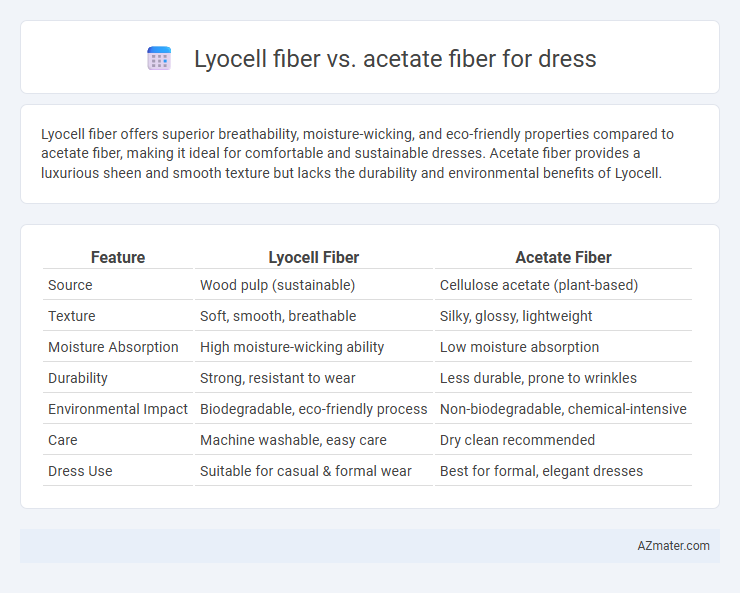
Lyocell fiber offers superior breathability, moisture-wicking, and eco-friendly properties compared to acetate fiber, making it ideal for comfortable and sustainable dresses. Acetate fiber provides a luxurious sheen and smooth texture but lacks the durability and environmental benefits of Lyocell.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lyocell Fiber | Acetate Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Wood pulp (sustainable) | Cellulose acetate (plant-based) |
| Texture | Soft, smooth, breathable | Silky, glossy, lightweight |
| Moisture Absorption | High moisture-wicking ability | Low moisture absorption |
| Durability | Strong, resistant to wear | Less durable, prone to wrinkles |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, eco-friendly process | Non-biodegradable, chemical-intensive |
| Care | Machine washable, easy care | Dry clean recommended |
| Dress Use | Suitable for casual & formal wear | Best for formal, elegant dresses |
Introduction to Lyocell and Acetate Fibers
Lyocell fiber, derived from sustainably sourced wood pulp, offers exceptional breathability, moisture-wicking properties, and a soft, smooth texture ideal for dressmaking. Acetate fiber, produced from cellulose acetate, is known for its luxurious sheen, silk-like appearance, and excellent drape, making it a popular choice for formal and evening wear. Both fibers provide unique tactile qualities and environmental considerations, where Lyocell emphasizes biodegradability and eco-friendly production while Acetate focuses on aesthetic appeal and vibrant dye retention.
Fiber Origin and Production Process
Lyocell fiber is derived from sustainably sourced wood pulp, primarily eucalyptus, through a closed-loop solvent spinning process that recycles water and chemicals, minimizing environmental impact. Acetate fiber originates from cellulose acetate produced by chemically treating wood pulp with acetic anhydride and acetic acid, involving a multistep acetylation and solvent spinning process that is more chemically intensive. The Lyocell production emphasizes eco-friendly methods and biodegradability, while acetate manufacturing relies on chemical modification, resulting in fibers with different environmental footprints and material properties.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Lyocell fiber, derived from sustainably sourced wood pulp, offers a biodegradable and eco-friendly alternative with a closed-loop production process that recycles water and solvents, minimizing environmental pollution. Acetate fiber, while semi-synthetic and biodegradable, relies on cellulose acetate processed with acetic acid and other chemicals, leading to higher chemical waste and energy consumption during manufacturing. Lyocell's lower carbon footprint and reduced water usage make it a more sustainable choice for environmentally conscious dress materials.
Breathability & Comfort for Dresses
Lyocell fiber offers superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for comfortable, breathable dresses that keep the wearer cool and dry. Acetate fiber, while silky and smooth, has lower breathability and tends to trap heat, which can reduce overall comfort in warm weather. Dresses made from Lyocell fiber provide enhanced airflow and softness, ensuring better comfort during extended wear compared to acetate alternatives.
Durability and Strength Differences
Lyocell fiber offers superior durability and tensile strength compared to acetate fiber, making it more resistant to wear and tear in dresses. Acetate fibers tend to have lower resistance to abrasion and can weaken over time, especially with exposure to moisture and heat. The robust cellulose structure in lyocell enhances its durability, while acetate's thermoplastic nature compromises its long-term strength.
Moisture Absorption & Wicking Properties
Lyocell fiber exhibits superior moisture absorption and wicking properties compared to acetate fiber, making it ideal for dress fabrics that require breathability and comfort. Lyocell can absorb up to 50% of its weight in moisture without feeling damp, efficiently drawing sweat away from the skin to maintain dryness. In contrast, acetate fiber has lower moisture absorption and limited wicking ability, often resulting in less breathability and a warmer, less comfortable wear.
Softness and Texture on Skin
Lyocell fiber offers exceptional softness and a smooth, breathable texture, making it ideal for sensitive skin in dress fabrics. Acetate fiber provides a silky, glossy finish but can feel less breathable and slightly rougher compared to Lyocell when worn for extended periods. For comfort and skin-friendly texture, Lyocell outperforms acetate with its moisture-wicking and hypoallergenic properties.
Color Retention and Dyeability
Lyocell fiber exhibits superior color retention and dyeability due to its smooth surface and high moisture absorbency, allowing vibrant, long-lasting colors on dresses. Acetate fiber, while easily dyed with brilliant hues, tends to fade faster under UV exposure and washing, resulting in diminished color retention over time. Dresses crafted from Lyocell maintain vivid tones and resist fading more effectively compared to those made with Acetate fiber.
Care, Maintenance, and Longevity
Lyocell fiber offers superior durability and resistance to shrinking compared to acetate fiber, making it easier to maintain through regular machine washing on gentle cycles and air drying. Acetate fiber requires more delicate care, typically hand washing or dry cleaning, to prevent damage such as discoloration and fiber weakening. The longevity of lyocell dresses surpasses acetate due to lyocell's moisture-wicking properties and resilience, ensuring garments retain their shape and color over time.
Cost and Accessibility for Dressmaking
Lyocell fiber offers moderate cost with increasing accessibility due to sustainable production methods and growing market demand, making it a viable choice for eco-conscious dressmakers. Acetate fiber is typically lower in cost and widely accessible, benefiting from established manufacturing processes and broad distribution, which suits budget-focused dressmaking projects. While Lyocell provides better environmental credentials and softer fabric feel, Acetate remains favored for affordability and easy sourcing in mass-produced dresses.
Infographic: Lyocell fiber vs Acetate fiber for Dress
 azmater.com
azmater.com