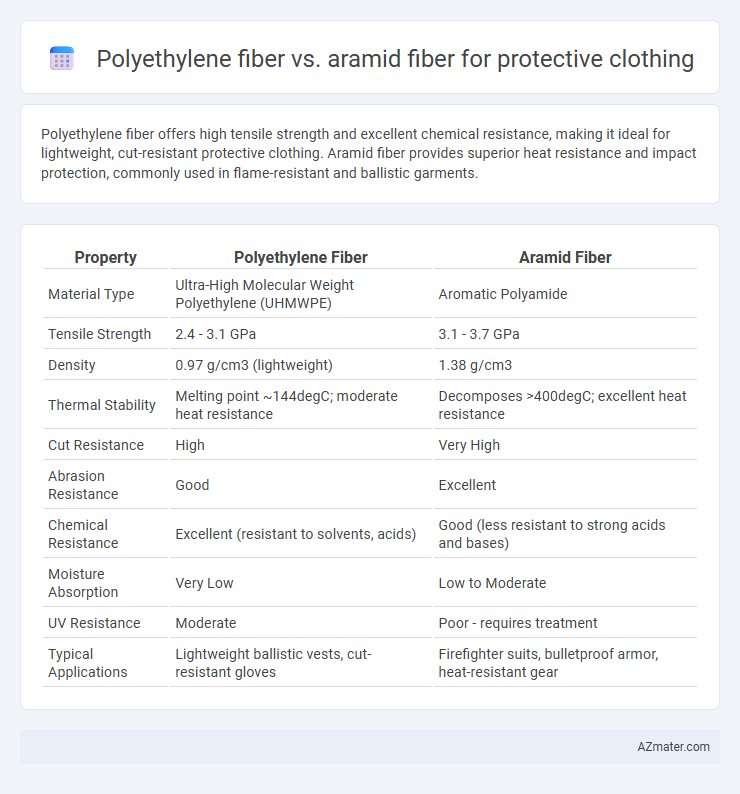
Polyethylene fiber offers high tensile strength and excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for lightweight, cut-resistant protective clothing. Aramid fiber provides superior heat resistance and impact protection, commonly used in flame-resistant and ballistic garments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) | Aromatic Polyamide |
| Tensile Strength | 2.4 - 3.1 GPa | 3.1 - 3.7 GPa |
| Density | 0.97 g/cm3 (lightweight) | 1.38 g/cm3 |
| Thermal Stability | Melting point ~144degC; moderate heat resistance | Decomposes >400degC; excellent heat resistance |
| Cut Resistance | High | Very High |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (resistant to solvents, acids) | Good (less resistant to strong acids and bases) |
| Moisture Absorption | Very Low | Low to Moderate |
| UV Resistance | Moderate | Poor - requires treatment |
| Typical Applications | Lightweight ballistic vests, cut-resistant gloves | Firefighter suits, bulletproof armor, heat-resistant gear |
Introduction to Protective Clothing Materials
Polyethylene fibers offer high tensile strength and excellent chemical resistance, making them ideal for lightweight protective clothing against cuts and abrasions. Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional heat resistance and flame retardant properties, provide superior protection in high-temperature environments such as firefighting and industrial settings. Both materials are integral to advanced protective clothing, with polyethylene favored for impact and cut resistance, while aramid excels in thermal protection and durability.
Overview of Polyethylene Fiber
Polyethylene fiber, particularly ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), is renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making it a popular choice in protective clothing for ballistic and cut-resistant applications. This fiber offers high tensile strength, excellent abrasion resistance, and low moisture absorption, contributing to lightweight and comfortable protective gear compared to heavier materials like aramid fibers such as Kevlar. Its chemical resistance and ability to maintain performance in wet conditions further enhance its suitability for demanding environments where durability and protection are crucial.
Overview of Aramid Fiber
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Twaron, are synthetic fibers recognized for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and high thermal stability, making them ideal for protective clothing. These fibers exhibit outstanding impact resistance and flame retardance, providing superior protection against ballistic threats, cuts, and heat compared to polyethylene fibers. The molecular structure of aramid fibers contributes to their durability and chemical resistance, which enhances performance in harsh environments requiring reliable protective gear.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polyethylene fibers, such as Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE), exhibit high tensile strength with values around 2.5-3.5 GPa, offering excellent impact resistance ideal for protective clothing. Aramid fibers, including Kevlar and Twaron, display tensile strengths typically ranging from 2.5 to 3.6 GPa, providing superior thermal stability and energy absorption. Both fibers deliver comparable mechanical strength, but polyethylene fibers tend to have higher cut resistance and lower density, enhancing comfort and durability in protective apparel.
Thermal Resistance and Heat Protection
Polyethylene fibers, such as ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), offer excellent thermal insulation due to their low thermal conductivity, making them effective against radiant heat but less resistant to high temperatures above 150degC. Aramid fibers like Kevlar and Nomex exhibit superior thermal resistance and heat protection, withstanding continuous exposure to temperatures up to 400degC and providing inherent flame retardancy critical for firefighting and industrial protective clothing. The choice between polyethylene and aramid fibers depends on application-specific thermal demands, with aramid favored in environments requiring high heat durability and polyethylene preferred where lightweight thermal insulation is prioritized.
Weight and Comfort Considerations
Polyethylene fiber offers a lightweight option for protective clothing, weighing significantly less than aramid fiber, which enhances wearer comfort during extended use. Its high strength-to-weight ratio allows for flexible and breathable garments without compromising protection. Aramid fiber, while heavier, provides superior heat resistance but may result in increased wearer fatigue due to its density and reduced ventilation.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Polyethylene fiber offers exceptional chemical resistance against acids, alkalis, and organic solvents, making it highly suitable for protective clothing in harsh chemical environments. Aramid fiber provides superior durability and heat resistance, maintaining structural integrity under extreme mechanical stress and high temperatures. Combining polyethylene's chemical inertness with aramid's mechanical strength enhances the overall protective performance for industrial safety gear.
Cost and Availability
Polyethylene fiber, known for its affordability and widespread availability, offers a cost-effective solution for protective clothing with high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent cut resistance. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, tends to be more expensive due to complex manufacturing processes and limited raw material sources but provides superior heat resistance and durability. The choice between polyethylene and aramid fibers often hinges on budget constraints and specific protective requirements, with polyethylene favored for cost-sensitive applications and aramid for high-performance gear.
Typical Applications in Protective Clothing
Polyethylene fiber is widely used in protective clothing for its high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent cut resistance, making it ideal for gloves, arm guards, and body armor inserts in law enforcement and industrial settings. Aramid fiber excels in heat resistance and flame retardancy, commonly found in firefighter turnout gear, military ballistic vests, and industrial protective suits requiring thermal protection. Both fibers provide ballistic protection, but polyethylene fibers offer superior lightweight performance while aramid fibers deliver enhanced durability in high-temperature environments.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Needs
Polyethylene fiber offers exceptional lightweight strength and excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for protective clothing in hazardous environments requiring high cut and abrasion resistance. Aramid fiber, known for its superior heat resistance and ballistic protection, provides enhanced durability against flames and impact, suitable for firefighting and military applications. Selecting the right fiber depends on specific performance needs such as thermal resistance, weight considerations, and exposure to chemicals or mechanical threats.
Infographic: Polyethylene fiber vs Aramid fiber for Protective clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com