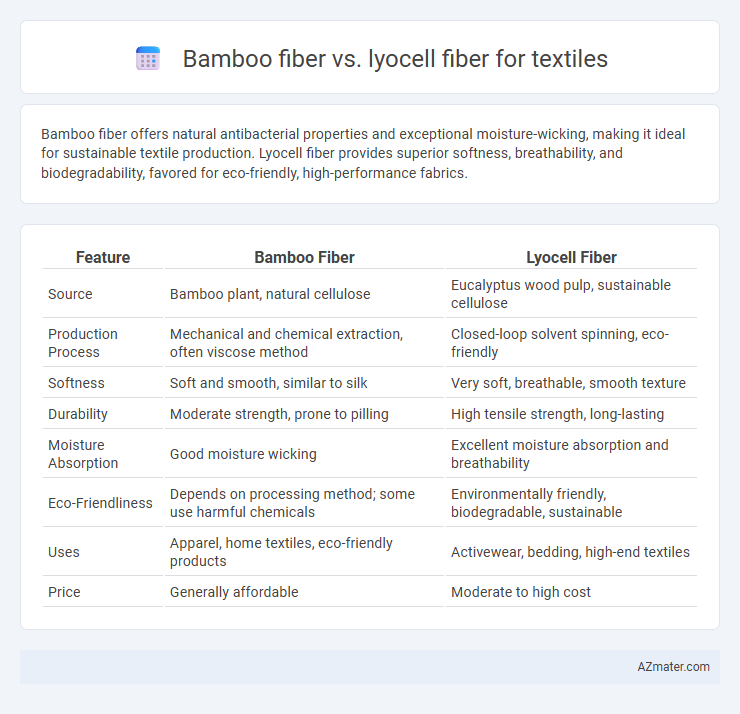
Bamboo fiber offers natural antibacterial properties and exceptional moisture-wicking, making it ideal for sustainable textile production. Lyocell fiber provides superior softness, breathability, and biodegradability, favored for eco-friendly, high-performance fabrics.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bamboo Fiber | Lyocell Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Bamboo plant, natural cellulose | Eucalyptus wood pulp, sustainable cellulose |
| Production Process | Mechanical and chemical extraction, often viscose method | Closed-loop solvent spinning, eco-friendly |
| Softness | Soft and smooth, similar to silk | Very soft, breathable, smooth texture |
| Durability | Moderate strength, prone to pilling | High tensile strength, long-lasting |
| Moisture Absorption | Good moisture wicking | Excellent moisture absorption and breathability |
| Eco-Friendliness | Depends on processing method; some use harmful chemicals | Environmentally friendly, biodegradable, sustainable |
| Uses | Apparel, home textiles, eco-friendly products | Activewear, bedding, high-end textiles |
| Price | Generally affordable | Moderate to high cost |
Introduction to Bamboo and Lyocell Fibers
Bamboo fiber, derived from the pulp of bamboo grass, offers natural antibacterial properties and exceptional moisture-wicking abilities, making it a popular choice for eco-friendly textiles. Lyocell fiber is a regenerated cellulose fiber produced from sustainably sourced wood pulp, known for its softness, breathability, and high tensile strength in fabric applications. Both fibers promote sustainability but differ in production processes; bamboo fiber uses a chemical-intensive method, while lyocell employs a closed-loop system that minimizes environmental impact.
Raw Material Sources and Sustainability
Bamboo fiber is derived from the fast-growing bamboo plant, which requires minimal water and no pesticides, making it a highly renewable raw material. Lyocell fiber is produced from sustainably harvested eucalyptus trees, processed through an eco-friendly closed-loop system that recycles solvents and reduces environmental impact. Both fibers offer sustainable alternatives in textiles, with bamboo emphasizing rapid renewability and lyocell focusing on responsible forestry and low-impact manufacturing.
Production Processes: Bamboo vs Lyocell
Bamboo fiber production involves mechanical crushing or chemical treatment to extract cellulose, often using harsh chemicals that raise environmental concerns. Lyocell fiber is produced through a closed-loop process dissolving wood pulp in an organic solvent, which is almost entirely recycled, minimizing waste and emissions. This closed-loop system in Lyocell production makes it a more sustainable and eco-friendly choice compared to conventional bamboo fiber manufacturing.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Bamboo fiber production often involves chemical-intensive processes that can result in significant water pollution unless properly managed, while lyocell fiber utilizes a closed-loop system that recycles solvents, minimizing environmental contamination. Lyocell fibers typically have a lower carbon footprint and require less water during cultivation compared to bamboo, which demands more intensive water resources for optimal growth. Both fibers offer biodegradable alternatives to synthetic textiles, but lyocell's manufacturing process is generally regarded as more eco-friendly and sustainable in terms of reducing chemical waste and conserving water.
Fiber Properties and Performance
Bamboo fiber exhibits natural antibacterial and moisture-wicking properties, enhancing comfort and odor control in textiles, with a relatively coarse texture that affects softness and durability. Lyocell fiber, derived from sustainably sourced wood pulp, offers superior strength, breathability, and a smooth, silky hand feel, making it highly resistant to wrinkles and shrinkage. Both fibers provide eco-friendly alternatives, but Lyocell tends to outperform bamboo in tensile strength and moisture management for high-performance textiles.
Comfort and Breathability
Bamboo fiber offers excellent moisture-wicking properties and natural antibacterial qualities, enhancing comfort and breathability in textiles. Lyocell fiber is renowned for its smooth texture and superior moisture management, providing a lightweight and airy feel ideal for sensitive skin. Both fibers promote airflow and temperature regulation, but bamboo excels in natural odor resistance while lyocell offers enhanced durability and softness.
Durability and Longevity
Bamboo fiber, known for its natural antibacterial properties, offers moderate durability but tends to weaken with repeated washing and prolonged exposure to sunlight, impacting longevity. Lyocell fiber, derived from sustainably sourced wood pulp, exhibits superior strength and resistance to pilling, maintaining its structural integrity through multiple wash cycles, which enhances overall durability and lifespan. Textile manufacturers often prefer lyocell for applications requiring long-lasting fabric performance due to its excellent tensile strength and resilience compared to bamboo fiber.
Applications in the Textile Industry
Bamboo fiber and lyocell fiber are both popular in the textile industry for sustainable fabric production, with bamboo fiber commonly used in casual wear, towels, and bedding due to its natural antibacterial properties and softness. Lyocell fiber, derived from wood pulp through an eco-friendly process, excels in activewear, denim, and high-performance textiles thanks to its strength, moisture-wicking abilities, and biodegradability. Both fibers contribute to eco-conscious fashion trends, but lyocell's durability and versatility make it more suitable for technical and functional textile applications.
Cost and Market Availability
Bamboo fiber offers a cost-effective alternative to Lyocell fiber due to its lower raw material and production expenses, making it more accessible for budget-sensitive textile manufacturers. Lyocell fiber commands a higher price point attributed to its environmentally friendly closed-loop production process and superior fabric qualities, which cater to premium market segments. Market availability for bamboo fiber is widespread, driven by its rapid growth and sustainable appeal, while Lyocell fiber, though growing in demand, remains less prevalent and typically found in niche sustainable textile collections.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Bamboo fiber and Lyocell fiber are gaining momentum in sustainable textile innovation due to their eco-friendly production processes and biodegradability. Future prospects highlight advancements in enzyme and solvent technologies to enhance softness, durability, and moisture management of both fibers, making them increasingly competitive in high-performance fashion and technical textiles. Research into hybrid blends combining bamboo fiber's natural antibacterial properties with Lyocell's strength and absorbency paves the way for smart textiles with improved functionality and environmental benefits.
Infographic: Bamboo fiber vs Lyocell fiber for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com