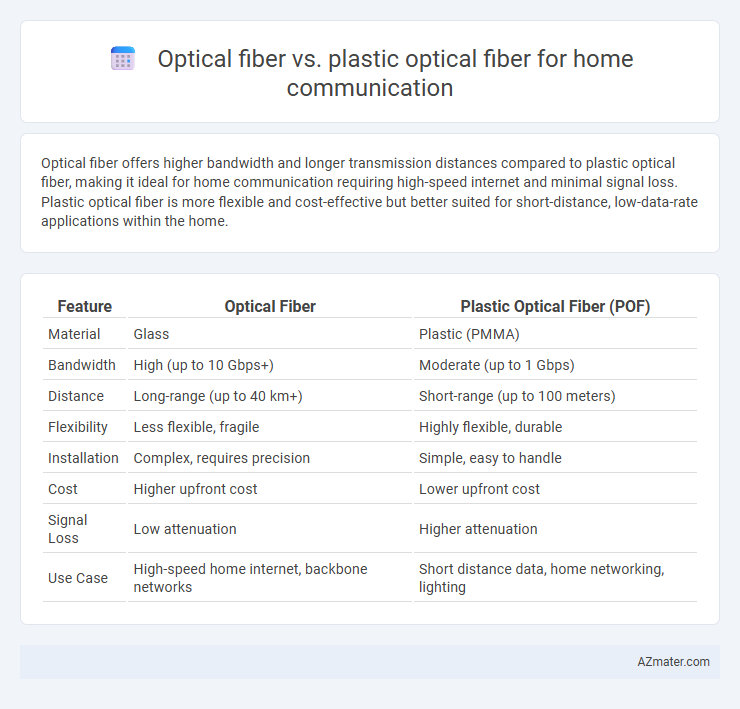
Optical fiber offers higher bandwidth and longer transmission distances compared to plastic optical fiber, making it ideal for home communication requiring high-speed internet and minimal signal loss. Plastic optical fiber is more flexible and cost-effective but better suited for short-distance, low-data-rate applications within the home.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Optical Fiber | Plastic Optical Fiber (POF) |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Glass | Plastic (PMMA) |
| Bandwidth | High (up to 10 Gbps+) | Moderate (up to 1 Gbps) |
| Distance | Long-range (up to 40 km+) | Short-range (up to 100 meters) |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, fragile | Highly flexible, durable |
| Installation | Complex, requires precision | Simple, easy to handle |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost | Lower upfront cost |
| Signal Loss | Low attenuation | Higher attenuation |
| Use Case | High-speed home internet, backbone networks | Short distance data, home networking, lighting |
Introduction to Optical Fiber Technologies
Optical fiber technology for home communication primarily uses glass optical fibers, which offer high bandwidth and long-distance transmission with minimal signal loss compared to plastic optical fibers (POF). Glass optical fibers support higher data rates and better reliability but require precise installation, whereas POF is easier to handle with lower cost and flexibility, making it suitable for short-distance home networks. Advancements in optical fiber technologies enhance home connectivity by balancing performance, durability, and installation ease.
What is Optical Fiber?
Optical fiber is a high-speed communication medium made of glass or plastic strands that transmit data using light signals, offering superior bandwidth and low signal loss. Plastic optical fiber (POF) is a subset engineered with polymer materials, providing easier installation and flexibility but with higher attenuation and limited transmission distance compared to glass optical fiber. For home communication, optical fiber delivers faster internet speeds and greater reliability, while POF suits short-range applications like in-home networking or multimedia distribution.
What is Plastic Optical Fiber (POF)?
Plastic Optical Fiber (POF) is a type of optical fiber made from polymer materials, primarily used for short-distance data transmission in home communication systems. Unlike traditional glass optical fiber, POF offers greater flexibility, easier installation, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for in-home networking and multimedia applications. Its larger core diameter allows for simpler connections and compatibility with consumer electronics, supporting high-speed data transfer over distances typically less than 100 meters.
Key Differences Between Glass and Plastic Optical Fiber
Glass optical fiber offers higher bandwidth and longer transmission distances compared to plastic optical fiber, making it ideal for high-speed home communication networks. Plastic optical fiber is more flexible, easier to install, and cost-effective for short-distance data transmission within homes. The core material differences cause glass fibers to have lower attenuation and higher signal quality, while plastic fibers excel in durability and bending radius.
Transmission Speed and Bandwidth Comparison
Optical fiber offers significantly higher transmission speeds and greater bandwidth capacity compared to plastic optical fiber, making it ideal for high-speed home communication networks. Glass-based optical fibers support data rates up to 100 Gbps and beyond, whereas plastic optical fibers typically handle speeds up to 1 Gbps due to higher signal attenuation and limited bandwidth. The superior performance of optical fiber ensures faster internet connectivity and supports more data-intensive applications in residential settings.
Durability and Flexibility in Home Installations
Optical fiber offers superior durability with its glass core, resisting signal loss over long distances and harsh environmental conditions, making it ideal for fixed home installations requiring high-speed internet. Plastic optical fiber (POF) provides enhanced flexibility and ease of handling, allowing simple and cost-effective routing through tight corners and complex home layouts, though it suffers from higher attenuation and limited transmission range. For home communication, selecting between optical fiber and POF depends on balancing long-term durability with installation flexibility in specific household environments.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Optical fiber for home communication demands precise installation techniques involving careful handling and specialized tools to ensure minimal signal loss, whereas plastic optical fiber (POF) offers easier installation with greater flexibility and less fragility, making it suitable for DIY setups. Maintenance of traditional optical fiber requires professional expertise to address potential issues like connector contamination or fiber breaks, while POF systems typically involve lower maintenance due to their robust nature and resistance to bending or environmental stress. Selecting between these fibers hinges on balancing installation complexity and long-term upkeep, with optical fiber favored for high-performance needs and POF preferred for user-friendly installation and cost-effectiveness.
Cost Analysis: Glass Fiber vs Plastic Optical Fiber
Glass optical fiber offers higher bandwidth and longer transmission distances but comes with significantly higher installation and material costs compared to plastic optical fiber (POF), which is more affordable and easier to handle for short-range home communication. The cost of glass fiber cables can be up to three times higher than POF, largely due to the need for specialized connectors, splicing equipment, and professional installation. For residential settings with limited distance requirements, plastic optical fiber presents a cost-effective solution without substantial compromise in performance.
Practical Applications in Home Communication
Optical fiber offers superior bandwidth and longer transmission distances for home communication, making it ideal for high-speed internet, streaming, and smart home networks. Plastic optical fiber (POF) provides a more flexible, cost-effective solution suitable for short-distance data transmission within rooms or between devices, such as connecting home entertainment systems. Both technologies support gigabit Ethernet standards, but optical fiber excels in maintaining signal integrity over longer runs, while POF is preferred for easy installation and bending resistance in confined home environments.
Which Fiber Type is Best for Home Use?
Optical fiber made from glass offers higher data transmission speeds and longer distance capabilities, making it ideal for future-proof home communication systems requiring ultra-fast internet and minimal signal loss. Plastic optical fiber (POF) provides easier installation, greater flexibility, and lower cost, fitting well for short-distance home networks or less demanding applications. For most home users aiming for reliable, high-performance connectivity, glass optical fiber remains the best choice due to its superior bandwidth and durability.
Infographic: Optical fiber vs Plastic optical fiber for Home communication
 azmater.com
azmater.com