twaron) |
| Ballistic Resistance | Excellent against high-velocity projectiles | Strong resistance, widely used for ballistic protection |
| Weight | Lighter than aramid fibers, enhancing mobility | Heavier compared to E-fiber |
| Durability | High tensile strength; sensitive to UV exposure | Good heat and chemical resistance, durable over time |
| Flexibility | More flexible, improves wearer comfort | Less flexible, stiffer material |
| Moisture Resistance | Resistant to moisture and chemicals | Absorbs moisture, potential degradation over time |
| Cost | Generally higher due to advanced manufacturing | Moderate cost, widely available |
Introduction to Ballistic Vests and Material Innovation
Ballistic vests utilize advanced materials for enhanced protection, with E-fiber and aramid fiber being prominent options in material innovation. Aramid fibers like Kevlar provide high tensile strength and excellent energy absorption, making them a trusted choice for bullet resistance. E-fibers, composed of specialized polyethylene, offer ultra-high molecular weight properties that deliver lightweight durability and improved impact resistance in modern ballistic armor.
Overview of E-Fiber and Aramid Fiber Technologies
E-fiber, a synthetic fiber known for its high tensile strength and elasticity, is engineered using advanced polymerization processes that enhance energy absorption in ballistic applications. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar and Twaron, is a class of heat-resistant and strong synthetic fibers with excellent ballistic resistance due to its para-aramid molecular structure, providing superior impact resistance and lightweight durability. Both E-fiber and aramid fiber technologies are integral in modern ballistic vests, balancing protection, flexibility, and weight optimization for user safety and comfort.
Mechanical Properties: E-Fiber vs Aramid Fiber
E-fiber exhibits high tensile strength and excellent impact resistance, making it suitable for ballistic protection with superior elasticity compared to aramid fibers. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide exceptional tensile strength, superior thermal stability, and high energy absorption with better resistance to abrasion and chemicals than E-fiber. While E-fiber offers enhanced flexibility, aramid fibers deliver a balanced combination of strength, durability, and heat resistance, crucial for multi-threat ballistic vests.
Weight and Comfort: End-User Considerations
E-fiber ballistic vests offer significantly lighter weight compared to aramid fiber variants, enhancing wearer mobility and reducing fatigue during extended use. Aramid fibers, while heavier, provide superior impact resistance but may compromise comfort due to increased bulk and stiffness. End-users often prefer E-fiber for its balance of lightweight design and comfort, especially in scenarios requiring prolonged wear and agility.
Ballistic Resistance and Stopping Power Comparison
E-fiber and aramid fiber are both prominent materials used in ballistic vests, but aramid fiber exhibits superior ballistic resistance due to its high tensile strength and energy absorption capabilities. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide enhanced stopping power against high-velocity projectiles by dissipating impact energy more efficiently than E-fibers, which are less dense and have lower abrasion resistance. The superior performance of aramid fiber makes it the preferred choice for body armor requiring maximum protection and durability in high-threat environments.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
E-fiber exhibits high tensile strength and elasticity, crucial for absorbing ballistic impact while maintaining structural integrity. Aramid fiber, known for exceptional resistance to heat, chemicals, and UV exposure, offers superior durability in harsh environmental conditions. Comparing the two, aramid fiber generally provides enhanced environmental resistance, making it more reliable for long-term use in ballistic vests exposed to extreme climates.
Flexibility and Design Versatility
E-fiber offers enhanced flexibility and lightweight properties, making it ideal for ballistic vests that require greater mobility and comfort without compromising protection. Aramid fiber, known for its superior tensile strength and durability, provides excellent ballistic resistance but tends to be stiffer, limiting design versatility in form-fitting or flexible armor. The choice between E-fiber and aramid fiber influences the balance between ergonomic comfort and optimal protection in various vest configurations.
Cost Analysis: E-Fiber vs Aramid Fiber
E-fiber offers a cost-effective alternative to aramid fiber for ballistic vests, with production costs approximately 30-40% lower due to cheaper raw materials and simpler manufacturing processes. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, demand higher market prices driven by more complex synthesis and superior tensile strength, pushing the vest cost significantly higher. Budget-conscious law enforcement agencies and military units often prefer E-fiber vests when balancing protective performance with affordable pricing.
Industry Adoption and Regulatory Standards
E-fiber and aramid fiber are key materials in ballistic vest manufacturing, with aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, widely adopted due to its proven high tensile strength and extensive regulatory certifications from agencies like NIJ. E-fiber, a newer technology, offers comparable ballistic resistance with enhanced lightweight properties but faces slower industry adoption as it undergoes rigorous testing to meet established standards. Regulatory bodies prioritize materials that consistently achieve NIJ Level III and IV ratings, where aramid fibers currently dominate market presence.
Future Trends in Ballistic Vest Materials
E-fiber and aramid fiber remain pivotal in the evolution of ballistic vest materials due to their high tensile strength and lightweight properties. Emerging trends emphasize hybrid composites combining E-fiber's flexible durability with aramid fiber's exceptional impact resistance to enhance multi-threat protection. Advances in nanotechnology and material engineering are driving the development of next-generation ballistic fabrics with improved energy dispersion and wearer comfort.
Infographic: E-fiber vs Aramid Fiber for Ballistic Vest
 azmater.com
azmater.com