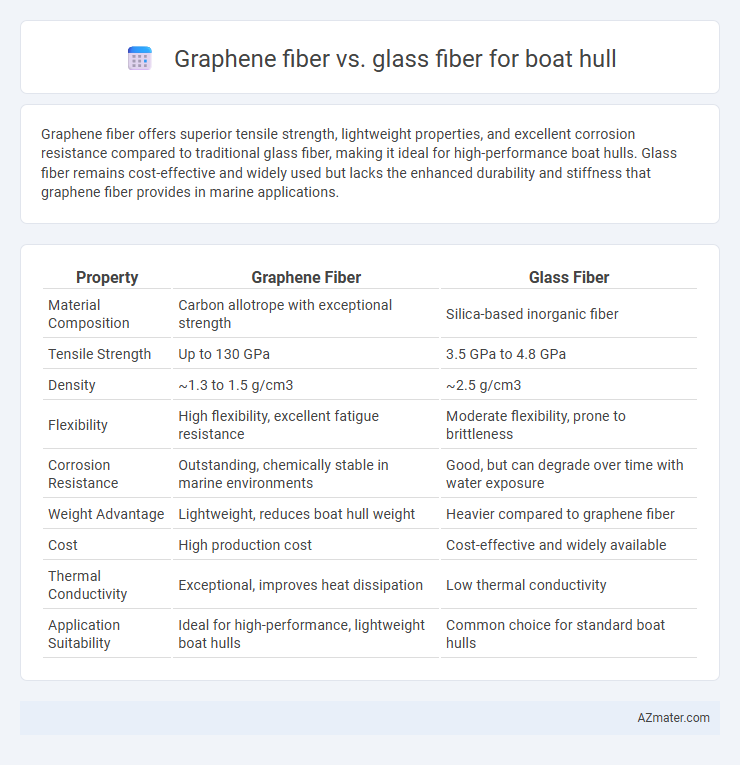
Graphene fiber offers superior tensile strength, lightweight properties, and excellent corrosion resistance compared to traditional glass fiber, making it ideal for high-performance boat hulls. Glass fiber remains cost-effective and widely used but lacks the enhanced durability and stiffness that graphene fiber provides in marine applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Graphene Fiber | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Carbon allotrope with exceptional strength | Silica-based inorganic fiber |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 130 GPa | 3.5 GPa to 4.8 GPa |
| Density | ~1.3 to 1.5 g/cm3 | ~2.5 g/cm3 |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, excellent fatigue resistance | Moderate flexibility, prone to brittleness |
| Corrosion Resistance | Outstanding, chemically stable in marine environments | Good, but can degrade over time with water exposure |
| Weight Advantage | Lightweight, reduces boat hull weight | Heavier compared to graphene fiber |
| Cost | High production cost | Cost-effective and widely available |
| Thermal Conductivity | Exceptional, improves heat dissipation | Low thermal conductivity |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for high-performance, lightweight boat hulls | Common choice for standard boat hulls |
Introduction to Advanced Boat Hull Materials
Graphene fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and lightweight properties, significantly enhancing boat hull durability and performance compared to traditional glass fiber. Its superior resistance to corrosion and fatigue extends the lifespan of hulls, making it a promising material in advanced marine applications. Glass fiber remains widely used due to cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing but lacks the enhanced mechanical and environmental advantages provided by graphene fiber composites.
Overview of Graphene Fiber Technology
Graphene fiber technology integrates graphene's exceptional strength, lightweight, and electrical conductivity properties, revolutionizing composite materials used in boat hull construction. Unlike traditional glass fiber, graphene-infused fibers offer superior tensile strength, enhanced durability, and improved resistance to corrosion and fatigue, leading to longer-lasting and more efficient marine vessels. This advanced technology enables lighter, stronger hulls that improve fuel efficiency and performance while reducing maintenance costs.
Properties of Glass Fiber in Marine Applications
Glass fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and corrosion resistance, making it a popular choice for boat hull construction in marine environments. Its excellent durability against saltwater and UV exposure ensures long-lasting performance with minimal maintenance. Additionally, glass fiber provides good impact resistance and cost-effectiveness compared to alternative materials like graphene fiber.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Graphene fiber exhibits significantly higher tensile strength and superior impact resistance compared to glass fiber, making it an ideal material for enhancing boat hull durability. Its exceptional stiffness and lightweight properties contribute to improved hull performance and fuel efficiency. Glass fiber, while cost-effective and corrosion-resistant, generally lacks the long-term durability and strength characteristics that graphene fiber offers under harsh marine environments.
Weight and Lightweight Performance
Graphene fiber offers significantly lower weight compared to traditional glass fiber, enhancing the lightweight performance of boat hulls by reducing overall mass without compromising strength. Its superior tensile strength-to-weight ratio results in improved fuel efficiency and faster acceleration for marine vessels. Glass fiber, while cost-effective and widely used, remains heavier, leading to increased hull weight and reduced agility.
Corrosion and Environmental Resistance
Graphene fiber exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to traditional glass fiber due to its impermeable carbon lattice structure, preventing moisture and chemical infiltration in boat hulls. Its environmental resistance is enhanced by high tensile strength and excellent thermal stability, allowing it to withstand harsh marine conditions without degradation. Glass fiber, while cost-effective, is more susceptible to water absorption and chemical attacks, leading to potential hull weakening and increased maintenance.
Flexibility and Impact Resistance
Graphene fiber offers superior flexibility and impact resistance compared to traditional glass fiber, making it an excellent choice for boat hull construction. Its high tensile strength and lightweight nature allow the hull to absorb and dissipate impact forces more effectively, reducing the risk of cracks and structural damage. Glass fiber, while cost-effective and widely used, tends to be more brittle and less flexible, which can lead to decreased durability under high-stress conditions.
Manufacturing and Cost Considerations
Graphene fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced durability in boat hull manufacturing compared to traditional glass fiber, enabling thinner and lighter hulls with improved performance. Manufacturing with graphene fiber involves advanced composite layup techniques and higher precision equipment, typically increasing production complexity and costs. Glass fiber remains more cost-effective and widely accessible for mass production, making it a preferred choice in budget-sensitive projects despite its heavier weight and lower mechanical properties.
Long-Term Maintenance and Repair
Graphene fiber boat hulls offer superior durability and resistance to wear, significantly reducing long-term maintenance compared to traditional glass fiber hulls. Glass fiber requires more frequent repairs due to its susceptibility to cracks and water absorption, leading to higher upkeep costs over time. The enhanced strength and flexibility of graphene fibers minimize structural damage, extending the lifespan and lowering repair frequency for marine vessels.
Future Trends in Boat Hull Reinforcement Materials
Graphene fiber is emerging as a revolutionary material for boat hull reinforcement due to its exceptional tensile strength, lightweight nature, and superior corrosion resistance compared to traditional glass fiber. Advances in nanotechnology and composite fabrication are driving the adoption of graphene-enhanced laminates, promising enhanced durability and fuel efficiency for marine vessels. Future trends indicate a growing preference for hybrid composites that integrate graphene fibers with glass fibers, optimizing mechanical properties and cost-efficiency in boat hull construction.
Infographic: Graphene fiber vs Glass fiber for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com