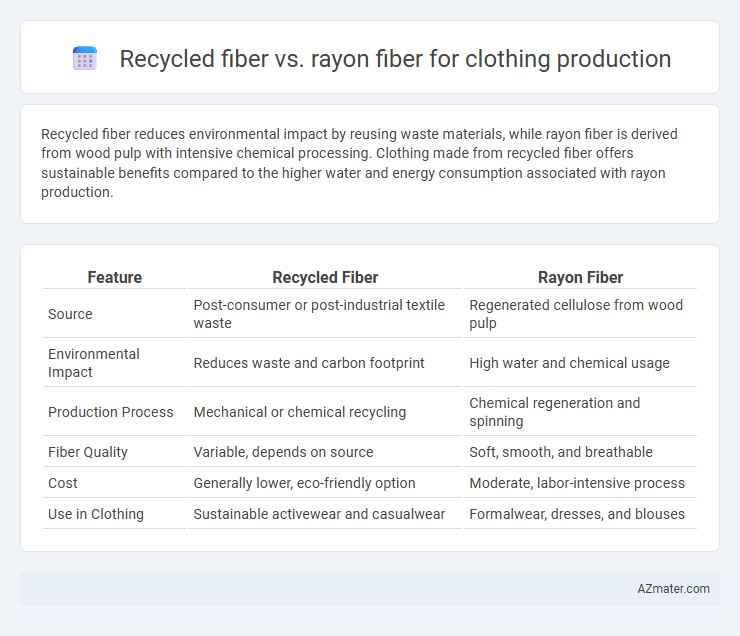
Recycled fiber reduces environmental impact by reusing waste materials, while rayon fiber is derived from wood pulp with intensive chemical processing. Clothing made from recycled fiber offers sustainable benefits compared to the higher water and energy consumption associated with rayon production.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled Fiber | Rayon Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Post-consumer or post-industrial textile waste | Regenerated cellulose from wood pulp |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste and carbon footprint | High water and chemical usage |
| Production Process | Mechanical or chemical recycling | Chemical regeneration and spinning |
| Fiber Quality | Variable, depends on source | Soft, smooth, and breathable |
| Cost | Generally lower, eco-friendly option | Moderate, labor-intensive process |
| Use in Clothing | Sustainable activewear and casualwear | Formalwear, dresses, and blouses |
Introduction to Recycled Fiber and Rayon Fiber
Recycled fiber, derived from repurposed textiles and post-consumer waste, offers an eco-friendly alternative that reduces landfill impact and conserves natural resources in clothing production. Rayon fiber, a semi-synthetic material made from regenerated cellulose, provides a soft, breathable fabric commonly used for its silk-like texture and draping qualities. Both fibers serve distinct roles in sustainable fashion, with recycled fiber emphasizing environmental conservation and rayon focusing on comfort and versatility.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Recycled fiber significantly reduces environmental impact by lowering waste, conserving water, and cutting energy use compared to rayon fiber, which is derived from chemically processed wood pulp and involves intensive water and chemical consumption. Rayon production often leads to deforestation and toxic effluent discharge, contributing to soil and water pollution, whereas recycled fibers promote circular economy principles by repurposing textile waste. Choosing recycled fibers in clothing production supports sustainability through reduced carbon emissions and minimized resource extraction relative to traditional rayon manufacturing.
Sourcing and Production Processes
Recycled fiber for clothing production is sourced from post-consumer or post-industrial waste, significantly reducing raw material consumption and environmental impact compared to traditional fiber production. Rayon fiber, derived from cellulose typically extracted from wood pulp, involves chemically intensive processes including the use of toxic solvents like carbon disulfide, raising environmental and safety concerns. The production of recycled fiber emphasizes circular economy principles with energy-efficient sorting and mechanical or chemical recycling methods, whereas rayon manufacturing relies on large-scale industrial refineries employing wet-spinning techniques.
Fiber Properties and Performance
Recycled fiber offers sustainability benefits with moderate strength and durability, making it suitable for eco-friendly clothing production but often exhibits lower moisture absorption compared to rayon fiber. Rayon fiber, derived from cellulose, provides excellent breathability, softness, and moisture-wicking properties, enhancing comfort and performance in garments. In terms of fiber properties, recycled fibers tend to have variable quality depending on the source material, whereas rayon fibers deliver consistent texture and drape ideal for fashion apparel.
Cost Efficiency in Clothing Manufacturing
Recycled fiber significantly reduces raw material costs in clothing manufacturing by utilizing post-consumer and post-industrial waste, lowering dependence on virgin resources compared to rayon fiber, which relies on wood pulp and involves more energy-intensive chemical processing. The energy and water consumption in rayon production elevate operational expenses, while recycled fiber processes tend to be more cost-effective due to improved sustainability practices and reduced input requirements. Manufacturers achieve better cost efficiency with recycled fibers through minimized waste management expenses and growing market demand for eco-friendly apparel, enhancing profitability and supply chain resilience.
Durability and Longevity of Fabrics
Recycled fiber in clothing production offers enhanced durability due to its resistance to wear and tear while maintaining eco-friendly benefits. Rayon fiber, derived from cellulose, tends to have a softer texture but generally exhibits lower longevity and may degrade faster under repeated use and washing. Choosing recycled fiber over rayon fiber can significantly extend the lifespan of garments, making it a more sustainable option for durable clothing.
Comfort and Wearability Factors
Recycled fiber offers enhanced breathability and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for sustainable clothing with long-lasting comfort. Rayon fiber, derived from cellulose, provides a smooth, silky texture and excellent drape, contributing to superior softness and wearability. Both fibers impact garment comfort differently, with recycled fibers focusing on eco-friendly performance and rayon emphasizing luxurious feel and flexibility.
Sustainability and Certifications
Recycled fiber in clothing production significantly reduces environmental impact by reutilizing post-consumer or post-industrial waste, requiring less water and energy compared to virgin fiber manufacturing, and often holds certifications like GRS (Global Recycled Standard) ensuring traceability and chemical safety. Rayon fiber, while biodegradable, relies heavily on wood pulp that contributes to deforestation and involves chemical-intensive processing, with certifications such as FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) or OEKO-TEX helping to mitigate environmental concerns and ensure sustainable sourcing. Choosing recycled fiber over traditional rayon promotes circular fashion practices and aligns closely with sustainability goals and certification standards prioritizing resource efficiency and reduced ecological footprint.
Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
Recycled fiber in clothing production is gaining significant market traction due to increasing consumer demand for sustainable and eco-friendly fashion choices, with global recycled fiber market projected to grow at a CAGR of over 10% through 2028. Rayon fiber, while valued for its softness and affordability, faces challenges related to environmental concerns and stricter regulations on viscose production. Consumer preferences are shifting toward recycled fiber garments as brands highlight transparency and circular economy principles, driving innovation and investment in recycled textile technologies.
Future Prospects for Eco-friendly Textiles
Recycled fiber offers a promising future in eco-friendly textiles due to its ability to reduce waste and lower carbon emissions compared to conventional rayon fiber, which is often derived from chemically intensive processes involving wood pulp. Innovations in recycling technology enhance the quality and durability of recycled fibers, making them increasingly viable for clothing production with minimal environmental impact. Sustainable brands and consumers are driving demand towards recycled fibers, signaling a shift in the textile industry towards circular economy models and greener manufacturing practices.
Infographic: Recycled fiber vs Rayon fiber for Clothing production
 azmater.com
azmater.com