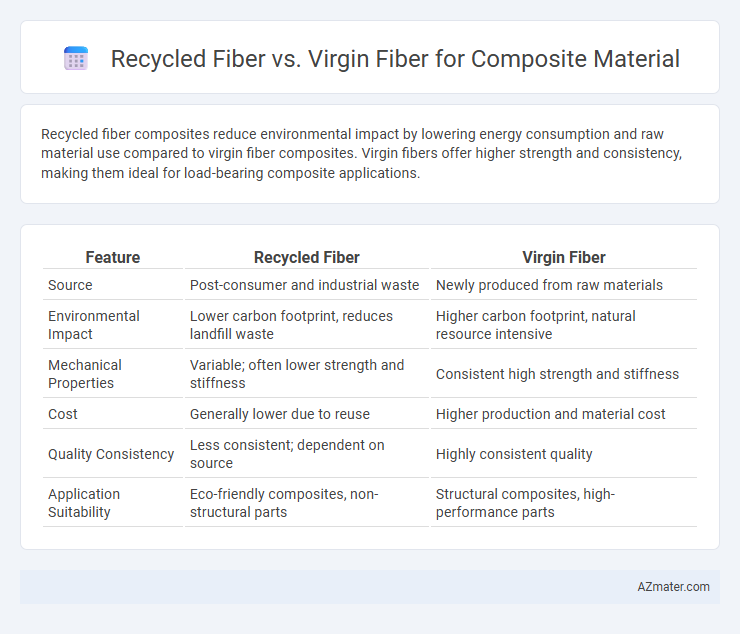
Recycled fiber composites reduce environmental impact by lowering energy consumption and raw material use compared to virgin fiber composites. Virgin fibers offer higher strength and consistency, making them ideal for load-bearing composite applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled Fiber | Virgin Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Post-consumer and industrial waste | Newly produced from raw materials |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, reduces landfill waste | Higher carbon footprint, natural resource intensive |
| Mechanical Properties | Variable; often lower strength and stiffness | Consistent high strength and stiffness |
| Cost | Generally lower due to reuse | Higher production and material cost |
| Quality Consistency | Less consistent; dependent on source | Highly consistent quality |
| Application Suitability | Eco-friendly composites, non-structural parts | Structural composites, high-performance parts |
Introduction to Composite Materials
Composite materials combine two or more constituent materials with distinct physical or chemical properties to create a material with enhanced mechanical performance. Virgin fibers, derived directly from natural or synthetic sources, offer superior strength and uniformity in composite fabrication, while recycled fibers contribute sustainability benefits by reducing waste and energy consumption. Balancing mechanical properties and environmental impact is crucial when selecting between virgin and recycled fibers for composite applications.
Defining Recycled Fiber and Virgin Fiber
Recycled fiber in composite materials refers to fibers reclaimed from post-consumer or industrial waste, processed to retain structural integrity while reducing environmental impact. Virgin fiber is derived directly from raw materials without previous usage, ensuring consistent strength, purity, and performance characteristics essential for high-quality composites. The choice between recycled and virgin fibers influences durability, cost, and sustainability metrics within composite manufacturing.
Manufacturing Processes: Recycled vs Virgin Fiber
Manufacturing processes for recycled fiber in composite materials often involve additional steps such as fiber cleaning, sorting, and reprocessing to ensure consistent quality, whereas virgin fiber manufacturing starts with raw materials that require fewer preparatory treatments. Recycled fibers can face variability in length and strength, necessitating specialized techniques like controlled extrusion or blending with virgin fibers to maintain composite integrity. Virgin fiber processes benefit from established, standardized methods that yield predictable mechanical properties and enhanced fiber-matrix adhesion in composites.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Recycled fiber composites generally exhibit lower tensile strength and stiffness compared to virgin fiber composites due to fiber degradation during processing. Virgin fibers retain higher mechanical properties such as impact resistance and fatigue durability, making them more suitable for high-performance applications. However, advancements in recycling technology are narrowing this gap by improving fiber quality and composite matrix bonding.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Recycled fiber in composite materials significantly reduces environmental impact by diverting waste from landfills and lowering carbon emissions compared to virgin fiber production, which requires intensive resource extraction and energy consumption. Life cycle assessments reveal recycled fibers offer up to 60% less energy usage and a 50% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, aligning with sustainability goals and circular economy principles. Incorporating recycled fibers enhances composite material sustainability by promoting resource efficiency and reducing ecological footprint without compromising performance.
Cost Analysis: Recycled vs Virgin Fiber
Recycled fiber significantly reduces material costs compared to virgin fiber, often lowering expenses by 20-40% due to less energy-intensive processing and use of waste materials. Virgin fibers demand higher raw material costs and energy inputs, resulting in increased production expenses but often deliver superior mechanical properties and consistency. The cost-effectiveness of recycled fiber benefits composite manufacturers aiming to balance sustainability with budget constraints, especially in large-scale applications where material savings accumulate.
Performance in Composite Applications
Recycled fiber in composite materials typically exhibits lower mechanical properties such as tensile strength and stiffness compared to virgin fiber, influencing performance in high-stress applications. Virgin fibers provide superior fiber-matrix bonding and consistent quality, resulting in enhanced durability and load-bearing capacity. Advances in recycling technology and fiber treatment are gradually narrowing the performance gap, enabling recycled fibers to meet specific composite application requirements where sustainability is prioritized.
Challenges and Limitations
Recycled fiber in composite materials faces challenges such as inconsistent fiber quality, reduced mechanical strength, and contamination risks that limit performance compared to virgin fiber. Virgin fiber offers superior tensile strength, durability, and uniformity but involves higher environmental costs and resource consumption. The recycling process also struggles with fiber degradation and difficulties in maintaining fiber length and surface properties essential for optimal composite bonding.
Recent Innovations and Advancements
Recent innovations in composite materials emphasize enhanced performance of recycled fibers through advanced surface treatments and fiber alignment technologies, significantly closing the gap with virgin fibers in strength and durability. Breakthroughs in chemical recycling methods allow recovered fibers to retain higher integrity, facilitating their integration into high-performance composites. These advancements contribute to sustainable manufacturing by reducing reliance on virgin fiber extraction, lowering environmental impact without compromising composite quality.
Future Trends in Fiber-Reinforced Composites
Future trends in fiber-reinforced composites emphasize the increasing adoption of recycled fibers over virgin fibers to enhance sustainability and reduce environmental impact. Advancements in recycling technology improve the mechanical properties and compatibility of recycled fibers, making them competitive alternatives in high-performance applications. The composite industry is shifting towards circular economy models, integrating recycled fibers to meet regulatory demands and consumer preferences for eco-friendly materials.
Infographic: Recycled fiber vs Virgin fiber for Composite material
 azmater.com
azmater.com