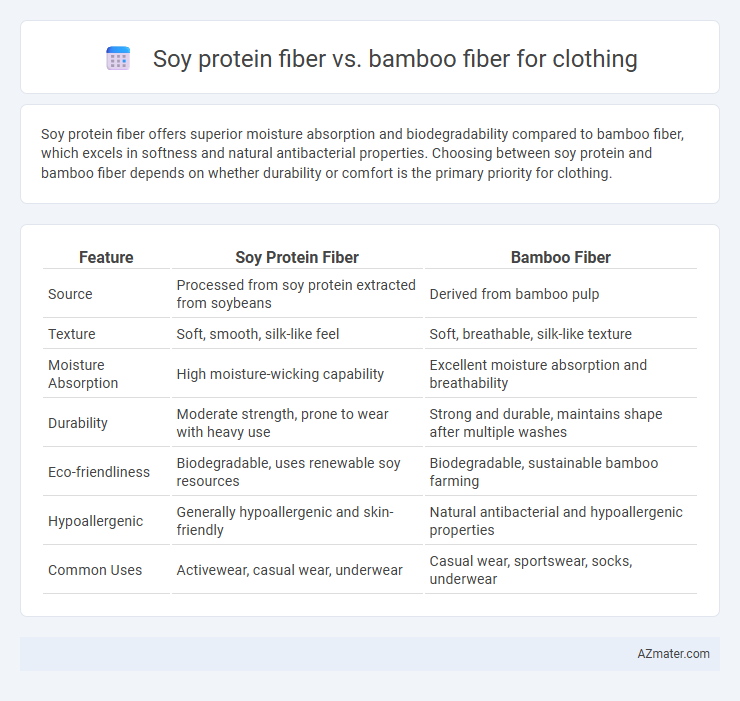
Soy protein fiber offers superior moisture absorption and biodegradability compared to bamboo fiber, which excels in softness and natural antibacterial properties. Choosing between soy protein and bamboo fiber depends on whether durability or comfort is the primary priority for clothing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Soy Protein Fiber | Bamboo Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Processed from soy protein extracted from soybeans | Derived from bamboo pulp |
| Texture | Soft, smooth, silk-like feel | Soft, breathable, silk-like texture |
| Moisture Absorption | High moisture-wicking capability | Excellent moisture absorption and breathability |
| Durability | Moderate strength, prone to wear with heavy use | Strong and durable, maintains shape after multiple washes |
| Eco-friendliness | Biodegradable, uses renewable soy resources | Biodegradable, sustainable bamboo farming |
| Hypoallergenic | Generally hypoallergenic and skin-friendly | Natural antibacterial and hypoallergenic properties |
| Common Uses | Activewear, casual wear, underwear | Casual wear, sportswear, socks, underwear |
Overview of Soy Protein Fiber and Bamboo Fiber
Soy protein fiber, derived from soybean processing byproducts, is a biodegradable textile material known for its softness, moisture absorption, and skin-friendly properties. Bamboo fiber, extracted from bamboo pulp, offers natural antibacterial qualities, high breathability, and rapid moisture-wicking performance, making it ideal for activewear and sensitive skin. Both fibers provide sustainable alternatives to traditional textiles, with soy protein fiber emphasizing comfort and bamboo fiber highlighting durability and antimicrobial benefits.
Production Processes: Soy vs Bamboo
Soy protein fiber production involves extracting protein from soybean residue, followed by chemical spinning processes that create a soft, sustainable fiber with a texture similar to silk. Bamboo fiber production typically requires either mechanical crushing and enzyme retting to obtain natural fibers or chemical processing using solvents to produce viscose-rayon fibers. The mechanical method retains bamboo's natural antimicrobial properties, while the chemical method, although less eco-friendly, produces softer, more pliable fabric suitable for clothing.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Soy protein fiber is biodegradable and derived from renewable soybean byproducts, significantly reducing waste and the reliance on synthetic fibers. Bamboo fiber, while renewable and fast-growing, requires chemical processing that can cause environmental pollution if not managed responsibly. Both fibers offer sustainable alternatives, but soy protein fiber generally has a lower overall environmental impact due to its biodegradability and use of agricultural waste.
Comfort and Wearability Factors
Soy protein fiber offers superior softness and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for comfortable, breathable clothing with excellent temperature regulation. Bamboo fiber is naturally antibacterial and hypoallergenic, enhancing wearability by reducing odors and irritation in sensitive skin. Both fibers provide eco-friendly alternatives, but soy protein fiber excels in durability and stretch, contributing to long-lasting comfort in everyday apparel.
Moisture Absorption and Breathability
Soy protein fiber features excellent moisture absorption due to its natural hydrophilic properties, making it highly effective at wicking sweat away from the skin for enhanced comfort. Bamboo fiber is renowned for its superior breathability and antimicrobial qualities, promoting airflow while naturally inhibiting odor-causing bacteria. Both fibers offer sustainable textile solutions, but soy protein fiber excels in moisture management, whereas bamboo fiber provides optimal ventilation and freshness in clothing applications.
Durability and Longevity
Soy protein fiber offers moderate durability with good elasticity and resistance to wear, making it suitable for casual garments that endure regular use. Bamboo fiber is exceptionally strong and breathable, exhibiting high tensile strength and resistance to pilling, which contributes to enhanced longevity in activewear and everyday clothing. Both fibers provide eco-friendly alternatives, but bamboo fiber generally outperforms soy protein fiber in maintaining fabric integrity over time.
Allergenicity and Skin Sensitivity
Soy protein fiber is derived from soybean protein and offers excellent moisture-wicking properties while being hypoallergenic, making it suitable for sensitive skin and reducing the risk of allergic reactions. Bamboo fiber, known for its natural antibacterial and antifungal properties, is also gentle on the skin but may pose a risk for individuals with bamboo or grass allergies. Choosing between soy protein fiber and bamboo fiber for clothing depends on individual skin sensitivity and allergenic responses, with soy protein fiber often preferred for its softness and lower allergy potential.
Dyeing and Color Retention
Soy protein fiber exhibits excellent dye absorption due to its protein composition, resulting in vibrant and long-lasting colors that resist fading over time. Bamboo fiber, with its cellulose structure, requires special dyeing techniques like reactive or vat dyes to achieve deep hues, yet it demonstrates superior moisture-wicking properties that help maintain color vibrancy during wear. Both fibers offer eco-friendly benefits, but soy protein fiber generally provides more consistent color retention after multiple washes compared to bamboo fiber.
Cost and Market Availability
Soy protein fiber generally costs more than bamboo fiber due to its complex production process, which involves extracting protein from soybean residues. Bamboo fiber enjoys wider market availability, driven by its rapid growth and sustainable harvesting methods, making it a popular choice for eco-friendly clothing brands. Both fibers offer unique benefits, but bamboo fiber's lower cost and greater accessibility make it more prevalent in mainstream textile markets.
Best Uses in Sustainable Fashion
Soy protein fiber offers a soft, breathable texture ideal for creating eco-friendly activewear and casual clothing that prioritizes comfort and moisture-wicking properties. Bamboo fiber excels in antibacterial, moisture-absorbent, and UV-resistant qualities, making it perfect for sustainable clothing designed for outdoor activities and sensitive skin. Both fibers contribute to reducing environmental impact, with soy protein promoting biodegradability and bamboo fiber supporting rapid renewable resource cycles.
Infographic: Soy protein fiber vs Bamboo fiber for Clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com