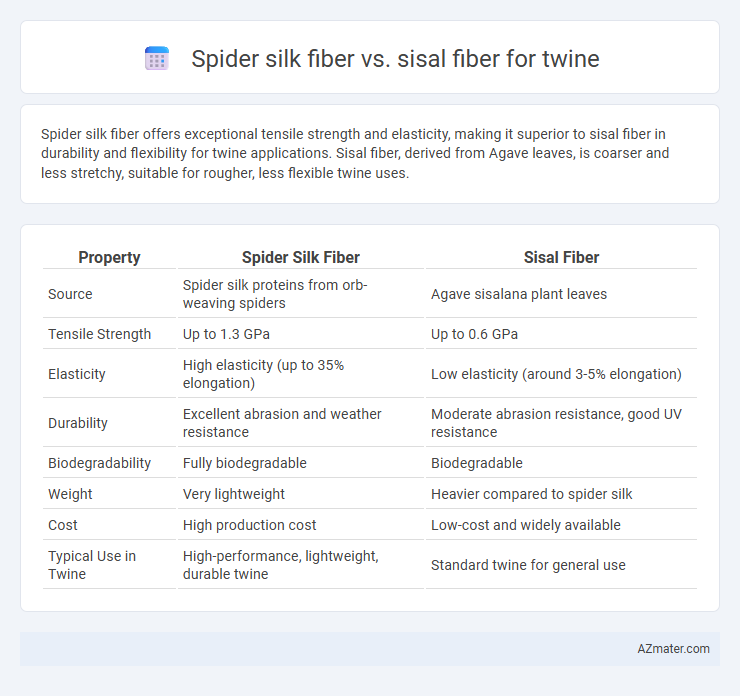
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, making it superior to sisal fiber in durability and flexibility for twine applications. Sisal fiber, derived from Agave leaves, is coarser and less stretchy, suitable for rougher, less flexible twine uses.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Spider Silk Fiber | Sisal Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Spider silk proteins from orb-weaving spiders | Agave sisalana plant leaves |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 1.3 GPa | Up to 0.6 GPa |
| Elasticity | High elasticity (up to 35% elongation) | Low elasticity (around 3-5% elongation) |
| Durability | Excellent abrasion and weather resistance | Moderate abrasion resistance, good UV resistance |
| Biodegradability | Fully biodegradable | Biodegradable |
| Weight | Very lightweight | Heavier compared to spider silk |
| Cost | High production cost | Low-cost and widely available |
| Typical Use in Twine | High-performance, lightweight, durable twine | Standard twine for general use |
Introduction to Twine Materials
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength and flexibility, making it a superior choice for high-performance twine applications requiring durability and lightweight properties. Sisal fiber, derived from Agave leaves, offers natural coarseness, biodegradability, and affordability, suitable for traditional twine uses where environmental sustainability and cost-effectiveness are prioritized. The selection between spider silk and sisal fibers depends on the balance of mechanical performance and ecological impact desired in twine material applications.
Overview of Spider Silk Fiber
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, making it significantly stronger and more durable than sisal fiber for twine applications. Its natural protein-based structure provides superior resistance to environmental factors such as moisture and UV exposure, unlike the coarser, less flexible cellulose-based sisal fiber. The biodegradable and lightweight properties of spider silk also enhance its sustainability and performance in high-stress, lightweight twine uses.
Overview of Sisal Fiber
Sisal fiber, derived from the leaves of the Agave sisalana plant, is a natural, durable, and coarse fiber commonly used in twine production due to its high tensile strength and resistance to moisture and biodegradation. Its eco-friendly nature and relative affordability make it a popular choice for agricultural and industrial twine applications compared to the more expensive and less readily available spider silk fiber, which offers superior elasticity and strength but at a significantly higher cost. Sisal's stiffness and coarse texture provide excellent grip and knot stability, making it a practical option for heavy-duty binding and packaging tasks.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength reaching up to 1.3 GPa, surpassing sisal fiber's typical tensile strength range of 300-700 MPa. The superior toughness and elasticity of spider silk provide enhanced durability and resistance to breakage under dynamic stress conditions, making it a more resilient option for twine applications. Sisal fiber, while more cost-effective and abundantly available, lacks the mechanical robustness and extensibility needed for high-performance twine products.
Durability and Longevity
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional durability and longevity compared to sisal fiber, thanks to its remarkable tensile strength and elasticity. Its resistance to environmental factors like moisture and UV radiation ensures that twine made from spider silk lasts significantly longer under harsh conditions. In contrast, sisal fiber tends to degrade faster due to its susceptibility to wear, rot, and brittleness, making it less ideal for long-term twine applications.
Flexibility and Elasticity
Spider silk fiber exhibits superior flexibility and elasticity compared to sisal fiber, making it ideal for twine applications requiring durability and stretch. Its natural protein structure allows spider silk to stretch up to five times its original length without breaking, outperforming the rigid and brittle nature of sisal fiber derived from Agave sisalana leaves. Sisal fiber, while strong and abrasion-resistant, lacks the extensibility of spider silk, resulting in twine that is less adaptable to dynamic loads and bending stresses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Spider silk fiber offers remarkable sustainability due to its biodegradable, renewable nature and minimal ecological footprint during production, as it requires no pesticides or intensive water use compared to sisal fiber. Sisal fiber, derived from the Agave plant, is renewable and biodegradable but often involves significant land, water, and chemical inputs that can contribute to habitat disruption and pollution. The superior tensile strength and biodegradability of spider silk fiber make it a more environmentally friendly choice for twine applications, promoting sustainable material cycles and reduced ecological impact.
Cost and Production Scalability
Spider silk fiber offers superior tensile strength and elasticity compared to sisal fiber, making it ideal for high-performance twine; however, its production remains costly and limited due to complex extraction and synthetic replication methods. Sisal fiber, derived from the agave plant, provides a cost-effective and widely produced natural alternative, with established agricultural and processing infrastructure supporting scalable twine manufacturing. While sisal's affordability and scalability meet large-scale demand, advancements in bioengineering aim to reduce spider silk production costs, potentially reshaping future market dynamics.
Applications in Twine Manufacturing
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, making it ideal for high-performance twine used in specialized applications such as medical sutures and biodegradable fishing lines. Sisal fiber, derived from Agave leaves, provides robust durability and resistance to moisture, commonly employed in industrial twines for agricultural baling and packaging. Combining spider silk's lightweight flexibility with sisal's coarse texture enhances twine manufacturing by optimizing strength-to-weight ratio and environmental sustainability.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional tensile strength, elasticity, and biodegradability, positioning it as a revolutionary material for future twine applications. Innovations in bioengineering and synthetic production techniques are rapidly increasing spider silk's scalability and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional sisal fiber, which is abundant but less durable and elastic. Emerging hybrid composites combining spider silk's mechanical properties with sisal's natural availability are expected to drive sustainable twine solutions in agriculture, packaging, and wearable technology.
Infographic: Spider silk fiber vs Sisal fiber for Twine
 azmater.com
azmater.com