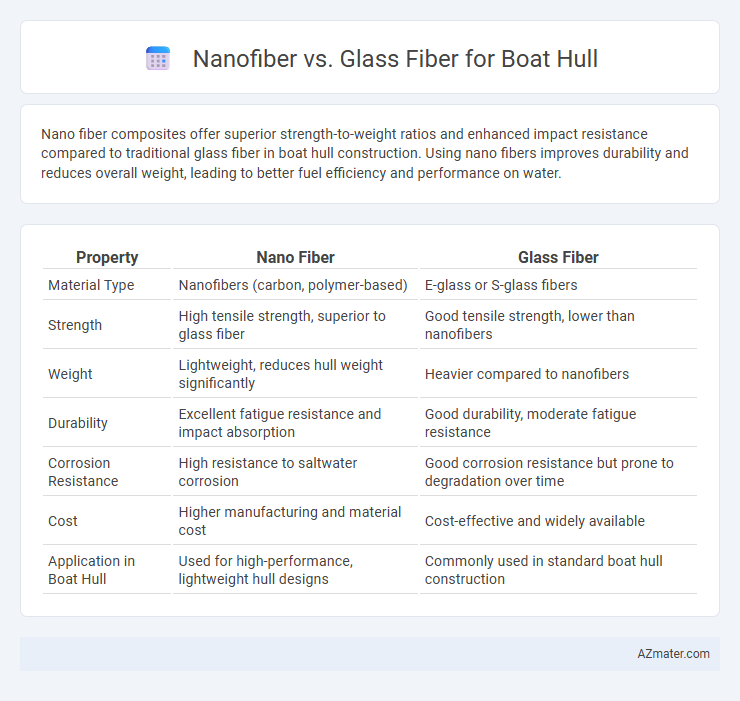
Nano fiber composites offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced impact resistance compared to traditional glass fiber in boat hull construction. Using nano fibers improves durability and reduces overall weight, leading to better fuel efficiency and performance on water.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nano Fiber | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Nanofibers (carbon, polymer-based) | E-glass or S-glass fibers |
| Strength | High tensile strength, superior to glass fiber | Good tensile strength, lower than nanofibers |
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces hull weight significantly | Heavier compared to nanofibers |
| Durability | Excellent fatigue resistance and impact absorption | Good durability, moderate fatigue resistance |
| Corrosion Resistance | High resistance to saltwater corrosion | Good corrosion resistance but prone to degradation over time |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing and material cost | Cost-effective and widely available |
| Application in Boat Hull | Used for high-performance, lightweight hull designs | Commonly used in standard boat hull construction |
Introduction to Nano Fiber and Glass Fiber Boat Hulls
Nano fiber boat hulls utilize advanced nanomaterials, offering superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced resistance to impact and corrosion compared to traditional materials. Glass fiber boat hulls, constructed from woven glass fibers embedded in resin, provide reliable durability, affordability, and ease of repair, making them a popular choice in marine construction. The integration of nano fibers improves mechanical properties and longevity, while glass fiber remains a benchmark for cost-effective marine structural integrity.
Material Composition: Nano Fiber vs Glass Fiber
Nano fibers in boat hulls consist of polymer-based materials with diameters measured in nanometers, offering superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced corrosion resistance compared to traditional glass fibers. Glass fibers are composed primarily of silica-based strands, providing good tensile strength and durability but with higher weight and less flexibility than nano fibers. The nano fiber's unique molecular structure enables improved impact resistance and reduced degradation from environmental factors, making them a cutting-edge alternative to conventional glass fiber composites in marine applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Nano fiber composites exhibit superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to traditional glass fiber reinforcements in boat hulls, significantly enhancing structural integrity. The exceptional durability of nano fibers stems from their high surface area to volume ratio, which improves fiber-matrix bonding and reduces micro-cracking under stress. While glass fiber remains cost-effective and widely used, nano fiber composites offer advanced performance by providing lightweight, damage-tolerant hulls that extend the service life and reduce maintenance frequency.
Weight and Buoyancy Differences
Nanofiber composites significantly reduce boat hull weight compared to traditional glass fiber, enhancing overall performance and fuel efficiency. The lower density of nanofibers contributes to increased buoyancy, allowing boats to sit higher on water and improve stability. Glass fiber, while durable, adds more weight, resulting in decreased buoyancy and less efficient water displacement.
Fabrication and Manufacturing Processes
Nano fiber composites offer enhanced strength-to-weight ratios and improved fatigue resistance compared to traditional glass fiber, enabling more efficient boat hull fabrication through advanced electrospinning and resin infusion techniques. Glass fiber remains widely used due to its cost-effectiveness and established manufacturing processes such as hand lay-up, spray-up, and vacuum bagging, providing durability and ease of production. The integration of nano fibers often requires precision equipment and controlled environments to achieve uniform dispersion and superior matrix bonding, which can increase manufacturing complexity and costs.
Cost Implications: Upfront and Long-term
Nano fiber composites typically have higher upfront costs compared to traditional glass fiber due to advanced manufacturing processes and raw material expenses. However, nano fiber offers enhanced durability, corrosion resistance, and lighter weight, resulting in lower maintenance costs and improved fuel efficiency over the boat's lifespan. Glass fiber remains a cost-effective option for initial investment but may incur higher long-term expenses related to repairs, weight-induced fuel consumption, and material degradation.
Performance Impact on Water
Nano fiber boat hulls exhibit superior water resistance and reduced hydrodynamic drag compared to traditional glass fiber, enhancing speed and fuel efficiency. The nano-scale structure improves impact resistance and durability against water-induced wear and osmosis. Glass fiber remains widely used due to cost-effectiveness but lacks the enhanced mechanical properties and water performance provided by nano fibers.
Maintenance and Repair Considerations
Nano fiber boat hulls offer enhanced durability and resistance to micro-cracking, reducing maintenance frequency compared to conventional glass fiber. Glass fiber hulls require regular inspections for delamination and gel coat repairs due to their susceptibility to UV degradation and water absorption. Repairing nano fiber composites demands specialized techniques and materials, whereas glass fiber repairs are more common and can often be performed with readily available resins and fabrics.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nano fiber composites typically offer a lower environmental footprint than traditional glass fiber due to their lighter weight and reduced material usage, which enhances fuel efficiency and lowers emissions during boat operation. Glass fiber production involves high energy consumption and significant CO2 emissions, whereas nano fibers can be derived from renewable sources or engineered for biodegradability, improving overall sustainability. The recyclability of nano fiber materials also exceeds that of glass fiber, enabling more efficient end-of-life management and reducing landfill waste from boat hull manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Boat Hull
Nano fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced impact resistance compared to traditional glass fiber, making it a cutting-edge choice for boat hull construction. Glass fiber remains a cost-effective, widely available option with proven durability and ease of repair, suitable for most recreational and commercial vessels. Selecting the right fiber depends on balancing performance requirements, budget constraints, and long-term maintenance considerations for optimal hull integrity.
Infographic: Nano fiber vs Glass fiber for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com