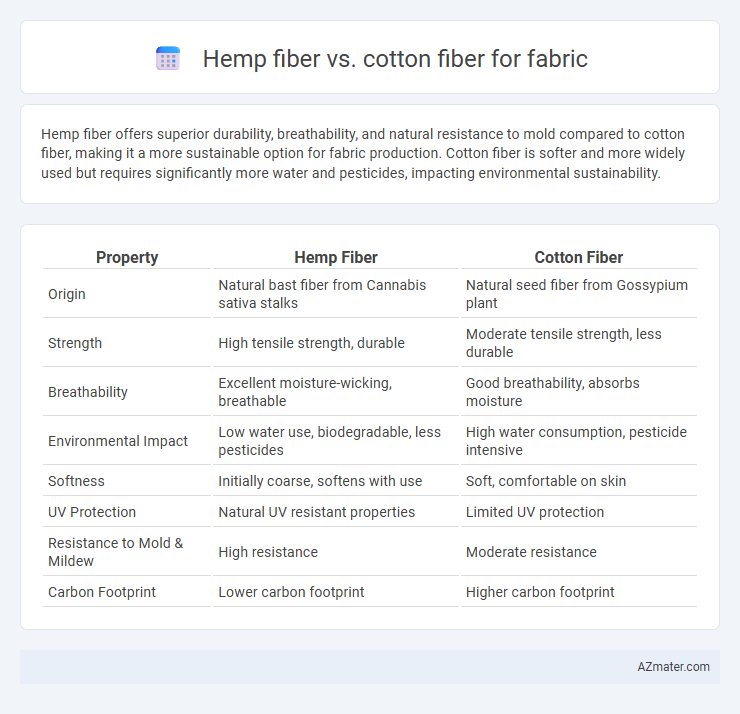
Hemp fiber offers superior durability, breathability, and natural resistance to mold compared to cotton fiber, making it a more sustainable option for fabric production. Cotton fiber is softer and more widely used but requires significantly more water and pesticides, impacting environmental sustainability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hemp Fiber | Cotton Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Natural bast fiber from Cannabis sativa stalks | Natural seed fiber from Gossypium plant |
| Strength | High tensile strength, durable | Moderate tensile strength, less durable |
| Breathability | Excellent moisture-wicking, breathable | Good breathability, absorbs moisture |
| Environmental Impact | Low water use, biodegradable, less pesticides | High water consumption, pesticide intensive |
| Softness | Initially coarse, softens with use | Soft, comfortable on skin |
| UV Protection | Natural UV resistant properties | Limited UV protection |
| Resistance to Mold & Mildew | High resistance | Moderate resistance |
| Carbon Footprint | Lower carbon footprint | Higher carbon footprint |
Introduction to Hemp and Cotton Fibers
Hemp fiber originates from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, known for its exceptional strength, durability, and eco-friendly cultivation without extensive pesticide use. Cotton fibers come from the seed hairs of the Gossypium plant, prized for their softness, breathability, and widespread availability. Both fibers serve as fundamental raw materials in the textile industry, with hemp offering superior tensile strength and moisture-wicking properties compared to the more delicate, comfortable cotton.
Environmental Impact: Hemp vs Cotton
Hemp fiber has a significantly lower environmental impact than cotton due to its high yield and minimal need for pesticides, herbicides, and synthetic fertilizers, reducing soil degradation and water pollution. Hemp requires up to 50% less water compared to cotton, making it a more sustainable choice in terms of water consumption and drought resistance. Additionally, hemp plants absorb more CO2 per hectare, contributing to carbon sequestration and reducing the overall carbon footprint of fabric production.
Cultivation and Resource Requirements
Hemp fiber cultivation demands significantly less water than cotton, requiring approximately 300-500 liters per kilogram compared to cotton's 7,000-10,000 liters, making it a more sustainable choice for fabric production. Hemp plants thrive with minimal pesticides and fertilizers due to their natural pest resistance and robust growth, whereas cotton farming relies heavily on chemical inputs, increasing environmental impact. The rapid growth cycle of hemp, typically 90-120 days, allows for multiple harvests annually in suitable climates, contrasting with cotton's longer growing season and higher land resource consumption.
Fiber Strength and Durability Comparison
Hemp fiber exhibits significantly higher tensile strength compared to cotton, making it one of the strongest natural fibers for fabric production. Its durability outperforms cotton, as hemp fibers resist wear, tear, and microbial attack more effectively, extending the fabric's lifespan. The robust fiber structure of hemp contributes to increased durability in high-stress applications, offering sustainable and long-lasting textile alternatives.
Breathability and Comfort in Fabrics
Hemp fiber offers superior breathability compared to cotton fiber due to its porous structure that allows better airflow and moisture wicking, enhancing comfort in warm and humid conditions. Cotton fiber is softer and provides a smoother feel against the skin, but it tends to retain moisture, which can reduce comfort in hot climates. Fabrics made from hemp blend durability with natural antimicrobial properties, making them ideal for breathable, comfortable, and long-lasting clothing.
Processing Techniques for Hemp and Cotton
Hemp fiber processing involves retting, decortication, and scutching to separate the bast fibers from the woody core, followed by carding and spinning to create a durable yarn suitable for textiles. Cotton fiber processing starts with ginning to remove seeds, followed by cleaning, carding, and combing to produce smooth, fine fibers ideal for soft, breathable fabrics. Both fibers require distinct mechanical and chemical treatments tailored to their structural differences, impacting the texture and strength of the final fabric.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendliness
Hemp fiber surpasses cotton fiber in sustainability due to its rapid growth cycle, requiring less water and pesticides while enriching soil health. Cotton cultivation demands substantial water resources and intense chemical use, contributing to environmental degradation. Fabrics made from hemp offer greater eco-friendliness by reducing agricultural impact and promoting biodegradability compared to conventional cotton textiles.
Cost and Market Availability
Hemp fiber typically costs more to process than cotton but offers superior durability and environmental benefits, making it increasingly attractive in sustainable textile markets. Cotton remains more widely available and less expensive due to its established global cultivation and processing infrastructure. Market availability of hemp fibers is expanding, driven by growing demand for eco-friendly fabrics, yet cotton maintains dominance in mainstream fabric production due to lower overall costs and extensive supply chains.
Applications in Fashion and Textiles
Hemp fiber offers superior durability and breathability compared to cotton, making it ideal for sustainable fashion and eco-friendly textiles. Its natural resistance to UV rays and mold enhances the longevity of garments, especially in activewear and outdoor clothing. Cotton remains popular for its softness and versatility but often requires higher water and pesticide use, impacting its environmental footprint in textile production.
Final Verdict: Which Fiber is Superior?
Hemp fiber offers superior durability, breathability, and environmental sustainability compared to cotton fiber, making it a better choice for long-lasting, eco-friendly fabrics. While cotton is softer and more widely used, hemp requires fewer pesticides and water during cultivation, significantly reducing its ecological footprint. Hemp fabric's resistance to UV rays, mold, and mildew further positions it as the superior fiber in terms of performance and sustainability.
Infographic: Hemp fiber vs Cotton fiber for Fabric
 azmater.com
azmater.com