Cellulose fiber enhances concrete by improving crack resistance and reducing shrinkage with natural, biodegradable properties, while steel fiber significantly increases tensile strength, impact resistance, and structural durability. Choosing between cellulose and steel fibers depends on project-specific requirements for sustainability and mechanical performance.
Table of Comparison
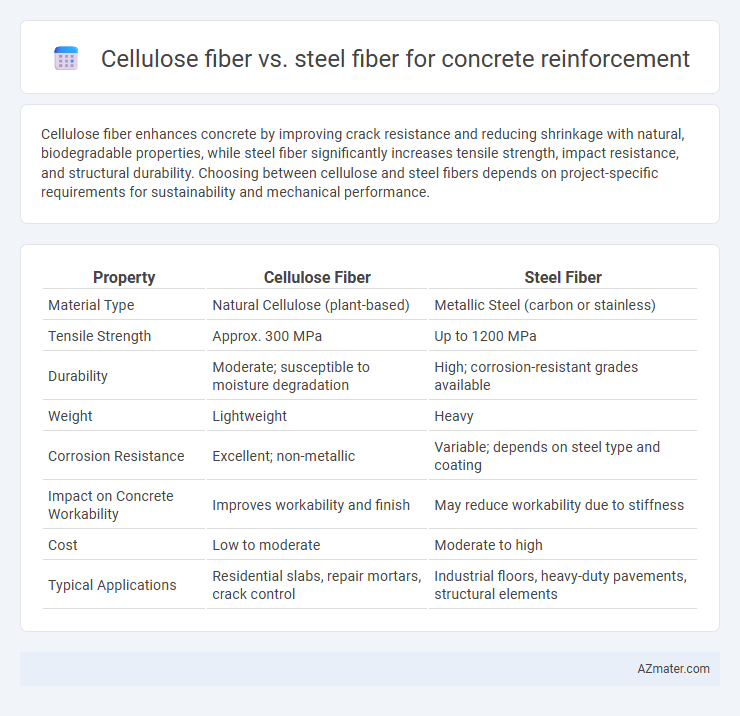
| Property | Cellulose Fiber | Steel Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Natural Cellulose (plant-based) | Metallic Steel (carbon or stainless) |
| Tensile Strength | Approx. 300 MPa | Up to 1200 MPa |
| Durability | Moderate; susceptible to moisture degradation | High; corrosion-resistant grades available |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavy |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent; non-metallic | Variable; depends on steel type and coating |
| Impact on Concrete Workability | Improves workability and finish | May reduce workability due to stiffness |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Moderate to high |
| Typical Applications | Residential slabs, repair mortars, crack control | Industrial floors, heavy-duty pavements, structural elements |
Introduction to Concrete Reinforcement Fibers
Concrete reinforcement fibers enhance structural integrity and durability by improving crack resistance and load distribution. Cellulose fibers, derived from natural sources, offer biodegradability and reduce shrinkage, making them ideal for controlling plastic shrinkage cracks. Steel fibers provide superior tensile strength and impact resistance, significantly increasing concrete's toughness and load-bearing capacity in heavy-duty applications.
Overview of Cellulose Fiber in Concrete
Cellulose fiber in concrete reinforcement offers enhanced crack resistance, improved durability, and reduced shrinkage due to its natural origin and micro-fibrillar structure. These fibers provide better dispersion within the concrete matrix, promoting increased tensile strength and impact resistance compared to traditional steel fibers. Cellulose fibers are also lightweight, corrosion-free, and eco-friendly, making them an optimal choice for sustainable concrete applications.
Overview of Steel Fiber in Concrete
Steel fiber in concrete significantly enhances tensile strength, impact resistance, and durability by providing effective crack control and energy absorption under stress. Compared to cellulose fiber, steel fibers offer superior load-bearing capacity and improved post-cracking behavior, making them ideal for industrial floors, pavements, and heavy-duty structural elements. High modulus of elasticity and corrosion resistance in steel fibers contribute to long-term performance and structural integrity in reinforced concrete applications.
Comparative Mechanical Properties
Cellulose fiber exhibits lower tensile strength and modulus of elasticity compared to steel fiber, resulting in reduced crack resistance and overall load-bearing capacity in concrete reinforcement. Steel fibers provide superior mechanical properties with high tensile strength, enhanced toughness, and excellent impact resistance, making them ideal for structural applications requiring high durability. The flexural strength and post-crack performance of steel fiber-reinforced concrete significantly surpass those of cellulose fiber-reinforced concrete, improving longevity and structural integrity.
Impact on Concrete Durability
Cellulose fiber enhances concrete durability by improving crack resistance and reducing shrinkage, which limits moisture penetration and mitigates freeze-thaw damage. In contrast, steel fiber significantly increases tensile strength and toughness, providing superior impact resistance but may be susceptible to corrosion if not properly protected. The choice between cellulose and steel fibers depends on environmental conditions and desired durability performance in reinforced concrete.
Influence on Workability and Finish
Cellulose fiber enhances concrete workability by improving water retention and reducing segregation, resulting in better surface finish and reduced shrinkage cracks. Steel fiber tends to decrease workability due to its stiffness and larger volume, potentially causing challenges in mixing and finishing processes. The choice between cellulose and steel fibers significantly influences concrete's ease of placement and the quality of its final appearance.
Cost Analysis: Cellulose vs Steel Fibers
Cellulose fibers typically offer a cost-effective alternative to steel fibers for concrete reinforcement, often reducing overall material expenses by up to 50%. Steel fibers provide superior tensile strength and durability but come at a significantly higher initial cost due to complex manufacturing processes and raw material prices. Evaluating project budgets, cellulose fibers suit applications prioritizing affordability and moderate performance, whereas steel fibers are justified for high-strength requirements despite their premium cost.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Cellulose fiber offers a renewable, biodegradable alternative to steel fiber in concrete reinforcement, significantly reducing environmental impact due to its lower embodied energy and carbon footprint. Steel fibers, while providing superior tensile strength and durability, involve energy-intensive extraction and manufacturing processes that contribute to higher greenhouse gas emissions. Incorporating cellulose fibers enhances sustainability by promoting waste valorization from plant-based materials and reducing reliance on finite metal resources in construction.
Typical Applications and Suitability
Cellulose fiber is commonly used in interior concrete applications such as floor slabs, walls, and ceilings due to its excellent crack resistance and shrinkage control, offering enhanced surface finish and fire resistance. Steel fiber is suitable for heavy-duty applications like industrial floors, shotcrete, bridge decks, and precast elements where high tensile strength and impact resistance are critical. Both fibers improve concrete durability, but cellulose fiber is preferred for lightweight, non-structural reinforcement, while steel fiber excels in structural and high-stress environments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Concrete
Cellulose fiber enhances concrete durability by improving crack resistance and reducing shrinkage, making it ideal for applications requiring lightweight and environmentally friendly materials. Steel fiber increases tensile strength and impact resistance, providing superior load-bearing capacity for heavy-duty infrastructure like bridges and industrial floors. Selecting the right fiber depends on project-specific requirements, balancing factors like mechanical performance, cost, and environmental impact.
Infographic: Cellulose fiber vs Steel fiber for Concrete reinforcement
 azmater.com
azmater.com