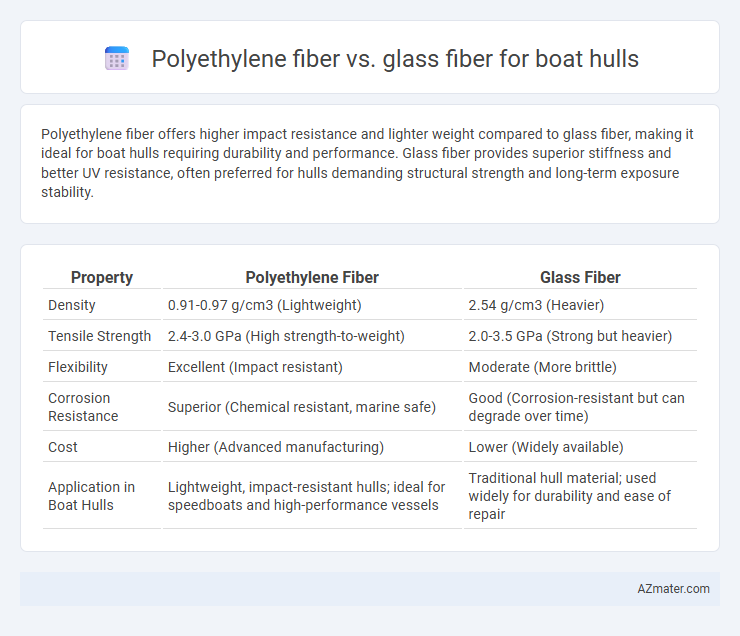
Polyethylene fiber offers higher impact resistance and lighter weight compared to glass fiber, making it ideal for boat hulls requiring durability and performance. Glass fiber provides superior stiffness and better UV resistance, often preferred for hulls demanding structural strength and long-term exposure stability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Fiber | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 0.91-0.97 g/cm3 (Lightweight) | 2.54 g/cm3 (Heavier) |
| Tensile Strength | 2.4-3.0 GPa (High strength-to-weight) | 2.0-3.5 GPa (Strong but heavier) |
| Flexibility | Excellent (Impact resistant) | Moderate (More brittle) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Superior (Chemical resistant, marine safe) | Good (Corrosion-resistant but can degrade over time) |
| Cost | Higher (Advanced manufacturing) | Lower (Widely available) |
| Application in Boat Hulls | Lightweight, impact-resistant hulls; ideal for speedboats and high-performance vessels | Traditional hull material; used widely for durability and ease of repair |
Introduction to Boat Hull Materials
Polyethylene fiber and glass fiber are two prominent materials used in boat hull construction, each offering distinct advantages in strength, flexibility, and weight. Polyethylene fiber, known for its high impact resistance and lightweight properties, provides enhanced durability and corrosion resistance in marine environments. Glass fiber, a traditional choice, delivers excellent tensile strength and stiffness, ensuring structural integrity while maintaining cost-effectiveness in boat hull fabrication.
Overview of Polyethylene Fiber
Polyethylene fiber offers exceptional impact resistance and superior flexibility compared to glass fiber, making it an ideal choice for boat hull applications requiring durability and lightweight performance. With a low density of around 0.97 g/cm3, polyethylene fiber significantly reduces overall hull weight while maintaining high tensile strength, typically between 2.4 to 3.1 GPa. Its excellent resistance to moisture, UV degradation, and chemical exposure ensures long-lasting structural integrity in harsh marine environments.
Overview of Glass Fiber
Glass fiber, known for its high tensile strength and excellent durability, is a popular choice for boat hull construction due to its resistance to corrosion and moisture. Its fiberglass composite structure offers enhanced impact resistance and structural integrity, making it suitable for various marine environments. Compared to polyethylene fiber, glass fiber provides superior rigidity and thermal stability, contributing to longer-lasting hull performance.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Polyethylene fiber offers exceptional impact resistance and high tensile strength, making it a durable choice for boat hulls exposed to rough conditions, with tensile strengths often exceeding 3 GPa. Glass fiber, commonly used in marine applications, provides good stiffness and moderate tensile strength around 2.5 GPa but is more brittle and prone to cracking under impact. The superior toughness and abrasion resistance of polyethylene fiber contribute to enhanced hull longevity, especially where flexibility and repeated stress tolerance are critical.
Weight and Buoyancy Differences
Polyethylene fiber exhibits significantly lower density compared to glass fiber, resulting in lighter boat hulls that enhance overall buoyancy and fuel efficiency. The inherent buoyant properties of polyethylene fibers improve flotation, reducing the need for additional buoyant materials in hull construction. Glass fiber, while strong, adds considerable weight to the hull, potentially decreasing buoyancy and impacting vessel performance.
Resistance to Corrosion and Water Absorption
Polyethylene fiber exhibits superior resistance to corrosion compared to glass fiber, making it ideal for marine environments where chemical exposure is prevalent. Its low water absorption rate prevents swelling and degradation, enhancing the structural integrity of boat hulls over time. Glass fiber, while strong, can absorb moisture leading to potential delamination and corrosion issues in prolonged exposure to water.
Ease of Manufacturing and Repairs
Polyethylene fiber offers superior ease of manufacturing for boat hulls due to its lightweight, flexibility, and resistance to abrasion, allowing simpler molding processes and quicker assembly. In contrast, glass fiber requires more complex handling, curing times, and specialized equipment, making fabrication more labor-intensive. Repairs on polyethylene fiber hulls are generally faster and less costly, with straightforward patching and less material compatibility issues compared to the rigid and brittle nature of glass fiber repairs.
Cost Analysis: Polyethylene vs Glass Fiber
Polyethylene fiber offers a lower initial cost compared to glass fiber, making it a budget-friendly option for boat hull construction. Glass fiber, while more expensive upfront, provides superior strength and durability, potentially reducing long-term maintenance expenses. Cost analysis must weigh polyethylene's affordability against glass fiber's lifecycle value in marine applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyethylene fiber offers superior environmental benefits for boat hulls due to its recyclability, lower energy consumption during production, and resistance to corrosion, which extends the vessel's lifespan and reduces waste. Glass fiber, while durable and widely used, relies heavily on energy-intensive manufacturing processes and is less biodegradable, leading to larger environmental footprints when disposed of. Selecting polyethylene fiber supports sustainable boat building by minimizing ecological disruption and promoting circular economy practices.
Best Applications: Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Boat Hull
Polyethylene fiber offers exceptional impact resistance and lightweight properties, making it ideal for boat hulls exposed to high-impact marine environments and requiring enhanced durability without added weight. Glass fiber provides superior stiffness and higher tensile strength, making it the preferred choice for hulls needing structural rigidity and cost-effective manufacturing in fiberglass boats. Selecting between polyethylene and glass fiber depends on prioritizing impact toughness versus structural strength for optimized boat hull performance.
Infographic: Polyethylene fiber vs Glass fiber for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com