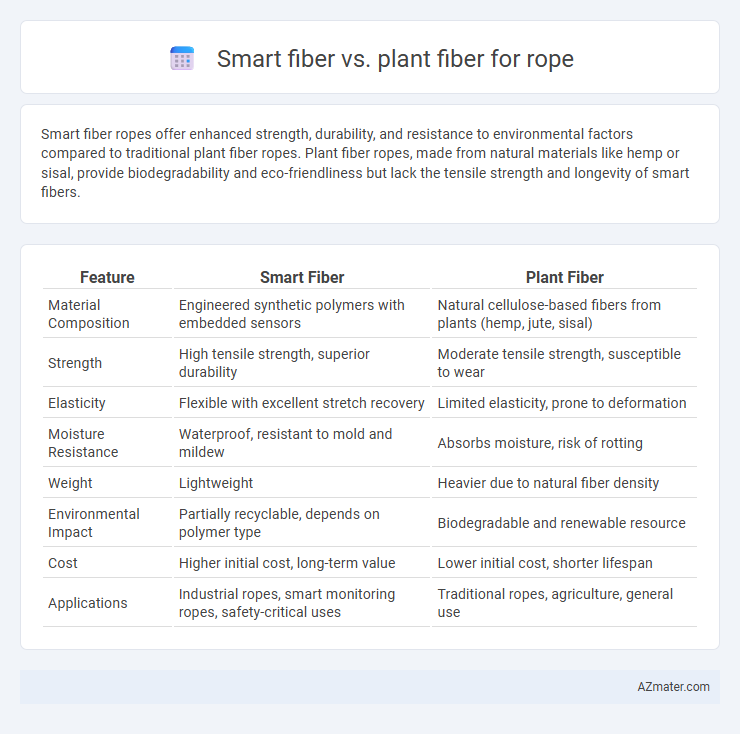
Smart fiber ropes offer enhanced strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors compared to traditional plant fiber ropes. Plant fiber ropes, made from natural materials like hemp or sisal, provide biodegradability and eco-friendliness but lack the tensile strength and longevity of smart fibers.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Smart Fiber | Plant Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Engineered synthetic polymers with embedded sensors | Natural cellulose-based fibers from plants (hemp, jute, sisal) |
| Strength | High tensile strength, superior durability | Moderate tensile strength, susceptible to wear |
| Elasticity | Flexible with excellent stretch recovery | Limited elasticity, prone to deformation |
| Moisture Resistance | Waterproof, resistant to mold and mildew | Absorbs moisture, risk of rotting |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier due to natural fiber density |
| Environmental Impact | Partially recyclable, depends on polymer type | Biodegradable and renewable resource |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, long-term value | Lower initial cost, shorter lifespan |
| Applications | Industrial ropes, smart monitoring ropes, safety-critical uses | Traditional ropes, agriculture, general use |
Introduction to Fiber Types in Rope Manufacturing
Smart fiber in rope manufacturing offers enhanced strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors compared to traditional plant fibers such as hemp, jute, or sisal. Plant fibers are natural, biodegradable, and widely used for their cost-effectiveness and flexibility but generally lack the high tensile strength and longevity found in synthetic smart fibers like aramid, carbon, or high-modulus polyethylene. Choosing between smart fibers and plant fibers depends on application-specific requirements, balancing factors such as load capacity, weather resistance, and sustainability preferences.
What Are Smart Fibers?
Smart fibers are advanced materials engineered to respond dynamically to environmental stimuli such as temperature, moisture, or pressure, enhancing the rope's performance and durability. Unlike traditional plant fibers like hemp or jute, smart fibers incorporate polymers or nanomaterials that provide increased strength, elasticity, and resistance to wear and environmental degradation. These innovative fibers enable the production of ropes with tailored properties for specific applications, improving safety and longevity in demanding conditions.
Understanding Plant Fiber Ropes
Plant fiber ropes, made from natural materials such as hemp, sisal, jute, and coir, offer biodegradability, affordability, and excellent grip, making them ideal for environmentally conscious applications and traditional uses. These ropes exhibit moderate strength, good flexibility, and resistance to UV damage but tend to absorb moisture, leading to rot and degradation over time when exposed to wet conditions. Understanding the characteristics of plant fiber ropes is essential for selecting the appropriate material in marine, agricultural, or decorative contexts where sustainability and natural texture are prioritized.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Smart fibers such as Kevlar and Dyneema exhibit significantly higher tensile strength and durability compared to traditional plant fibers like hemp or sisal, making them ideal for heavy-duty rope applications. These synthetic fibers resist abrasion, moisture, and UV degradation better than natural fibers, resulting in longer service life and superior performance under harsh conditions. While plant fibers offer eco-friendly benefits, their lower tensile strength and susceptibility to environmental damage limit their usability in high-stress scenarios.
Flexibility and Weight Differences
Smart fiber ropes exhibit superior flexibility compared to traditional plant fiber ropes, allowing for easier knotting and handling in various applications such as climbing and marine use. These synthetic fibers, often made from materials like nylon or polyester, weigh significantly less than plant fibers like hemp or jute, enhancing portability and reducing fatigue during prolonged use. The lightweight nature and enhanced elasticity of smart fibers contribute to increased durability and performance under dynamic loads.
Environmental Impact: Smart vs. Plant Fibers
Smart fibers, often made from synthetic polymers like nylon or polyester, typically have a higher environmental footprint due to reliance on fossil fuels and slower biodegradability compared to plant fibers. Plant fibers such as hemp, jute, and sisal are renewable, biodegradable, and lower energy-intensive to produce, contributing less to pollution and landfill waste. The sustainable cultivation and natural decomposition of plant fibers make them a more environmentally friendly choice for rope manufacturing.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Smart fibers, typically engineered from synthetic materials, offer higher cost efficiency due to mass production and consistent quality, making them widely available in industrial markets. Plant fibers like hemp, sisal, and jute are renewable and biodegradable but often incur higher costs from labor-intensive harvesting and processing, with availability fluctuating based on agricultural conditions. For rope manufacturing, smart fibers provide predictable supply chains and lower long-term expenses, whereas plant fibers appeal to eco-conscious applications despite variable availability and potential price volatility.
Applications and Ideal Use Cases
Smart fibers, made from advanced materials like carbon nanotubes and conductive polymers, offer superior strength, durability, and functionality, making them ideal for high-performance applications such as aerospace, military gear, and wearable electronics. Plant fibers, including hemp, jute, and sisal, provide eco-friendly, biodegradable options best suited for agricultural uses, packaging, and traditional rope-making where sustainability and cost-effectiveness are prioritized. The choice between smart fibers and plant fibers depends on the specific requirements for strength, flexibility, environmental impact, and technological integration in the rope's intended application.
Maintenance and Longevity
Smart fiber ropes offer superior resistance to environmental factors such as UV exposure, moisture, and abrasion, resulting in lower maintenance requirements compared to plant fiber ropes. Plant fiber ropes, often made from materials like hemp or sisal, tend to degrade faster due to susceptibility to rot, mildew, and wear, necessitating frequent inspections and replacements. The enhanced durability and resistance of smart fibers significantly extend rope longevity, making them a cost-effective choice for long-term applications.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Needs
Smart fibers, engineered with enhanced strength, flexibility, and resistance to environmental factors, offer superior durability for rope applications requiring high performance and longevity. Plant fibers like hemp, jute, and sisal provide natural biodegradability and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for eco-friendly and traditional uses where moderate strength suffices. Selecting the right fiber depends on the specific requirements of tensile strength, environmental resistance, and sustainability goals to ensure optimal rope performance.
Infographic: Smart fiber vs Plant fiber for Rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com